MOOCs offer flexible, self-paced learning with diverse subjects accessible globally, ideal for independent learners seeking broad knowledge. Cohort-based courses emphasize real-time interaction, peer collaboration, and structured timelines, fostering accountability and deeper engagement. Choosing between them depends on individual learning preferences, commitment levels, and desired educational outcomes.
Table of Comparison
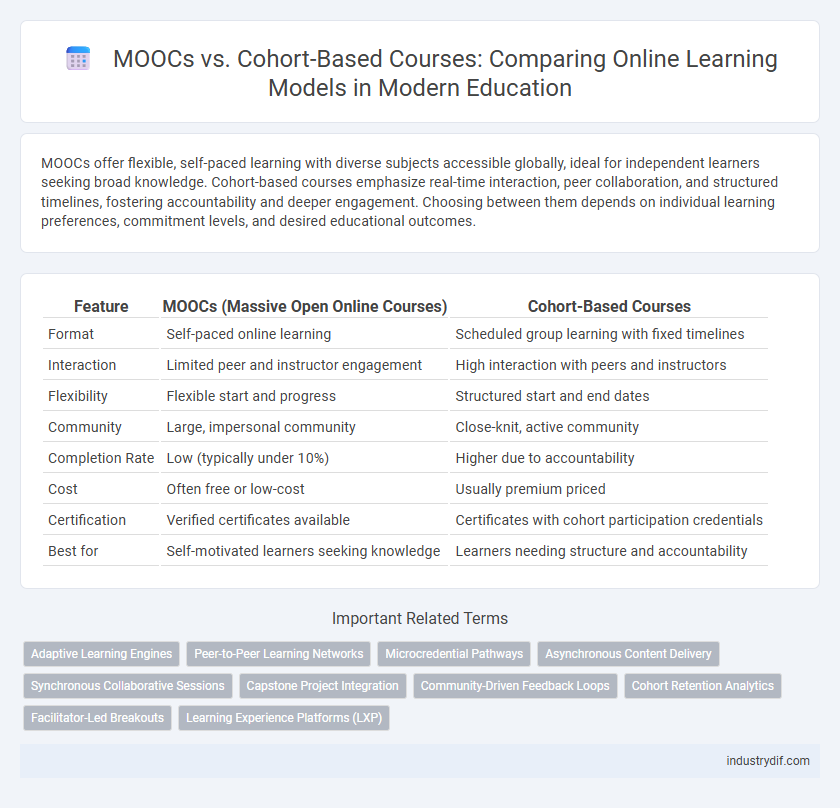
| Feature | MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) | Cohort-Based Courses |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Self-paced online learning | Scheduled group learning with fixed timelines |
| Interaction | Limited peer and instructor engagement | High interaction with peers and instructors |
| Flexibility | Flexible start and progress | Structured start and end dates |
| Community | Large, impersonal community | Close-knit, active community |
| Completion Rate | Low (typically under 10%) | Higher due to accountability |
| Cost | Often free or low-cost | Usually premium priced |
| Certification | Verified certificates available | Certificates with cohort participation credentials |
| Best for | Self-motivated learners seeking knowledge | Learners needing structure and accountability |
Understanding MOOCs: Definition and Structure
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) offer flexible, self-paced learning with open enrollment, enabling thousands of learners worldwide to access diverse subjects without time constraints. Unlike cohort-based courses, MOOCs typically feature pre-recorded lectures, quizzes, and forums but lack synchronized interaction with instructors or peers. This structure supports individualized progression but may limit real-time collaboration and community building among participants.
What Are Cohort-Based Courses?
Cohort-based courses are structured educational programs where learners progress through the material together in scheduled sessions, fostering interaction and collaboration. Unlike MOOCs, which allow self-paced learning, cohort courses emphasize real-time engagement, peer support, and accountability. This format improves completion rates and enhances understanding through group discussions and collective problem-solving.
Key Differences Between MOOCs and Cohort-Based Learning
MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) offer flexible, self-paced learning accessible to thousands worldwide, emphasizing broad content delivery without personalized interaction. Cohort-based courses involve smaller, scheduled groups fostering peer collaboration, real-time feedback, and structured progress through interactive learning. These distinct formats cater to different learner needs, balancing scalability with engagement and accountability.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Online Education
MOOCs offer unparalleled flexibility, allowing learners to access course materials anytime and anywhere, accommodating diverse schedules and pacing. Cohort-based courses enhance accessibility through structured timelines and peer interaction, fostering accountability and collaborative learning environments. Both models democratize education by breaking geographical and temporal barriers, yet MOOCs excel in self-paced study, while cohort-based courses provide guided engagement.
Engagement and Interaction: Comparing Learning Models
MOOCs often offer flexibility and accessibility but struggle with lower engagement due to limited real-time interaction and passive learning formats. Cohort-based courses foster higher engagement through scheduled sessions, peer collaboration, and active discussions, enhancing motivation and accountability. Research shows cohort models increase course completion rates and deeper knowledge retention compared to self-paced MOOCs.
Course Completion Rates: MOOCs vs Cohorts
Cohort-based courses consistently demonstrate higher completion rates, often exceeding 70%, compared to MOOCs where completion rates average below 10%. The structured schedule and peer interaction in cohort-based courses enhance learner engagement and accountability. MOOCs typically suffer from lower commitment levels and lack personalized support, contributing to higher dropout rates.
Cost and Affordability Factors
MOOCs typically offer free or low-cost access to high-quality content from top universities, making them highly affordable for self-paced learners. Cohort-based courses often require higher tuition fees due to personalized instruction, live interaction, and community support, which can increase the overall cost. Budget-conscious students prioritize MOOCs for cost-effectiveness but may invest in cohort-based models for enhanced engagement and networking opportunities.
Best Use Cases for MOOCs
MOOCs excel in providing flexible, scalable learning opportunities for diverse, global audiences seeking foundational knowledge or skill enhancement at their own pace. Ideal for self-motivated learners and professionals aiming to access high-quality courses from top universities without geographical constraints, MOOCs support continuous education in rapidly evolving fields like technology and business. Their strength lies in democratizing education through cost-effective, accessible content, making them best suited for broad, introductory learning rather than intensive, collaborative experiences.
Ideal Scenarios for Cohort-Based Courses
Cohort-based courses excel in scenarios requiring real-time interaction and collaborative learning, such as professional training and skill development workshops. These courses foster accountability and community through synchronized schedules, enhancing motivation and deeper engagement among participants. Ideal for complex subjects demanding peer feedback and instructor guidance, cohort-based formats outperform MOOCs by providing structured support and networking opportunities.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Learning Goals
MOOCs offer flexible, self-paced learning ideal for acquiring broad knowledge and exploring new subjects without time constraints. Cohort-based courses foster collaboration and accountability through scheduled sessions and peer interaction, enhancing motivation and deep understanding. Selecting the right model depends on your learning objectives, time availability, and preference for structured guidance versus independent study.
Related Important Terms
Adaptive Learning Engines
Adaptive learning engines in MOOCs leverage large-scale data analytics to personalize content for diverse learners, optimizing engagement through real-time feedback and progress tracking. Cohort-based courses utilize adaptive technologies to facilitate tailored group interactions and scaffolded support, enhancing collaborative learning dynamics and retention rates.
Peer-to-Peer Learning Networks
MOOCs often lack structured peer-to-peer learning networks, which limits collaborative engagement and real-time feedback, whereas cohort-based courses foster robust interaction among learners through scheduled discussions and group projects, enhancing knowledge retention and critical thinking. Peer-to-peer learning in cohort-based settings cultivates accountability and diverse perspectives, driving deeper understanding compared to the isolated, self-paced model typical of MOOCs.
Microcredential Pathways
MOOCs offer flexible, self-paced learning opportunities but often lack structured guidance, whereas cohort-based courses provide collaborative engagement crucial for microcredential pathways that emphasize skill validation and career readiness. Microcredential pathways in cohort-based models enhance learner accountability and networking, resulting in higher completion rates and improved workforce relevance compared to traditional MOOCs.
Asynchronous Content Delivery
MOOCs offer asynchronous content delivery that enables learners to access lectures and materials at their convenience, promoting flexibility and self-paced study. Cohort-based courses often blend asynchronous content with scheduled interactions, encouraging peer collaboration while maintaining structured timelines.
Synchronous Collaborative Sessions
Synchronous collaborative sessions in cohort-based courses enhance real-time interaction and peer engagement, fostering deeper understanding compared to the mostly asynchronous nature of MOOCs. These live discussions and group activities improve motivation and accountability, leading to higher course completion rates and more effective skill acquisition.
Capstone Project Integration
MOOCs typically offer self-paced learning with optional capstone projects that vary in complexity, while cohort-based courses integrate mandatory, collaborative capstone projects designed to reinforce skills through real-world applications and peer interaction. This structured capstone approach in cohort-based courses enhances practical knowledge retention and fosters networking opportunities, setting them apart from the more flexible but less interactive MOOC models.
Community-Driven Feedback Loops
MOOCs offer vast accessibility but often lack personalized community-driven feedback loops that cohort-based courses provide, fostering deeper peer interaction and collaborative learning. Cohort-based courses enhance educational outcomes through structured group dynamics, enabling real-time, iterative feedback that accelerates skill mastery and engagement.
Cohort Retention Analytics
Cohort-based courses exhibit higher retention rates compared to MOOCs, with analytics showing retention improvements of up to 40% due to structured peer interaction and scheduled milestones. Data-driven cohort retention analytics enable educators to identify at-risk students early, personalize interventions, and optimize course completion outcomes effectively.
Facilitator-Led Breakouts
Facilitator-led breakouts in cohort-based courses enhance engagement by enabling real-time interaction, personalized feedback, and collaborative learning, which are often limited in MOOCs. This dynamic format fosters deeper understanding and accountability among learners, significantly improving retention and skill application.
Learning Experience Platforms (LXP)
Learning Experience Platforms (LXP) enhance the personalized learning journey by integrating adaptive content delivery and social learning features, contrasting with the fixed, self-paced structure of MOOCs that often lack interactive engagement. Cohort-Based Courses on LXP foster collaborative environments and real-time feedback, driving higher completion rates and deeper knowledge retention compared to traditional mass online offerings.
MOOCs vs Cohort-Based Courses Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com