Tutoring offers personalized instruction tailored to a student's specific needs, often accelerating comprehension and skill development. Peer-to-peer learning fosters collaboration and critical thinking by encouraging students to engage with diverse perspectives and explain concepts to one another. Combining both methods can enhance educational outcomes by balancing expert guidance with interactive, student-driven exploration.
Table of Comparison
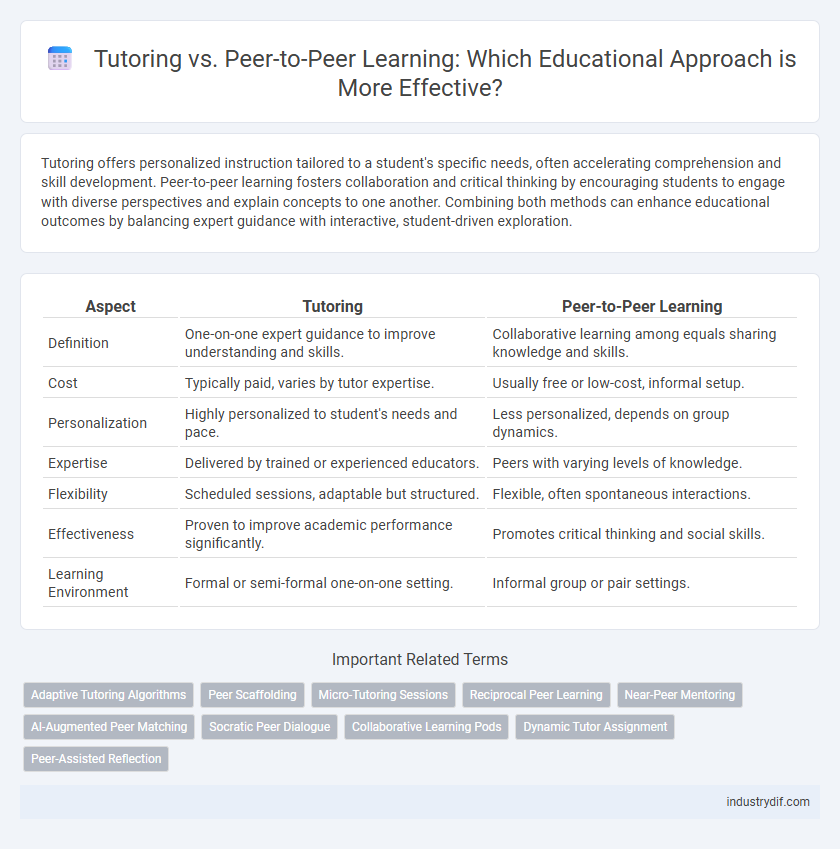
| Aspect | Tutoring | Peer-to-Peer Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One-on-one expert guidance to improve understanding and skills. | Collaborative learning among equals sharing knowledge and skills. |
| Cost | Typically paid, varies by tutor expertise. | Usually free or low-cost, informal setup. |
| Personalization | Highly personalized to student's needs and pace. | Less personalized, depends on group dynamics. |
| Expertise | Delivered by trained or experienced educators. | Peers with varying levels of knowledge. |
| Flexibility | Scheduled sessions, adaptable but structured. | Flexible, often spontaneous interactions. |
| Effectiveness | Proven to improve academic performance significantly. | Promotes critical thinking and social skills. |
| Learning Environment | Formal or semi-formal one-on-one setting. | Informal group or pair settings. |
Defining Tutoring in Modern Education
Tutoring in modern education involves personalized instruction where an expert or trained individual provides targeted academic support to enhance a student's understanding and performance. This approach leverages tailored lesson plans and one-on-one interaction to address specific learning gaps and foster skill mastery. Tutoring often utilizes adaptive techniques and technology to create a customized learning experience that accelerates academic progress.
Understanding Peer-to-Peer Learning Models
Peer-to-peer learning models emphasize collaborative knowledge exchange where students teach and learn from each other, fostering active engagement and deeper comprehension. Unlike traditional tutoring, which involves expert-led instruction, peer-to-peer approaches leverage reciprocal interaction, promoting critical thinking and social skills development. Research shows peer-to-peer frameworks can enhance motivation and retention by creating a supportive learning community.
Key Differences Between Tutoring and Peer-to-Peer Learning
Tutoring involves a knowledgeable instructor providing personalized guidance to support a student's learning needs, often in a one-on-one setting, ensuring targeted skill development and accountability. Peer-to-peer learning, by contrast, is a collaborative process where students engage with each other to share knowledge, problem-solve, and reinforce concepts through reciprocal teaching and discussion. The key differences lie in the expertise level of the facilitator, the directionality of knowledge transfer, and the structured nature of tutoring versus the mutual, often informal, exchange typical of peer-to-peer interactions.
Benefits of Tutoring for Student Achievement
Tutoring provides personalized instruction tailored to individual student needs, leading to improved comprehension and academic performance. Research shows that students receiving tutoring demonstrate higher test scores and increased retention rates compared to those relying solely on peer-to-peer learning. The structured guidance and expert feedback in tutoring sessions accelerate mastery of complex subjects and foster long-term academic success.
Advantages of Peer-to-Peer Learning Environments
Peer-to-peer learning environments foster collaborative skills and enhance critical thinking by encouraging active participation among students. These settings promote social interaction, which improves communication abilities and reinforces knowledge through teaching others. Research shows that peer learning increases motivation and retention rates compared to traditional tutoring methods by creating a supportive and relatable learning atmosphere.
Challenges in Implementing Tutoring Programs
Implementing tutoring programs faces challenges such as limited funding, scheduling conflicts, and matching students with qualified tutors. Ensuring consistent tutor training and maintaining student engagement also prove difficult, impacting program effectiveness. Managing scalability while addressing diverse learning needs further complicates the rollout of successful tutoring initiatives.
Obstacles in Peer-to-Peer Learning Adoption
Barriers to peer-to-peer learning adoption include lack of structured guidance, which can result in inconsistent knowledge transfer and reduced learning outcomes. Social dynamics such as mismatched skill levels and interpersonal conflicts often hinder effective collaboration among students. Limited institutional support and inadequate technological infrastructure further restrict widespread implementation of peer learning models in educational settings.
Case Studies: Tutoring vs Peer-to-Peer Learning Outcomes
Case studies reveal that tutoring often leads to higher academic performance due to personalized instruction tailored to individual learning styles and needs. Peer-to-peer learning, however, enhances collaborative skills and reinforces knowledge through active discussion and explanation among learners of similar knowledge levels. Data from multiple educational settings show a blend of tutoring and peer-to-peer strategies maximizes comprehension and retention rates compared to relying solely on one method.
Technology’s Role in Tutoring and Peer-to-Peer Learning
Technology enhances tutoring through personalized learning platforms using AI algorithms to tailor content to individual student needs, improving engagement and outcomes. In peer-to-peer learning, digital forums, video conferencing, and collaborative tools facilitate real-time interaction and knowledge exchange regardless of geographical barriers. Both approaches benefit from adaptive learning analytics and gamification features, increasing motivation and tracking progress effectively.
Choosing the Best Approach for Varied Learning Needs
Tutoring offers personalized instruction tailored to individual strengths and weaknesses, making it ideal for learners needing targeted support or accelerated progress. Peer-to-peer learning fosters collaboration and communication skills by encouraging students to share knowledge and solve problems together, which benefits those seeking interactive and social learning environments. Selecting the best approach depends on factors such as the learner's goals, preferred learning style, and the complexity of the subject matter.
Related Important Terms
Adaptive Tutoring Algorithms
Adaptive tutoring algorithms leverage artificial intelligence to personalize learning experiences by continuously assessing student performance and tailoring content accordingly, significantly improving knowledge retention and engagement. Peer-to-peer learning fosters collaborative skills and social interaction but often lacks the precise customization and responsiveness provided by data-driven adaptive tutoring systems.
Peer Scaffolding
Peer scaffolding enhances learning by enabling students to support each other's understanding through collaborative problem-solving and knowledge sharing, which fosters deeper comprehension and critical thinking skills. This approach contrasts with traditional tutoring by emphasizing mutual guidance and active engagement rather than one-way instruction.
Micro-Tutoring Sessions
Micro-tutoring sessions enhance individualized learning by providing targeted support tailored to specific student needs, often outperforming traditional peer-to-peer learning in content retention and problem-solving skills. These brief, focused interactions leverage expert guidance, fostering deeper understanding and accelerating academic progress more effectively than broader peer collaboration formats.
Reciprocal Peer Learning
Reciprocal peer learning enhances understanding through collaborative knowledge exchange, leveraging the strengths of both tutor roles and learner contributions in a shared educational environment. This method promotes critical thinking and retention by encouraging students to explain concepts to each other, fostering deeper engagement compared to traditional one-way tutoring.
Near-Peer Mentoring
Near-peer mentoring enhances educational outcomes by leveraging the small age and experience gap between mentors and mentees, fostering relatable guidance and increased engagement compared to traditional tutoring. This approach stimulates collaborative learning environments, promotes critical thinking, and improves retention through shared academic and social experiences.
AI-Augmented Peer Matching
AI-augmented peer matching enhances peer-to-peer learning by using algorithms to pair students based on complementary skills and learning styles, increasing engagement and knowledge retention. In contrast to traditional tutoring, this technology-driven approach fosters collaborative problem-solving and personalized support without the high costs associated with one-on-one tutoring services.
Socratic Peer Dialogue
Socratic peer dialogue enhances peer-to-peer learning by fostering critical thinking and deeper understanding through guided questioning rather than direct instruction typical in tutoring. This method promotes active engagement, collaborative problem-solving, and the development of metacognitive skills essential for lifelong learning.
Collaborative Learning Pods
Collaborative learning pods foster peer-to-peer interaction that enhances critical thinking and communication skills through shared problem-solving experiences. Unlike traditional tutoring, these pods promote autonomy and collective accountability, leading to deeper understanding and sustained academic motivation among students.
Dynamic Tutor Assignment
Dynamic tutor assignment enhances tutoring effectiveness by matching students with tutors based on real-time assessment of learning needs and progress, enabling personalized guidance. Peer-to-peer learning benefits less from dynamic assignment as it relies more on collaborative knowledge exchange and mutual support among learners rather than tailored expertise.
Peer-Assisted Reflection
Peer-assisted reflection enhances learning by encouraging students to critically evaluate and discuss each other's work, fostering deeper understanding and collaborative problem-solving compared to traditional tutoring. This method leverages peer interactions to develop metacognitive skills, promoting self-regulation and improved academic performance across diverse educational settings.
Tutoring vs Peer-to-Peer Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com