A curriculum centers on structured learning objectives and standardized content designed to ensure consistent knowledge acquisition across diverse student populations. A culturally responsive curriculum goes beyond standard content by integrating students' cultural backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives to create more relevant and engaging learning environments. This approach fosters inclusivity, promotes critical thinking, and supports academic success by validating and reflecting diverse identities within the educational context.
Table of Comparison
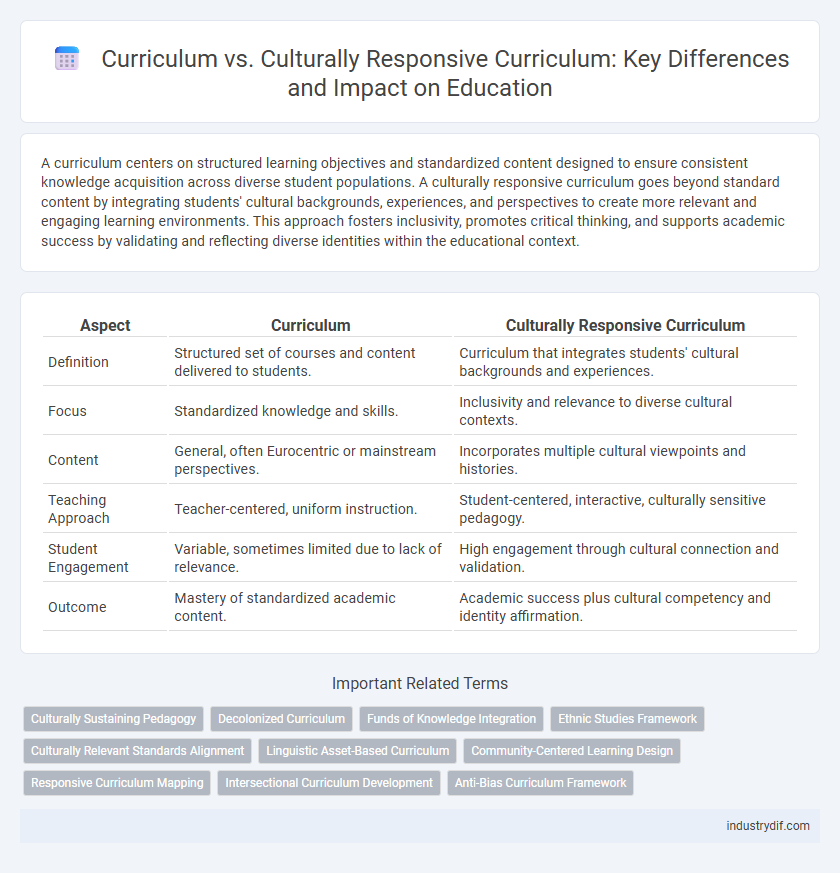
| Aspect | Curriculum | Culturally Responsive Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured set of courses and content delivered to students. | Curriculum that integrates students' cultural backgrounds and experiences. |
| Focus | Standardized knowledge and skills. | Inclusivity and relevance to diverse cultural contexts. |
| Content | General, often Eurocentric or mainstream perspectives. | Incorporates multiple cultural viewpoints and histories. |
| Teaching Approach | Teacher-centered, uniform instruction. | Student-centered, interactive, culturally sensitive pedagogy. |
| Student Engagement | Variable, sometimes limited due to lack of relevance. | High engagement through cultural connection and validation. |
| Outcome | Mastery of standardized academic content. | Academic success plus cultural competency and identity affirmation. |
Defining Traditional Curriculum
Traditional curriculum emphasizes a standardized, content-driven approach focused on core subjects with uniform objectives and assessments. It often reflects dominant cultural narratives, prioritizing established knowledge and skills over diverse perspectives. This curriculum model aims to ensure consistent academic standards but may lack relevance to the cultural backgrounds of all students.
What Is a Culturally Responsive Curriculum?
A culturally responsive curriculum integrates students' diverse cultural backgrounds into lesson plans and instructional methods to enhance engagement and learning outcomes. It prioritizes inclusivity, acknowledges different cultural perspectives, and adapts teaching materials to reflect the experiences and histories of all students. This approach contrasts with traditional curricula by fostering equity and relevance in education through culturally relevant content and pedagogical strategies.
Key Differences Between Standard and Culturally Responsive Curricula
Standard curricula often follow a uniform, prescriptive framework emphasizing core subjects and generalized content designed for a broad student population. Culturally responsive curricula integrate students' diverse cultural backgrounds, values, and experiences into lesson plans, promoting inclusivity and relevance in learning. The key differences lie in the adaptability of content, the acknowledgment of multicultural perspectives, and the emphasis on building critical thinking through cultural awareness.
The Role of Culture in Shaping Educational Content
Culturally responsive curriculum integrates students' diverse cultural backgrounds, enhancing engagement and relevance in learning by reflecting their identities and experiences. Traditional curriculum often follows a standardized framework, which may overlook the cultural context that shapes how students understand and relate to educational content. Emphasizing culture in curriculum development fosters inclusivity and critical thinking by connecting academic concepts to real-world cultural perspectives.
Benefits of Culturally Responsive Curriculum for Diverse Learners
Culturally responsive curriculum enhances engagement and improves academic outcomes by reflecting students' diverse backgrounds and experiences, fostering a sense of belonging. It promotes critical thinking and empathy by integrating multiple perspectives and encouraging respectful dialogues among learners. This approach supports equity in education by addressing cultural gaps and reducing achievement disparities for students from marginalized communities.
Challenges in Implementing Culturally Responsive Practices
Implementing culturally responsive curriculum faces challenges such as teacher preparedness, inadequate training on cultural competence, and resistance to change within traditional education systems. Limited resources and standardized testing pressures often hinder flexibility in content and teaching methods, reducing opportunities to address diverse student backgrounds effectively. Engaging families and communities to ensure curriculum relevance also presents difficulties, particularly in areas with varied cultural identities and languages.
Equity and Inclusion in Curriculum Design
Equity and inclusion in curriculum design prioritize culturally responsive curriculum by integrating students' diverse cultural backgrounds, promoting meaningful engagement, and addressing historical biases often present in traditional curricula. Unlike standard curricula, culturally responsive curriculum employs principles of culturally sustaining pedagogy to foster academic success and positive identity development among marginalized groups. This approach enhances equitable educational outcomes by ensuring all learners see their experiences reflected and valued in the content and teaching methods.
Teacher Preparation for Culturally Responsive Teaching
Teacher preparation for culturally responsive teaching emphasizes deep understanding of diverse student backgrounds and integrating inclusive pedagogical strategies within the curriculum. Developing skills to recognize implicit biases and adapt instructional materials ensures that educators effectively engage students from varied cultural contexts. This approach enriches traditional curriculum frameworks by prioritizing equity, relevance, and meaningful student connection.
Evaluating Curriculum Effectiveness: Traditional vs. Culturally Responsive
Evaluating curriculum effectiveness requires analyzing student engagement, academic achievement, and cultural relevance within traditional and culturally responsive frameworks. Traditional curricula often emphasize standardized content mastery, whereas culturally responsive curricula incorporate students' cultural backgrounds to enhance understanding and critical thinking. Research shows culturally responsive curricula improve student motivation and equity outcomes by fostering inclusive learning environments tailored to diverse communities.
Future Trends in Curriculum Development
Future trends in curriculum development emphasize the integration of culturally responsive curriculum to address diverse student backgrounds and promote inclusivity. This approach contrasts with traditional curricula by embedding cultural contexts and values, enhancing student engagement and academic achievement. Educational frameworks are increasingly leveraging technology and interdisciplinary methods to create adaptive, personalized learning experiences that reflect global and multicultural perspectives.
Related Important Terms
Culturally Sustaining Pedagogy
Culturally sustaining pedagogy extends beyond culturally responsive curriculum by actively preserving and revitalizing students' cultural identities within the learning environment, supporting linguistic diversity and heritage practices. It fosters academic success while promoting critical consciousness and empowering students to navigate and challenge societal inequities through culturally affirming content and instructional strategies.
Decolonized Curriculum
A decolonized curriculum challenges traditional Eurocentric narratives by integrating Indigenous knowledge systems, diverse cultural perspectives, and critically examining colonial histories to promote equity and inclusion in education. This approach fosters critical thinking, empowers marginalized voices, and transforms the curriculum into a tool for social justice and reconciliation.
Funds of Knowledge Integration
Curriculum that integrates funds of knowledge leverages students' cultural backgrounds and lived experiences to enhance learning relevance and engagement. Culturally responsive curriculum prioritizes this integration by validating diverse epistemologies, thereby promoting deeper understanding and academic success.
Ethnic Studies Framework
Ethnic Studies Framework emphasizes a culturally responsive curriculum that integrates diverse histories, identities, and perspectives to promote inclusivity and critical thinking, contrasting traditional curricula that often center dominant cultural narratives. This approach enhances student engagement and equity by validating marginalized experiences and fostering a deeper understanding of sociocultural dynamics within education.
Culturally Relevant Standards Alignment
Culturally responsive curriculum aligns with culturally relevant standards by integrating students' diverse cultural backgrounds into learning objectives, promoting inclusivity and equity in education. This approach enhances student engagement and achievement by validating their identities and experiences within the academic framework.
Linguistic Asset-Based Curriculum
A Linguistic Asset-Based Curriculum recognizes and incorporates students' diverse language backgrounds as valuable resources, fostering academic achievement and identity affirmation. This approach contrasts traditional curricula by emphasizing multilingualism and cultural relevance to promote equity and inclusivity in education.
Community-Centered Learning Design
Community-centered learning design in a culturally responsive curriculum integrates students' cultural backgrounds and local experiences to enhance relevance and engagement, fostering deeper understanding and inclusion. Unlike traditional curricula, this approach prioritizes community knowledge, values, and assets, promoting equity and empowering learners through meaningful connections to their environment.
Responsive Curriculum Mapping
Responsive curriculum mapping integrates students' cultural backgrounds into lesson planning, ensuring learning materials reflect diverse perspectives and experiences to enhance engagement and comprehension. This approach contrasts with traditional curriculum design by prioritizing inclusivity and adaptability, promoting equity in education through culturally relevant content and teaching strategies.
Intersectional Curriculum Development
Intersectional curriculum development integrates diverse cultural perspectives and identities, ensuring that educational content reflects the complexity of students' lived experiences and promotes equity. Unlike traditional curricula, culturally responsive curricula emphasize inclusivity by addressing systemic biases and fostering critical thinking about social justice and identity.
Anti-Bias Curriculum Framework
Culturally responsive curricula integrate the Anti-Bias Curriculum Framework to challenge stereotypes, promote equity, and validate diverse cultural identities, contrasting traditional curricula that often reflect dominant cultural narratives. This framework emphasizes critical consciousness, respect for diversity, and social justice, fostering an inclusive learning environment that actively combats discrimination and bias.
Curriculum vs Culturally Responsive Curriculum Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com