Traditional grading often relies on cumulative scores that may emphasize memorization and penalize mistakes, potentially hindering a student's motivation and individual growth. Mastery-based grading centers on students demonstrating understanding of specific skills or concepts before advancing, promoting deeper learning and personalized pacing. This approach encourages continuous improvement and provides clearer insights into a learner's strengths and areas needing development.
Table of Comparison
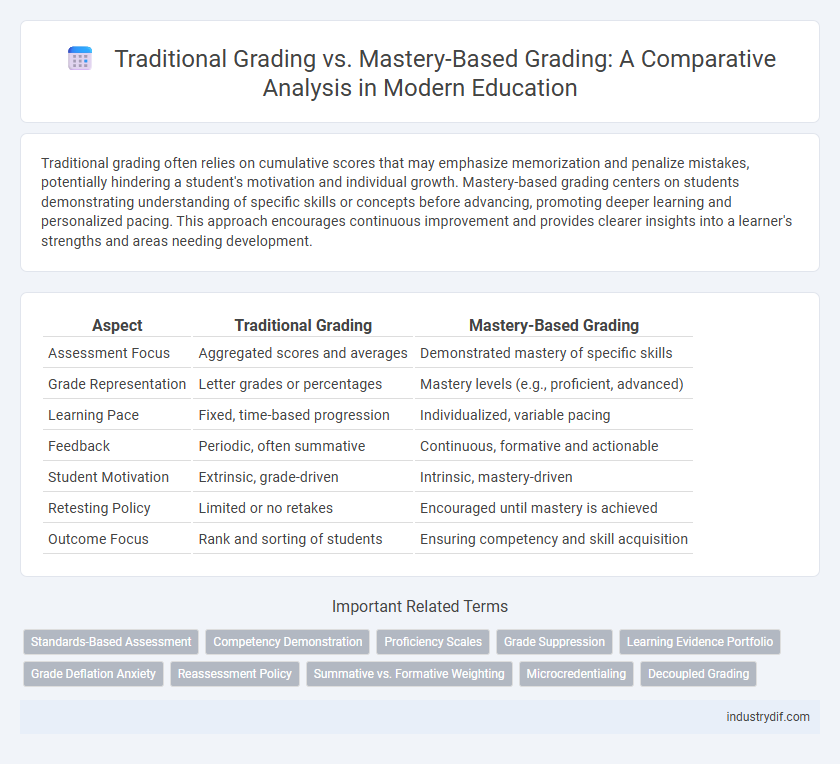
| Aspect | Traditional Grading | Mastery-Based Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment Focus | Aggregated scores and averages | Demonstrated mastery of specific skills |
| Grade Representation | Letter grades or percentages | Mastery levels (e.g., proficient, advanced) |
| Learning Pace | Fixed, time-based progression | Individualized, variable pacing |
| Feedback | Periodic, often summative | Continuous, formative and actionable |
| Student Motivation | Extrinsic, grade-driven | Intrinsic, mastery-driven |
| Retesting Policy | Limited or no retakes | Encouraged until mastery is achieved |
| Outcome Focus | Rank and sorting of students | Ensuring competency and skill acquisition |
Defining Traditional Grading in Education
Traditional grading in education assigns students letter grades or percentages based on cumulative performance in exams, homework, and class participation. This system emphasizes comparative ranking and often relies on standardized testing to measure achievement. Critics argue that it may not accurately reflect individual learning growth or mastery of specific skills.
What Is Mastery-Based Grading?
Mastery-Based Grading assesses students' understanding and proficiency in specific skills and concepts rather than assigning overall letter grades based on cumulative performance. This approach allows students to demonstrate mastery at their own pace, emphasizing personalized learning and continuous improvement. It shifts the focus from ranking and points to ensuring students attain a deep, lasting comprehension of the subject matter.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Mastery-Based Grading
Traditional grading relies on cumulative point systems and letter grades to measure student performance, often emphasizing timed assessments and homework completion. Mastery-based grading focuses on demonstrating proficiency in specific skills or standards, allowing for multiple attempts and personalized pacing. The key difference lies in assessment criteria: traditional grading aggregates performance over time, while mastery-based grading ensures students achieve a defined level of understanding before progressing.
Historical Evolution of Grading Systems
Grading systems have evolved significantly since their inception in the late 18th century, transitioning from subjective narrative evaluations to standardized letter grades in the early 20th century. Mastery-based grading emerged in the late 20th century as a response to the limitations of traditional grading, emphasizing student competence and learning outcomes over averaged scores. This shift reflects an ongoing effort to better align assessment methods with educational goals and student-centered learning models.
Benefits of Traditional Grading Methods
Traditional grading methods provide a clear, standardized way to evaluate student performance, making it easier for educators to compare achievement across diverse groups. These grades offer immediate feedback on student progress and help identify areas needing improvement through familiar letter grades or percentages. Many institutions and employers understand and trust traditional grading, facilitating smooth academic and career transitions.
Advantages of Mastery-Based Grading Approaches
Mastery-based grading emphasizes students' understanding and skill development by allowing multiple opportunities to demonstrate proficiency, which reduces stress and fosters intrinsic motivation. This approach provides personalized feedback that targets specific learning gaps, enabling tailored instructional support and continuous improvement. It promotes a growth mindset, encouraging students to take ownership of their learning and focus on mastery rather than comparing scores.
Challenges in Implementing Mastery-Based Grading
Implementing mastery-based grading faces challenges such as the need for extensive teacher training to accurately assess student competencies and the demand for significant adjustments in curriculum design and assessment methods. Schools often struggle with inconsistent standards and the increased time required for personalized feedback and tracking individual student progress. Resistance from stakeholders accustomed to traditional grading systems also hampers widespread adoption and effective integration.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Traditional grading systems often rely on numeric scores and letter grades, which can create anxiety and competition among students, potentially diminishing intrinsic motivation. Mastery-based grading emphasizes learning progress and skill acquisition, encouraging students to engage deeply with the material and view challenges as opportunities for growth. Research indicates that mastery-based approaches enhance student motivation by fostering a growth mindset and increasing personalized feedback.
Assessment Strategies in Modern Classrooms
Mastery-based grading emphasizes continuous assessment through formative evaluations, enabling personalized feedback and targeting specific skill mastery. Traditional grading relies heavily on summative assessments, often focusing on cumulative performance and ranking students against peers. Modern classrooms adopt a blend of these strategies to promote deeper learning and accurately measure student understanding and growth.
Future Trends in Educational Grading Systems
Future trends in educational grading systems emphasize a shift from traditional grading, which often relies on cumulative scores and letter grades, to mastery-based grading frameworks that prioritize student proficiency and learning outcomes. Advances in educational technology enable more personalized assessments, real-time feedback, and data analytics to support mastery learning and continuous improvement. Increasing adoption of competency-based education models signals a movement towards grading systems that better reflect individual student growth and readiness for post-secondary challenges.
Related Important Terms
Standards-Based Assessment
Standards-based assessment in mastery-based grading emphasizes students demonstrating proficiency in specific learning objectives, providing detailed feedback on their strengths and areas for improvement, unlike traditional grading which often aggregates scores into a single grade. This approach promotes personalized learning and mastery of content over time, aligning assessment with clear educational standards and fostering deeper understanding.
Competency Demonstration
Mastery-based grading emphasizes students demonstrating clear competency in specific skills or knowledge before progressing, ensuring a deeper understanding compared to traditional grading's reliance on cumulative points or percentages. This approach fosters personalized learning paths by requiring mastery of individual concepts rather than averaging performance across assessments.
Proficiency Scales
Proficiency scales in mastery-based grading provide clear, consistent criteria that define levels of student understanding, enabling personalized feedback and targeted learning goals. Unlike traditional grading, which often relies on aggregated scores and subjective interpretation, proficiency scales emphasize specific competencies, fostering deeper skill development and academic growth.
Grade Suppression
Grade suppression in traditional grading often obscures students' true understanding by averaging scores and penalizing early mistakes, whereas mastery-based grading highlights individual progress by requiring demonstrated competence in specific skills before assigning final grades. This approach reduces the negative impact of low initial performance and fosters a deeper, more accurate reflection of student learning outcomes.
Learning Evidence Portfolio
Learning Evidence Portfolios in mastery-based grading provide comprehensive documentation of student progress through diverse assessments and reflections, contrasting traditional grading's reliance on singular test scores. This approach emphasizes skill mastery and personalized feedback, fostering deeper understanding and continuous growth beyond the limitations of letter grades.
Grade Deflation Anxiety
Grade deflation anxiety often intensifies under traditional grading systems due to reliance on cumulative, percentage-based scores that may not accurately reflect a student's true understanding or skills. Mastery-based grading alleviates this anxiety by emphasizing competency and continuous improvement, allowing students to demonstrate proficiency without the pressure of competing for curved grades.
Reassessment Policy
Mastery-based grading allows students to reassess and demonstrate improved understanding over time, promoting continuous learning and skill mastery. Traditional grading policies often limit reassessment opportunities, which can hinder students' motivation to improve after initial evaluations.
Summative vs. Formative Weighting
Traditional grading systems prioritize summative assessments, assigning significant weight to final exams and major projects that evaluate cumulative knowledge. Mastery-based grading emphasizes formative assessments, continuously measuring student progress through quizzes, feedback, and practice activities to support ongoing learning and skill development.
Microcredentialing
Microcredentialing in mastery-based grading offers personalized skill validation through digital badges that represent specific competencies, enhancing student motivation and clearer learning outcomes compared to traditional grading's broad letter or number scales. This approach supports continuous assessment and real-world skill application, providing educators and employers with precise evidence of proficiency beyond aggregate grades.
Decoupled Grading
Decoupled grading separates academic achievement from behavioral assessments, providing a clearer measure of student mastery by evaluating knowledge independently from effort or participation. This approach enhances the accuracy of traditional grading systems by prioritizing demonstrated skills and understanding over subjective criteria.
Traditional Grading vs Mastery-Based Grading Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com