Distance education offers comprehensive learning experiences through virtual classrooms and extended coursework, ideal for in-depth study and professional development. Microlearning delivers focused, bite-sized content designed to enhance retention and fit into busy schedules, making it perfect for quick skill acquisition. Balancing these methods can optimize educational outcomes by combining extensive knowledge with flexible, time-efficient learning.
Table of Comparison
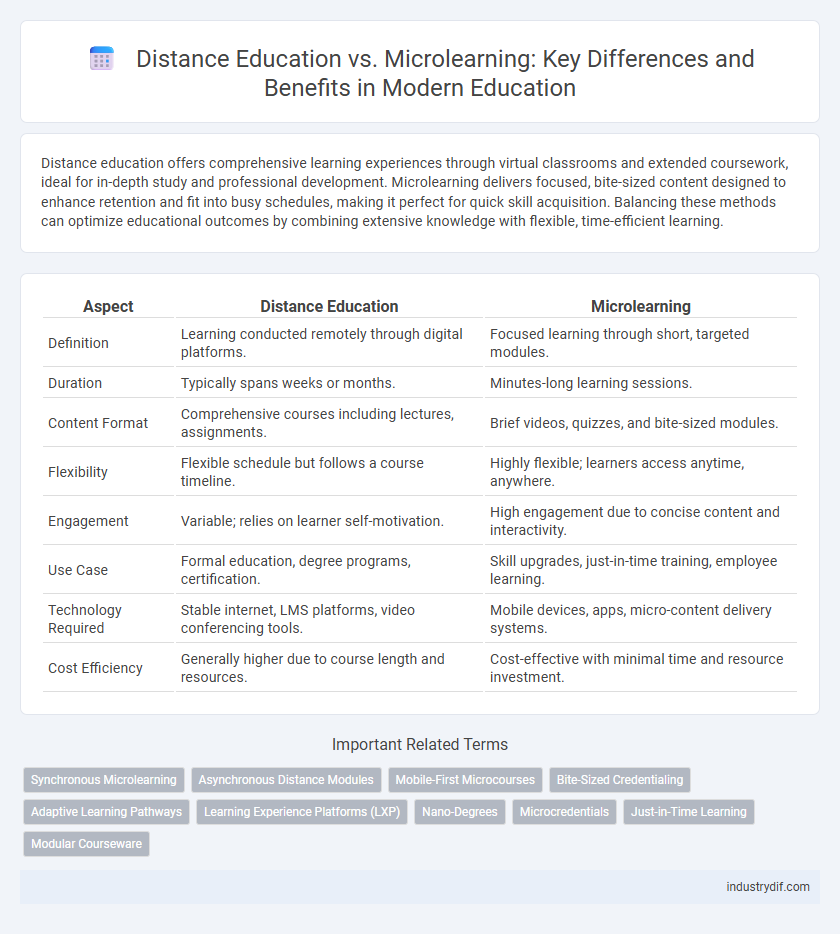
| Aspect | Distance Education | Microlearning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning conducted remotely through digital platforms. | Focused learning through short, targeted modules. |
| Duration | Typically spans weeks or months. | Minutes-long learning sessions. |
| Content Format | Comprehensive courses including lectures, assignments. | Brief videos, quizzes, and bite-sized modules. |
| Flexibility | Flexible schedule but follows a course timeline. | Highly flexible; learners access anytime, anywhere. |
| Engagement | Variable; relies on learner self-motivation. | High engagement due to concise content and interactivity. |
| Use Case | Formal education, degree programs, certification. | Skill upgrades, just-in-time training, employee learning. |
| Technology Required | Stable internet, LMS platforms, video conferencing tools. | Mobile devices, apps, micro-content delivery systems. |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally higher due to course length and resources. | Cost-effective with minimal time and resource investment. |
Defining Distance Education and Microlearning
Distance education refers to instructional delivery methods where learners engage with educational content remotely, often through online platforms, video lectures, or correspondence, enabling flexibility in time and location. Microlearning breaks down complex subjects into bite-sized, focused lessons typically lasting 3 to 5 minutes, designed to enhance retention and accommodate busy schedules. Both approaches leverage digital technology but differ in scope and duration, with distance education covering complete courses and microlearning targeting specific knowledge components.
Historical Evolution of Learning Modalities
Distance education originated in the 19th century with correspondence courses, evolving through radio, television, and the internet to enable remote learning on a large scale. Microlearning emerged in the early 21st century as a response to shorter attention spans and the demand for just-in-time knowledge, delivering highly focused, bite-sized content. The historical evolution from broadly accessible distance education to precise, flexible microlearning reflects technological advancements and shifting learner preferences in modern education.
Delivery Methods: Virtual Classrooms vs Bite-sized Modules
Distance education leverages virtual classrooms to facilitate real-time interaction, enabling students and instructors to engage in synchronous learning regardless of location. Microlearning focuses on delivering bite-sized modules that promote flexible, on-demand access to concise content, optimizing retention and accommodating diverse schedules. Virtual classrooms emphasize comprehensive lesson delivery, while bite-sized modules prioritize quick, targeted knowledge acquisition.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Education
Distance education offers learners the flexibility to access comprehensive courses remotely, accommodating diverse schedules and geographic locations, while microlearning provides highly accessible, bite-sized content that fits into brief time slots and mobile devices. Both models enhance educational accessibility by breaking down traditional barriers, with distance education supporting full curriculum delivery and microlearning enabling continuous skill development through on-demand modules. The integration of these approaches allows institutions to cater to varied learning preferences, promoting inclusivity and personalized learning paths in education.
Suitability for Different Learning Objectives
Distance education offers comprehensive curricula suitable for in-depth mastery of complex subjects, making it ideal for discipline-specific degree programs and professional certifications. Microlearning delivers concise, targeted content designed for quick skill acquisition and knowledge reinforcement, fitting well with just-in-time training and performance support scenarios. Choosing between distance education and microlearning depends on whether the learning objective prioritizes breadth and depth or rapid, focused knowledge application.
Engagement and Knowledge Retention
Distance education leverages technology to provide comprehensive learning experiences with structured coursework, fostering sustained engagement through interactive platforms and multimedia content. Microlearning delivers concise, targeted lessons that enhance knowledge retention by focusing on specific skills or concepts, optimizing learner attention and minimizing cognitive overload. Combining both methods can maximize engagement and retention by tailoring content length and delivery to learner needs and preferences.
Assessment and Feedback Mechanisms
Distance education employs comprehensive assessment methods such as exams, essays, and projects, providing detailed feedback through digital platforms to monitor learner progress effectively. Microlearning emphasizes frequent, bite-sized assessments with instant feedback, promoting quick knowledge retention and continuous skill improvement. Both approaches utilize technology-driven feedback mechanisms, but distance education offers in-depth evaluation while microlearning supports rapid, formative assessments.
Cost and Resource Implications
Distance education typically demands higher initial investments in technology infrastructure and course development, while microlearning reduces costs by delivering concise, easily updateable content that requires fewer resources. Organizations benefit from microlearning's scalability and lower bandwidth requirements, making it a cost-effective solution compared to the broader scope and maintenance of full distance education programs. Budget allocation for distance education often includes extensive support staff and complex learning management systems, whereas microlearning leverages automation and targeted content delivery to optimize resource use.
Technology Integration in Distance Education and Microlearning
Distance education leverages advanced technologies such as Learning Management Systems (LMS), video conferencing, and adaptive analytics to create scalable and interactive learning environments. Microlearning incorporates mobile apps, gamification, and AI-driven content personalization to deliver concise, targeted lessons that enhance retention and engagement. Both approaches utilize cloud computing and real-time data tracking, but microlearning emphasizes bite-sized content optimized for on-the-go access, while distance education focuses on comprehensive curriculum delivery through robust digital platforms.
Future Trends in Distance Education and Microlearning
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven adaptive learning and augmented reality are revolutionizing distance education by creating highly personalized and interactive experiences. Microlearning's bite-sized modules increasingly integrate with mobile platforms, enhancing accessibility and learner engagement across diverse demographics. These future trends indicate a shift towards seamless, on-demand education that blends flexibility with targeted knowledge acquisition.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Microlearning
Synchronous microlearning integrates brief, focused learning modules with real-time interaction, enhancing engagement and knowledge retention compared to traditional distance education methods. This approach leverages live digital tools and instant feedback to create a dynamic learning environment that supports immediate application and adaptive learning strategies.
Asynchronous Distance Modules
Asynchronous distance modules in distance education offer flexible, self-paced learning environments that enable students to access course materials anytime, fostering personalized comprehension and better retention. Microlearning complements this by breaking down complex subjects into concise, targeted units, enhancing engagement and knowledge retention within the asynchronous framework.
Mobile-First Microcourses
Mobile-first microcourses deliver concise, focused learning units optimized for smartphones, enhancing engagement and retention through accessibility and adaptive pacing. Distance education offers broader curriculum access but often lacks the immediacy and interactivity that mobile-first microlearning provides for on-the-go skill acquisition.
Bite-Sized Credentialing
Distance education leverages online platforms to provide flexible, comprehensive learning experiences, while microlearning emphasizes bite-sized credentialing through short, focused modules that enhance skill acquisition and retention. Bite-sized credentialing in microlearning offers learners immediate recognition for specific competencies, making it ideal for ongoing professional development and rapid knowledge validation.
Adaptive Learning Pathways
Distance education leverages adaptive learning pathways to customize courses based on learners' progress and preferences, enhancing engagement and knowledge retention in remote settings. Microlearning integrates these adaptive pathways by delivering concise, targeted content that dynamically adjusts to individual skill gaps for efficient, personalized learning experiences.
Learning Experience Platforms (LXP)
Learning Experience Platforms (LXPs) enhance distance education by providing personalized, interactive microlearning modules that boost engagement and retention through adaptive content and real-time analytics. These platforms bridge the gap between traditional distance learning and microlearning by delivering curated, bite-sized lessons tailored to individual learner profiles for efficient skill acquisition.
Nano-Degrees
Nano-Degrees offer a focused, skill-specific alternative to traditional distance education by delivering concise, industry-relevant content through microlearning modules. This approach enhances learner engagement and retention by breaking down complex subjects into manageable lessons tailored to rapid skill acquisition and career advancement.
Microcredentials
Microcredentials, often delivered through microlearning modules, provide focused, skill-specific education that enables learners to acquire competencies in a flexible, time-efficient manner, contrasting with broader, longer-term distance education programs. These bite-sized credentials enhance employability by validating targeted expertise and facilitating continuous professional development in rapidly evolving industries.
Just-in-Time Learning
Distance education offers flexible, asynchronous access to comprehensive courses, while microlearning delivers targeted, bite-sized lessons designed for just-in-time learning, enhancing immediate knowledge application. Microlearning's concise modules improve retention and engagement by providing learners with relevant information exactly when needed, complementing the broader scope of distance education.
Modular Courseware
Distance education leverages modular courseware to deliver comprehensive, self-paced learning experiences that cover extensive subject matter, while microlearning breaks content into brief, focused modules designed for quick knowledge acquisition and immediate application. Modular courseware in distance education ensures structured progression and deep engagement, whereas microlearning's bite-sized format enhances retention and flexibility for learners.
Distance Education vs Microlearning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com