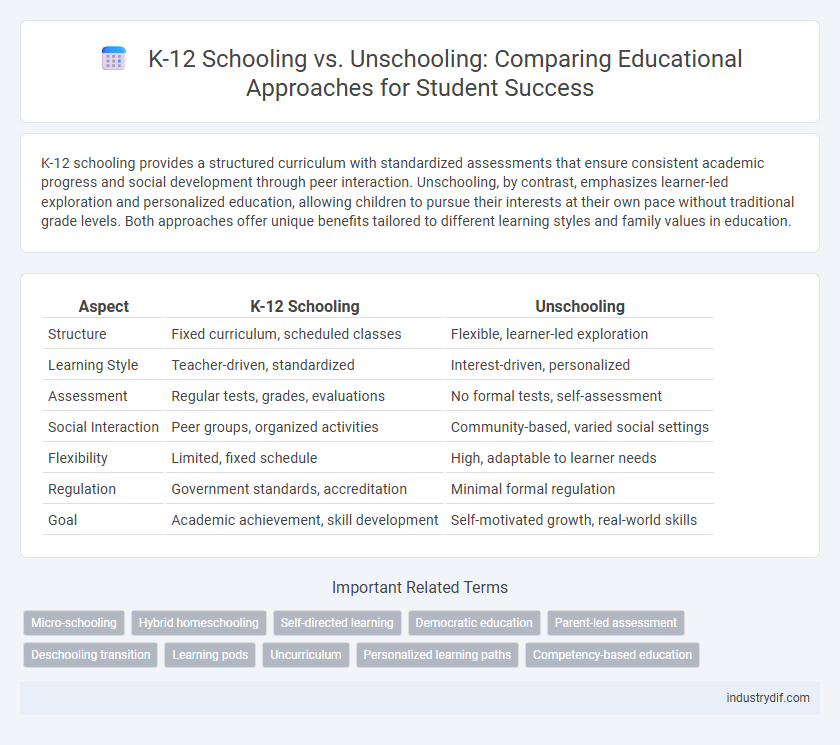
K-12 schooling provides a structured curriculum with standardized assessments that ensure consistent academic progress and social development through peer interaction. Unschooling, by contrast, emphasizes learner-led exploration and personalized education, allowing children to pursue their interests at their own pace without traditional grade levels. Both approaches offer unique benefits tailored to different learning styles and family values in education.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | K-12 Schooling | Unschooling |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fixed curriculum, scheduled classes | Flexible, learner-led exploration |
| Learning Style | Teacher-driven, standardized | Interest-driven, personalized |
| Assessment | Regular tests, grades, evaluations | No formal tests, self-assessment |
| Social Interaction | Peer groups, organized activities | Community-based, varied social settings |
| Flexibility | Limited, fixed schedule | High, adaptable to learner needs |
| Regulation | Government standards, accreditation | Minimal formal regulation |
| Goal | Academic achievement, skill development | Self-motivated growth, real-world skills |
Understanding K-12 Schooling: Traditional Framework
K-12 schooling follows a structured curriculum divided into twelve grades, designed to provide comprehensive education in core subjects such as math, science, language arts, and social studies. This traditional framework emphasizes standardized testing, teacher-led instruction, and age-based grade progression to ensure consistent learning outcomes. The system aims to prepare students for higher education and workforce readiness through a regulated schedule and certified educators.
What Is Unschooling? Core Principles Explained
Unschooling is a learner-directed educational approach that emphasizes natural curiosity and experiential learning over structured curricula in K-12 schooling. Core principles center on self-motivation, personalized learning paths, and the belief that children learn best through real-life experiences rather than traditional classroom settings. This method fosters critical thinking, creativity, and lifelong learning by allowing students to explore subjects at their own pace and according to their interests.
Curriculum Structure: K-12 vs. Unschooling
K-12 schooling follows a standardized curriculum structured by grade level, ensuring consistent progression through subjects like math, science, and language arts. Unschooling, in contrast, offers a flexible, child-led learning experience without a formal curriculum, allowing students to explore interests at their own pace. The structured approach of K-12 supports benchmark assessments, while unschooling emphasizes personalized growth and intrinsic motivation.
Teacher Roles: Educators vs. Facilitators
In K-12 schooling, teachers act as structured educators, delivering standardized curriculum and assessing student progress through formal evaluations. In unschooling, facilitators guide learners by fostering curiosity and supporting self-directed learning without rigid lesson plans or grades. This shift from educator to facilitator transforms the teacher's role from authority figure to collaborative mentor in the learning process.
Assessment Methods: Standardized Testing vs. Personalized Evaluation
K-12 schooling predominantly relies on standardized testing to evaluate student performance, offering uniform metrics that facilitate benchmarking across diverse populations. Unschooling emphasizes personalized evaluation, tailoring assessments to individual interests, learning pace, and real-world skills, which enhances intrinsic motivation and holistic development. These contrasting methods impact educational outcomes by prioritizing quantifiable results versus adaptive, learner-centered growth.
Socialization: Classroom Interactions vs. Real-world Experiences
K-12 schooling offers structured socialization through daily classroom interactions, group projects, and extracurricular activities that foster collaboration and peer engagement. Unschooling emphasizes real-world experiences where children develop social skills organically by interacting with diverse age groups and community members in varied settings. Both approaches provide distinct socialization benefits, with traditional schooling promoting consistent peer interaction and unschooling encouraging adaptability and real-life communication skills.
Flexibility in Learning: Scheduled Classes vs. Self-Directed Study
K-12 schooling offers structured learning environments with fixed schedules and standardized curricula designed to ensure comprehensive coverage of required subjects. Unschooling prioritizes flexibility through self-directed study, allowing students to explore topics based on individual interests and learning pace without rigid timetables. This adaptability in unschooling can foster creativity and intrinsic motivation, contrasting with the predictability and consistency of traditional K-12 education.
Academic Outcomes: Measuring Success and Achievement
K-12 schooling provides structured curriculum aligned with standardized testing, facilitating measurable academic outcomes and consistent achievement benchmarks. Unschooling emphasizes learner-driven exploration, resulting in varied outcomes that challenge traditional metrics of academic success. Comparing these approaches requires evaluating not only test scores but also critical thinking, creativity, and lifelong learning skills.
Parental Involvement in K-12 and Unschooling
Parental involvement in K-12 schooling often requires adherence to structured curricula, frequent communication with teachers, and participation in school events, fostering a collaborative educational environment. In contrast, unschooling places parents as primary facilitators of learning, encouraging individualized exploration and self-directed education that adapts to the child's interests. Research indicates that effective parental engagement in both models significantly influences academic outcomes and emotional development.
Future Readiness: College, Careers, and Lifelong Learning
K-12 schooling provides structured curricula designed to meet college admission standards and career prerequisites, fostering foundational skills and critical thinking essential for future academic and professional success. Unschooling emphasizes self-directed learning, nurturing adaptability, creativity, and intrinsic motivation, which align with lifelong learning and evolving career landscapes. Both approaches offer unique pathways to future readiness, balancing formal education with personal growth and autonomous skill development.
Related Important Terms
Micro-schooling
Micro-schooling offers a flexible alternative to traditional K-12 education by blending personalized learning and small class sizes, fostering deeper student engagement and tailored instruction that unschooling emphasizes without sacrificing structure. This hybrid approach supports skill development and social interaction, bridging the gap between formal schooling frameworks and the self-directed, interest-driven learning of unschooling.
Hybrid homeschooling
Hybrid homeschooling combines structured K-12 curricula with flexible unschooling methods, allowing personalized learning while meeting educational standards. This approach supports student autonomy and parental involvement, enhancing academic engagement and skill development through a tailored balance of formal instruction and experiential learning.
Self-directed learning
Self-directed learning in K-12 schooling often follows structured curricula with teacher guidance, while unschooling prioritizes learner autonomy, allowing students to explore interests at their own pace without formal constraints. Studies show self-directed learning enhances critical thinking and motivation, but outcomes depend heavily on the learner's environment and available resources.
Democratic education
Democratic education promotes student autonomy and collaborative decision-making, aligning closely with unschooling's emphasis on self-directed learning and individualized interests, contrasting with the structured curriculum and standardized assessments typical of K-12 schooling. Research shows democratic schools foster critical thinking and social responsibility, preparing students for active citizenship beyond conventional academic achievement.
Parent-led assessment
Parent-led assessment in K-12 schooling often follows standardized tests and curriculum benchmarks, offering measurable progress aligned with educational standards, while unschooling relies on observational and interest-based evaluations driven by parental insights into a child's unique learning journey. This approach in unschooling allows for flexible, individualized growth tracking that adapts to the child's evolving interests and developmental pace rather than fixed academic schedules.
Deschooling transition
Deschooling is a crucial transition phase for students moving from structured K-12 schooling to unschooling, allowing them to unlearn traditional educational norms and develop self-directed learning habits. This period helps in reducing dependency on formal schedules and assessments, fostering intrinsic motivation and personalized knowledge acquisition.
Learning pods
Learning pods offer a flexible alternative that combines structured K-12 schooling curricula with the autonomy of unschooling, allowing students to engage in personalized, collaborative learning environments. These pods leverage small-group dynamics to enhance socialization while facilitating tailored educational experiences beyond traditional classroom constraints.
Uncurriculum
Unschooling emphasizes learner-driven education without a fixed curriculum, allowing students to explore interests organically rather than following predetermined standards found in traditional K-12 schooling. This approach fosters critical thinking and creativity by prioritizing real-world experiences and personalized learning paths over rigid subject-based instruction.
Personalized learning paths
K-12 schooling offers structured curricula with standardized assessments, providing a consistent educational framework, while unschooling emphasizes personalized learning paths tailored to a child's interests and pace. Personalized learning paths in unschooling foster intrinsic motivation and adaptability, whereas K-12 schooling balances individualized support within a regulated syllabus.
Competency-based education
K-12 schooling typically follows a standardized curriculum with competency-based education emphasizing mastery of specific skills and knowledge at each grade level, ensuring measurable learning outcomes. Unschooling promotes learner-driven exploration without fixed standards, which can challenge the implementation of competency-based assessment but fosters personalized skill development.
K-12 Schooling vs Unschooling Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com