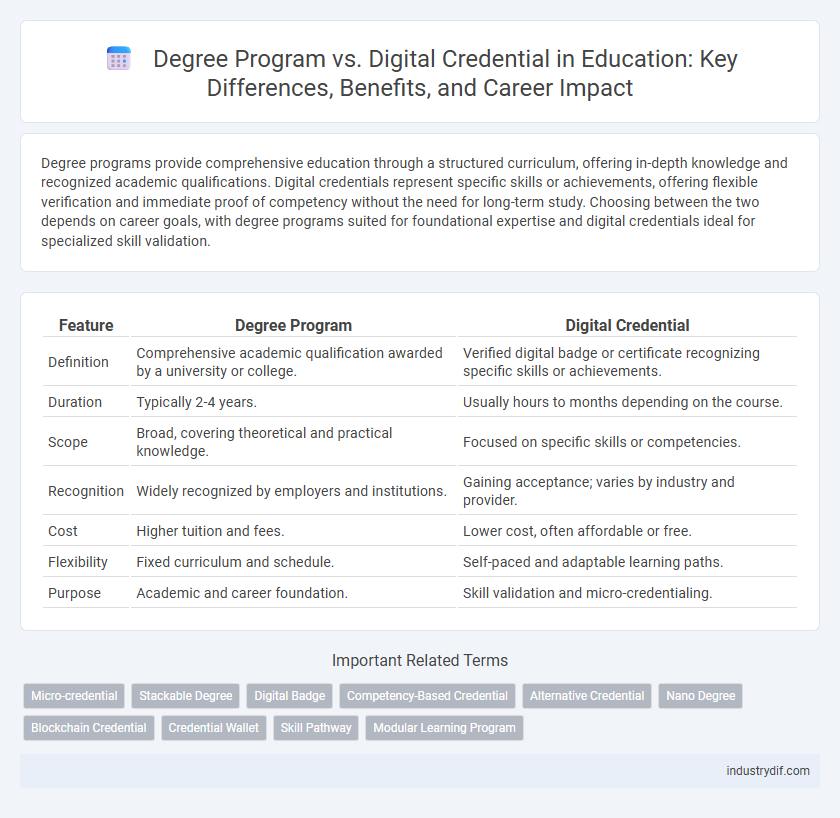
Degree programs provide comprehensive education through a structured curriculum, offering in-depth knowledge and recognized academic qualifications. Digital credentials represent specific skills or achievements, offering flexible verification and immediate proof of competency without the need for long-term study. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, with degree programs suited for foundational expertise and digital credentials ideal for specialized skill validation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Degree Program | Digital Credential |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive academic qualification awarded by a university or college. | Verified digital badge or certificate recognizing specific skills or achievements. |
| Duration | Typically 2-4 years. | Usually hours to months depending on the course. |
| Scope | Broad, covering theoretical and practical knowledge. | Focused on specific skills or competencies. |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by employers and institutions. | Gaining acceptance; varies by industry and provider. |
| Cost | Higher tuition and fees. | Lower cost, often affordable or free. |
| Flexibility | Fixed curriculum and schedule. | Self-paced and adaptable learning paths. |
| Purpose | Academic and career foundation. | Skill validation and micro-credentialing. |
Understanding Degree Programs in Modern Education
Degree programs in modern education provide comprehensive, structured curricula designed to develop in-depth knowledge and critical skills over multiple years, culminating in widely recognized academic qualifications such as bachelor's, master's, or doctoral degrees. Digital credentials, including micro-credentials and badges, offer flexible, skill-specific recognition that complements traditional degrees by validating targeted competencies in a rapidly evolving job market. Institutions increasingly integrate digital credentials with degree programs to enhance lifelong learning pathways and respond to the demand for both broad and specialized expertise.
What Are Digital Credentials?
Digital credentials are verified, electronic representations of skills, achievements, or qualifications earned through specific learning experiences or assessments. Unlike traditional degree programs, digital credentials offer flexible, stackable recognition that can be shared instantly on professional networks and resumes. These credentials enhance lifelong learning by providing immediate proof of competencies in a rapidly evolving job market.
Key Differences Between Degree Programs and Digital Credentials
Degree programs offer comprehensive, multi-year academic education culminating in a formal qualification such as a bachelor's or master's degree, recognized globally for career advancement. Digital credentials represent concise, verifiable achievements or skills earned through short-term courses or training, often issued on blockchain or digital platforms for instant validation. Degree programs emphasize deep theoretical knowledge and broad skill development, while digital credentials focus on specific competencies and flexible, stackable learning paths.
Recognized Value: Accreditation and Industry Acceptance
Degree programs offer recognized value through formal accreditation by established educational authorities and widespread industry acceptance, ensuring credibility and comprehensive knowledge validation. Digital credentials, while gaining popularity for skill-specific recognition, often lack uniform accreditation and variable industry acceptance, limiting their perceived equivalency to traditional degrees. Employers increasingly acknowledge digital credentials for micro-credentials and continuous learning but still prioritize accredited degree programs for foundational qualifications.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Learning Pathways
Degree programs typically require fixed schedules and campus attendance, limiting flexibility and accessibility for many learners. Digital credentials offer modular, stackable learning pathways that can be completed anytime and anywhere, enhancing personalized education and inclusivity. This shift enables learners to acquire skills progressively while balancing other commitments.
Time and Cost Investment: Degree Programs vs Digital Credentials
Degree programs require significant time investment, often spanning multiple years and substantial financial costs including tuition, fees, and materials. Digital credentials offer a flexible, cost-effective alternative with shorter completion times and lower expenses, allowing learners to quickly acquire specific skills relevant to the job market. Choosing digital credentials can optimize educational outcomes by minimizing time and cost while focusing on targeted competencies.
Skills Acquired: Deep Learning vs Microlearning
Degree programs deliver comprehensive skills through deep learning, emphasizing mastery of broad, interconnected concepts over extended periods. Digital credentials emphasize microlearning, focusing on specific, skill-based competencies acquired in short, targeted modules for rapid, practical application. This contrast highlights how traditional education builds foundational expertise, while digital credentials cater to flexible, precise skill validation tailored to evolving job market demands.
Career Opportunities and Employer Perceptions
Degree programs typically provide comprehensive education and are widely recognized by employers, enhancing career opportunities through established academic credibility and deep subject knowledge. Digital credentials offer flexible, skill-specific recognition that appeals to employers seeking proof of specialized competencies and up-to-date industry-relevant abilities. Employers increasingly value digital credentials for their efficiency in verifying skills, but degree programs remain essential for roles requiring foundational expertise and formal qualifications.
Lifelong Learning: Adapting to Evolving Workforce Needs
Degree programs offer comprehensive, structured education that provides foundational knowledge and credentials recognized across industries. Digital credentials enable learners to acquire and demonstrate specific skills quickly, supporting continuous skill development aligned with evolving workforce demands. Lifelong learning thrives through the integration of formal degree programs and agile digital credentials, ensuring adaptability and relevance in rapidly changing job markets.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a degree program and a digital credential depends on factors like career goals, industry standards, and time commitment. Degree programs offer comprehensive knowledge and are widely recognized by employers, while digital credentials provide specialized skills and flexibility for rapid skill acquisition. Evaluating job market demands and personal learning preferences helps determine the optimal educational pathway.
Related Important Terms
Micro-credential
Micro-credentials offer flexible, targeted learning opportunities that complement traditional degree programs by validating specific skills and competencies in shorter timeframes. These digital badges or certificates enhance employability and lifelong learning by providing verifiable credentials aligned with industry needs.
Stackable Degree
Stackable degrees combine multiple digital credentials that represent specific skills or competencies, allowing learners to gradually accumulate credits toward a full degree program with increased flexibility and personalized learning paths. This approach enhances employability by providing verifiable, modular qualifications that align with evolving industry demands and promote lifelong education.
Digital Badge
Digital badges represent a modern form of digital credential that verifies specific skills or competencies earned through short-term learning experiences or professional development, offering flexibility and targeted validation beyond traditional degree programs. Unlike degree programs, which encompass comprehensive curricula and often require years of study, digital badges provide immediate recognition and shareable proof of achievements that can be integrated into online profiles and resumes.
Competency-Based Credential
Competency-based credentials emphasize mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to demonstrate practical expertise through assessments tailored to industry standards. Unlike traditional degree programs, these digital credentials offer flexible, personalized pathways that align with workforce demands and enable rapid validation of competencies for career advancement.
Alternative Credential
Alternative credentials offer flexible, skills-focused recognition compared to traditional degree programs, enabling learners to quickly acquire and demonstrate specific competencies in rapidly evolving fields. Digital credentials, such as badges and certificates, provide verifiable, portable proof of expertise that complements or substitutes conventional degrees in the modern education landscape.
Nano Degree
A degree program offers comprehensive academic education typically spanning several years, while a nano degree provides specialized, industry-aligned skills through short, focused courses that enhance employability in specific fields. Digital credentials like nano degrees enable learners to showcase verified micro-credentials, facilitating continuous learning and rapid career advancement in the evolving job market.
Blockchain Credential
Degree programs represent traditional, comprehensive academic pathways culminating in diplomas, whereas digital credentials, particularly blockchain-based certificates, offer secure, easily verifiable proof of specific skills or achievements. Blockchain credentials enhance trust by enabling immutable records, instant verification, and improved accessibility, revolutionizing how educational qualifications are recognized and shared globally.
Credential Wallet
Degree programs provide comprehensive academic training and recognized qualifications, while digital credentials offer flexible, verifiable records of skills and achievements stored securely in a credential wallet. Credential wallets enhance control and accessibility, allowing learners to share verified educational accomplishments instantly across institutions and employers.
Skill Pathway
Degree programs offer comprehensive education and recognized qualifications, while digital credentials emphasize specific skill pathways by verifying targeted competencies through micro-credentials and badges. Skill pathways in digital credentials provide flexible, stackable learning opportunities tailored to evolving industry demands, enhancing workforce readiness and continuous professional development.
Modular Learning Program
Modular learning programs offer flexible, bite-sized education components that can be stacked to earn traditional degrees or digital credentials, enhancing learner agility and skill acquisition. These programs bridge the gap between formal degree programs and digital credentials by allowing students to accumulate verified modules that align with industry demands and lifelong learning goals.
Degree Program vs Digital Credential Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com