Lecture-based teaching delivers structured content efficiently, allowing educators to cover extensive material in a limited time. Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking and student engagement by encouraging exploration, questioning, and problem-solving. Combining both methods can create a dynamic learning environment that addresses diverse student needs and promotes deeper understanding.
Table of Comparison
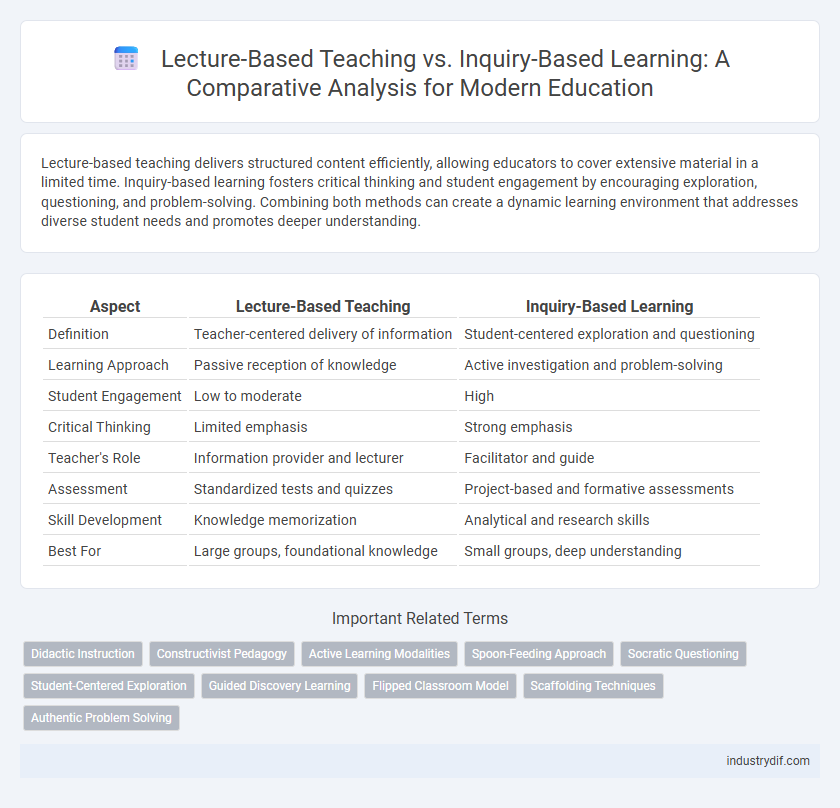
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Teaching | Inquiry-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered delivery of information | Student-centered exploration and questioning |
| Learning Approach | Passive reception of knowledge | Active investigation and problem-solving |
| Student Engagement | Low to moderate | High |
| Critical Thinking | Limited emphasis | Strong emphasis |
| Teacher's Role | Information provider and lecturer | Facilitator and guide |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and quizzes | Project-based and formative assessments |
| Skill Development | Knowledge memorization | Analytical and research skills |
| Best For | Large groups, foundational knowledge | Small groups, deep understanding |
Defining Lecture-Based Teaching in Education
Lecture-based teaching in education is a traditional instructional method where the teacher delivers content verbally to students, emphasizing direct knowledge transmission. This approach centers on structured presentations, focusing on facts, theories, and concepts to provide foundational understanding. It is often favored for efficiently covering extensive material to large groups within a limited time.
Understanding Inquiry-Based Learning Models
Inquiry-based learning models emphasize active student participation, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging exploration and questioning rather than passive reception of information. These models align with constructivist theories, promoting deeper understanding through hands-on investigations and collaborative discussions. Research highlights that inquiry-based approaches improve retention and application of knowledge compared to traditional lecture-based teaching methods.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Methodologies
Lecture-Based Teaching originated in ancient Greece and remained the dominant educational method through the Middle Ages and Renaissance, characterized by teacher-centered instruction and passive student absorption of knowledge. Inquiry-Based Learning emerged more prominently in the 20th century, influenced by educational theorists like John Dewey who emphasized active student engagement, critical thinking, and exploration. This evolution reflects a shift from rote memorization to fostering analytical skills and deeper understanding in modern pedagogical practices.
Key Differences Between Lecture-Based and Inquiry-Based Approaches
Lecture-based teaching centers on structured content delivery where instructors impart knowledge through presentations, emphasizing memorization and passive learning. Inquiry-based learning fosters student engagement by encouraging exploration, critical thinking, and problem-solving through questioning and hands-on activities. The key difference lies in the role of the teacher as a knowledge transmitter versus a facilitator guiding active investigation and discovery.
Advantages of Lecture-Based Instruction
Lecture-based instruction efficiently delivers core curriculum content to large groups, ensuring consistent knowledge transfer and alignment with standardized testing requirements. It allows educators to structure information logically, facilitating easier note-taking and review for students. This method also maximizes classroom time by minimizing off-task behavior and keeping learners focused on key concepts.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning for Student Engagement
Inquiry-based learning significantly boosts student engagement by fostering curiosity and active participation in the learning process. This approach encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, allowing students to explore concepts deeply and retain information more effectively. Research shows that learners in inquiry-based environments exhibit higher motivation, improved academic performance, and enhanced collaboration abilities compared to traditional lecture-based teaching methods.
Addressing Diverse Learning Styles in the Classroom
Lecture-based teaching offers structured delivery that benefits auditory learners through clear explanations and organized content, while inquiry-based learning engages kinesthetic and visual learners by promoting exploration and hands-on activities. Incorporating both methods addresses diverse learning styles, enhancing comprehension and retention by catering to individual student preferences and strengths. Adaptive teaching strategies that blend direct instruction with inquiry foster inclusive classrooms where all students can thrive academically.
Teacher Roles: Facilitator vs Information Provider
In lecture-based teaching, the teacher primarily acts as an information provider, delivering content directly to students through structured presentations and explanations. In contrast, inquiry-based learning positions the teacher as a facilitator, guiding students to explore concepts, ask questions, and construct knowledge independently. This shift enhances critical thinking and student engagement by promoting active participation and collaborative learning environments.
Impact on Student Outcomes and Critical Thinking Skills
Lecture-based teaching often emphasizes passive information absorption, which may limit development of critical thinking skills and reduce long-term retention of knowledge. Inquiry-based learning promotes active engagement and problem-solving, leading to improved student outcomes by fostering deeper understanding and enhancing analytical abilities. Research indicates that students exposed to inquiry-based approaches demonstrate higher critical thinking proficiency and greater academic achievement compared to traditional lecture formats.
Implementing Hybrid Teaching Strategies in Modern Education
Implementing hybrid teaching strategies in modern education combines the structured knowledge delivery of lecture-based teaching with the exploratory, student-centered approach of inquiry-based learning, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. Integrating multimedia presentations and guided research projects enhances engagement while accommodating diverse learning styles and pacing. This balanced methodology prepares students to apply theoretical concepts practically, promoting retention and active participation.
Related Important Terms
Didactic Instruction
Didactic instruction in lecture-based teaching emphasizes structured content delivery and direct knowledge transmission from educator to student, fostering foundational understanding and clarity. Inquiry-based learning contrasts by promoting student-driven exploration, critical thinking, and active problem-solving, which often leads to deeper engagement but may require more facilitation and time.
Constructivist Pedagogy
Lecture-based teaching delivers structured content directly from instructor to students, emphasizing knowledge transmission and memorization, while inquiry-based learning engages learners actively in exploring questions and constructing understanding through hands-on experiences, aligning closely with constructivist pedagogy that promotes meaningful learning by connecting new information to prior knowledge. Constructivist pedagogy supports inquiry-based approaches by fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and deeper comprehension, contrasting the passive reception typical of lecture-based instruction.
Active Learning Modalities
Lecture-based teaching primarily emphasizes passive information delivery, often limiting student engagement and critical thinking development, whereas inquiry-based learning promotes active learning modalities by encouraging students to explore, question, and construct knowledge through hands-on activities and collaborative problem-solving. Active learning techniques such as group discussions, experiments, and case studies significantly enhance cognitive retention and foster deeper understanding compared to traditional lecture formats.
Spoon-Feeding Approach
Lecture-based teaching often relies on a spoon-feeding approach where information is passively delivered to students, limiting critical thinking and problem-solving skills development. Inquiry-based learning, in contrast, encourages active student engagement and exploration, fostering deeper understanding and long-term knowledge retention.
Socratic Questioning
Socratic questioning in inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to explore concepts deeply and articulate their understanding, contrasting with lecture-based teaching that primarily delivers information passively. This method promotes active engagement and deeper cognitive processing, leading to improved problem-solving skills and knowledge retention.
Student-Centered Exploration
Inquiry-based learning promotes active student-centered exploration by encouraging learners to ask questions, investigate, and construct knowledge through hands-on experiences. Unlike traditional lecture-based teaching, this approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper understanding by prioritizing student engagement and autonomy in the learning process.
Guided Discovery Learning
Guided discovery learning, a subset of inquiry-based learning, empowers students to explore concepts through structured questions and prompts, promoting deeper understanding and critical thinking. Unlike lecture-based teaching that emphasizes passive reception of information, this method encourages active engagement and fosters long-term retention of knowledge.
Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model enhances inquiry-based learning by shifting traditional lecture content outside the classroom, allowing students to engage actively with problems and discussions during class time. This approach contrasts with lecture-based teaching by promoting deeper understanding, critical thinking, and collaborative skills through student-centered activities and real-time feedback.
Scaffolding Techniques
Lecture-based teaching relies heavily on direct instruction where scaffolding techniques involve structured outlines and guided notes to support student comprehension, while inquiry-based learning utilizes scaffolding through strategic questioning, collaborative problem-solving, and gradual release of responsibility to foster critical thinking and independent exploration. Effective scaffolding in inquiry-based approaches adapts to learners' evolving understanding, promoting deeper engagement and retention compared to the often static support in lecture formats.
Authentic Problem Solving
Inquiry-based learning fosters authentic problem solving by encouraging students to investigate real-world issues and develop critical thinking skills, whereas lecture-based teaching primarily delivers information passively, limiting opportunities for practical application. Emphasizing hands-on exploration and student-driven inquiry enhances engagement and deeper understanding, which are essential for mastering complex concepts in education.
Lecture-Based Teaching vs Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com