Synchronous learning fosters real-time interaction and immediate feedback, enhancing engagement in educational pets settings. Asynchronous collaborative learning allows learners to engage with content and peers at their own pace, promoting deeper reflection and flexibility. Both approaches support diverse learning styles, making them essential for effective pet education programs.
Table of Comparison
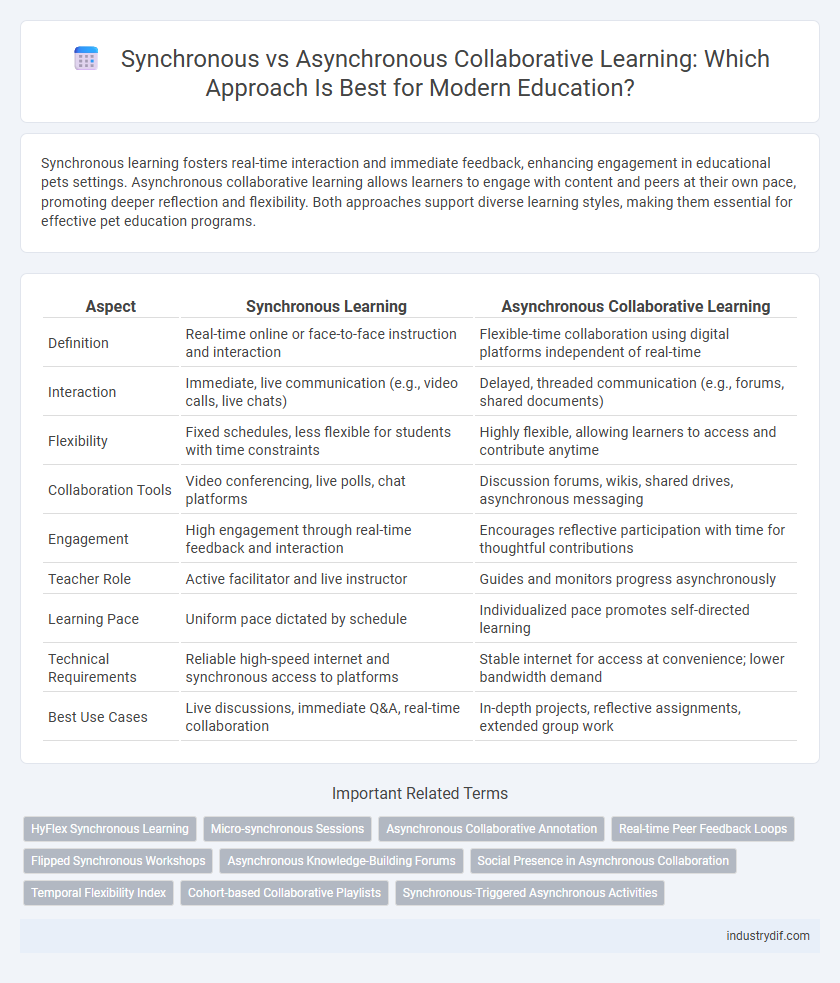
| Aspect | Synchronous Learning | Asynchronous Collaborative Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time online or face-to-face instruction and interaction | Flexible-time collaboration using digital platforms independent of real-time |
| Interaction | Immediate, live communication (e.g., video calls, live chats) | Delayed, threaded communication (e.g., forums, shared documents) |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedules, less flexible for students with time constraints | Highly flexible, allowing learners to access and contribute anytime |
| Collaboration Tools | Video conferencing, live polls, chat platforms | Discussion forums, wikis, shared drives, asynchronous messaging |
| Engagement | High engagement through real-time feedback and interaction | Encourages reflective participation with time for thoughtful contributions |
| Teacher Role | Active facilitator and live instructor | Guides and monitors progress asynchronously |
| Learning Pace | Uniform pace dictated by schedule | Individualized pace promotes self-directed learning |
| Technical Requirements | Reliable high-speed internet and synchronous access to platforms | Stable internet for access at convenience; lower bandwidth demand |
| Best Use Cases | Live discussions, immediate Q&A, real-time collaboration | In-depth projects, reflective assignments, extended group work |
Defining Synchronous Learning in Modern Education
Synchronous learning in modern education involves real-time, interactive instruction where students and educators engage simultaneously through virtual classrooms or live video sessions. This approach facilitates immediate feedback, dynamic discussions, and collaborative problem-solving, enhancing engagement and comprehension. By leveraging tools like video conferencing platforms and live chat, synchronous learning replicates traditional classroom dynamics within digital environments.
Understanding Asynchronous Collaborative Learning Models
Asynchronous collaborative learning models enable learners to engage with course materials and peers at different times, fostering flexibility and deeper reflection. These models utilize discussion boards, shared documents, and recorded lectures to promote continuous interaction without requiring simultaneous attendance. Research indicates that asynchronous collaboration enhances critical thinking and supports diverse learning paces, making it an effective alternative to traditional synchronous learning environments.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Collaboration
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction where students and instructors engage simultaneously via video calls, live chats, or virtual classrooms, enhancing immediate feedback and dynamic discussions. Asynchronous collaborative learning allows participants to contribute at their own pace through forums, shared documents, and recorded lectures, promoting flexibility and deeper reflection on course materials. Key differences include timing of participation, communication immediacy, and adaptability to diverse schedules, impacting student engagement and learning outcomes.
Technological Tools Powering Synchronous Learning
Technological tools powering synchronous learning include video conferencing platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet, which facilitate real-time interaction and immediate feedback. Interactive whiteboards and collaborative software such as Jamboard and Miro enhance engagement by allowing simultaneous participation. Real-time chat features and polling tools integrated within platforms support dynamic discussions and instant assessments, optimizing the synchronous learning experience.
Essential Platforms for Asynchronous Collaborative Learning
Essential platforms for asynchronous collaborative learning include tools like Google Workspace, Microsoft Teams, and Slack, which facilitate real-time document editing, file sharing, and communication across different time zones. Learning management systems (LMS) such as Moodle and Canvas provide structured environments for discussion forums, assignment submissions, and peer feedback, enhancing flexibility and learner engagement. These platforms support asynchronous interaction, enabling learners to collaborate effectively without needing simultaneous participation.
Student Engagement: Synchronous vs Asynchronous Strategies
Synchronous learning fosters immediate interaction and real-time feedback, enhancing student engagement through live discussions and collaborative activities. In contrast, asynchronous collaborative learning allows students to engage at their own pace, promoting deeper reflection and flexible participation in discussion forums and project collaboration. Combining both strategies can optimize engagement by balancing active communication with reflective learning.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Learning Modalities
Synchronous learning offers real-time interaction that fosters immediate feedback but requires fixed schedules, which can limit flexibility for students balancing multiple commitments. Asynchronous collaborative learning enhances accessibility by allowing learners to engage with materials and peers at their own pace, accommodating diverse time zones and personal responsibilities. Both modalities support effective education, but asynchronous formats provide greater flexibility, making learning more inclusive for varied lifestyles and accessibility needs.
Impact on Learning Outcomes: Real-Time vs Self-Paced Collaboration
Synchronous learning fosters immediate interaction and instant feedback through real-time collaboration, enhancing engagement and quick problem-solving skills. Asynchronous collaborative learning allows students to process information at their own pace, promoting deeper reflection and critical thinking. Research indicates that combining both methods can lead to improved learning outcomes by balancing active participation with thoughtful analysis.
Instructor Roles in Synchronous and Asynchronous Environments
In synchronous learning environments, instructors actively facilitate real-time interactions, providing immediate feedback and guiding discussions to foster engagement and comprehension. In asynchronous collaborative learning, instructors design structured tasks, curate resources, and monitor progress to promote independent critical thinking and flexible participation. Effective instructor roles adapt to each setting by combining direct facilitation with strategic support to optimize student collaboration and learning outcomes.
Future Trends in Blended and Hybrid Learning Approaches
Future trends in blended and hybrid learning emphasize a balanced integration of synchronous learning, which provides real-time interaction and immediate feedback, and asynchronous collaborative learning that fosters flexibility and deeper reflection through discussion forums and shared digital workspaces. Advances in artificial intelligence and adaptive learning technologies enhance personalized learning experiences by dynamically adjusting content delivery in both synchronous lectures and asynchronous activities. Emerging educational models increasingly leverage data analytics to optimize student engagement and success across diverse learning environments, ensuring scalable and effective hybrid education frameworks.
Related Important Terms
HyFlex Synchronous Learning
HyFlex synchronous learning integrates live, real-time instruction with flexible participation options, allowing students to choose between in-person or remote attendance while engaging simultaneously. This approach enhances collaboration and immediate feedback, contrasting with asynchronous learning's flexible timing but delayed interaction, making HyFlex ideal for dynamic educational environments seeking to balance accessibility and active engagement.
Micro-synchronous Sessions
Micro-synchronous sessions in synchronous learning enable real-time interaction and immediate feedback, enhancing student engagement and collaboration within short, focused time frames. These brief, scheduled interactions contrast with asynchronous collaborative learning, where participants contribute at their convenience, fostering flexibility but potentially reducing immediate peer response and dynamic group interaction.
Asynchronous Collaborative Annotation
Asynchronous collaborative annotation enhances student engagement by allowing learners to interact with course materials and peers at their own pace, fostering deeper critical thinking and reflection. This method supports flexible schedules and diverse learning styles, improving knowledge retention and facilitating comprehensive discourse compared to synchronous learning environments.
Real-time Peer Feedback Loops
Synchronous learning facilitates real-time peer feedback loops, enabling immediate clarification and dynamic interaction that enhance collaborative understanding and engagement. Asynchronous collaborative learning, while offering flexibility, relies on delayed responses, potentially slowing the feedback process but allowing for more reflective and detailed input.
Flipped Synchronous Workshops
Flipped synchronous workshops combine pre-recorded lectures with live interactive sessions, allowing learners to engage actively during real-time discussions and collaborative tasks, enhancing comprehension and retention. This approach leverages the benefits of synchronous learning's immediate feedback while supporting asynchronous preparation, fostering deeper understanding and student engagement.
Asynchronous Knowledge-Building Forums
Asynchronous knowledge-building forums enable learners to engage deeply with educational content and peers at their own pace, fostering reflective dialogue and critical thinking without time constraints. This flexible approach enhances collaboration by allowing participants to contribute thoughtfully, creating a rich repository of shared knowledge that supports diverse learning styles and schedules.
Social Presence in Asynchronous Collaboration
Asynchronous collaborative learning enhances social presence by allowing students to engage thoughtfully through forums, shared documents, and recorded discussions, fostering deeper reflection and interaction over time. This approach supports diverse communication styles and flexible participation, which can strengthen peer relationships and collective knowledge construction despite time delays.
Temporal Flexibility Index
Synchronous learning offers real-time interaction but limits temporal flexibility, requiring participants to engage simultaneously, whereas asynchronous collaborative learning maximizes the Temporal Flexibility Index by allowing students to access, contribute, and review educational content at their own pace. This enhanced temporal flexibility supports diverse learning schedules and fosters deeper reflection and individual accountability in collaborative educational environments.
Cohort-based Collaborative Playlists
Cohort-based collaborative playlists enhance synchronous learning by enabling real-time interaction and immediate feedback among students, fostering a dynamic group learning environment. In asynchronous collaborative learning, these playlists allow learners to contribute and reflect at their own pace, promoting deeper engagement and sustained knowledge construction within diverse cohorts.
Synchronous-Triggered Asynchronous Activities
Synchronous-triggered asynchronous activities integrate real-time interactions with independent study, enhancing comprehension and retention by allowing students to revisit live discussions through recorded sessions and follow-up assignments. This hybrid approach leverages immediate feedback and collaborative problem-solving during synchronous sessions while promoting deep reflection and personalized learning in subsequent asynchronous tasks.
Synchronous Learning vs Asynchronous Collaborative Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com