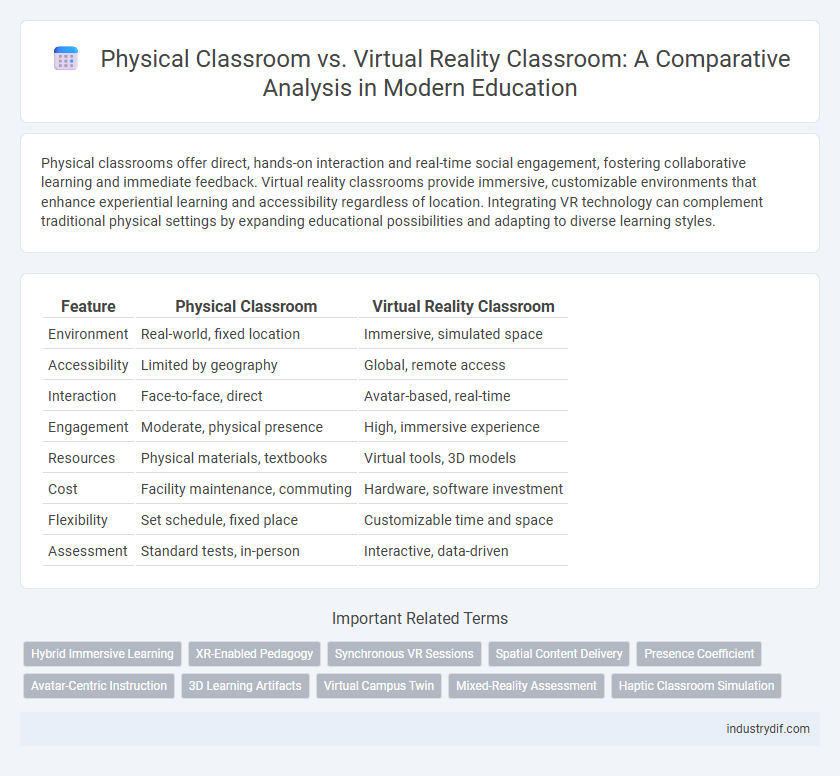
Physical classrooms offer direct, hands-on interaction and real-time social engagement, fostering collaborative learning and immediate feedback. Virtual reality classrooms provide immersive, customizable environments that enhance experiential learning and accessibility regardless of location. Integrating VR technology can complement traditional physical settings by expanding educational possibilities and adapting to diverse learning styles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Physical Classroom | Virtual Reality Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Real-world, fixed location | Immersive, simulated space |
| Accessibility | Limited by geography | Global, remote access |
| Interaction | Face-to-face, direct | Avatar-based, real-time |
| Engagement | Moderate, physical presence | High, immersive experience |
| Resources | Physical materials, textbooks | Virtual tools, 3D models |
| Cost | Facility maintenance, commuting | Hardware, software investment |
| Flexibility | Set schedule, fixed place | Customizable time and space |
| Assessment | Standard tests, in-person | Interactive, data-driven |
Defining Physical Classrooms and Virtual Reality Classrooms
Physical classrooms are traditional learning environments where students and teachers interact face-to-face within a designated space equipped with desks, whiteboards, and other educational tools. Virtual reality classrooms utilize immersive 3D technology to simulate real-world or imaginative learning settings, allowing remote participants to engage in interactive lessons through VR headsets. Both settings offer distinct sensory experiences and engagement methods tailored to different educational needs.
Evolution of Educational Environments
Physical classrooms have traditionally provided structured learning spaces with direct teacher-student interaction and tangible resources, fostering social skills and immediate feedback. Virtual reality classrooms represent a significant evolution, offering immersive, interactive environments that enable experiential learning, personalized pacing, and global collaboration without geographic constraints. This shift enhances engagement and accessibility while integrating advanced technologies like AI-driven adaptations and real-time analytics to optimize educational outcomes.
Key Features of Traditional Physical Classrooms
Traditional physical classrooms offer direct face-to-face interaction, fostering immediate communication and social engagement among students and teachers. The tactile environment supports hands-on learning with physical materials, enhancing kinesthetic understanding and collaboration. Designed with structured seating and controlled environments, they provide consistent routines and minimize technological barriers for effective instruction delivery.
Immersive Learning in Virtual Reality Classrooms
Immersive learning in virtual reality classrooms enhances student engagement by providing interactive, 3D environments that simulate real-world scenarios and complex concepts. Unlike traditional physical classrooms, virtual reality enables personalized learning experiences with immediate feedback and adaptive challenges that cater to diverse learning styles. Research indicates VR classrooms improve knowledge retention rates by up to 30% compared to conventional teaching methods.
Student Engagement and Interactive Experience Comparison
Physical classrooms offer direct, face-to-face interaction that fosters immediate student engagement through hands-on activities and real-time feedback. Virtual reality classrooms provide immersive experiences that enhance interactivity by simulating realistic scenarios and enabling experiential learning beyond traditional settings. Both environments impact student engagement differently, with VR classrooms promoting active participation through customizable, engaging content while physical classrooms benefit from personal social dynamics and spontaneous collaboration.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Both Modalities
Physical classrooms provide immediate social interaction and tactile learning tools, but they often face limitations in accessibility for students with disabilities or those in remote areas. Virtual reality classrooms enhance inclusivity by offering customizable environments that accommodate diverse learning needs and eliminate geographical barriers. Both modalities require ongoing efforts to integrate assistive technologies and adaptable content to maximize educational equity.
Cost Analysis: Physical vs Virtual Reality Implementation
Physical classrooms require substantial upfront costs for infrastructure, maintenance, and utilities, often involving long-term financial commitments. Virtual reality classrooms reduce expenses related to physical space and traditional materials but necessitate investments in VR hardware, software development, and high-speed internet connectivity. Analyzing total cost of ownership reveals VR classrooms offer scalability and lower incremental costs, making them economically viable for institutions aiming to expand access while managing budget constraints.
Teacher Roles and Instructional Delivery Differences
In physical classrooms, teachers act as direct facilitators, using body language and real-time feedback to engage students, whereas virtual reality classrooms require instructors to navigate immersive digital environments and employ augmented tools for interaction. Instructional delivery in physical settings relies heavily on traditional methods like lectures and hands-on activities, while virtual reality enables experiential learning through simulations and interactive scenarios. The shift to virtual reality demands teachers adopt new technical skills and adapt pedagogical strategies to maintain student engagement in a fully digital space.
Assessment Methods in Physical and VR Classrooms
Assessment methods in physical classrooms typically rely on traditional tools such as written exams, oral presentations, and hands-on practical evaluations that enable direct observation of student skills and behaviors. Virtual reality (VR) classrooms leverage immersive technology to provide interactive assessments, including simulated scenarios, real-time skill demonstrations, and analytics on student engagement and decision-making processes. The integration of VR in assessment enhances personalized feedback and allows educators to measure competencies in environments replicating real-world challenges, offering a dynamic alternative to conventional testing formats.
Future Trends in Classroom Learning Technologies
Physical classrooms continue to integrate augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) tools to enhance immersive learning experiences, while virtual reality classrooms evolve with AI-driven personalized content and real-time collaboration features. Emerging technologies such as mixed reality and haptic feedback systems are set to redefine student engagement and experiential learning by simulating realistic environments and interactions. Future trends emphasize hybrid models combining physical presence and virtual immersion, leveraging 5G connectivity and cloud computing to deliver seamless, scalable educational experiences.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Immersive Learning
Hybrid immersive learning combines the tangible engagement of physical classrooms with the interactive, simulated environments of virtual reality, enhancing student comprehension and retention through multisensory experiences. This approach leverages VR's ability to create customizable scenarios alongside traditional teaching methods, promoting active participation and personalized learning outcomes.
XR-Enabled Pedagogy
XR-enabled pedagogy transforms traditional education by integrating augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies into the physical classroom, enhancing immersive learning experiences and increasing student engagement. Virtual reality classrooms leverage XR to provide interactive simulations and real-time collaboration beyond physical constraints, improving comprehension and retention in complex subjects like science, engineering, and medical training.
Synchronous VR Sessions
Synchronous VR sessions in virtual reality classrooms enhance student engagement by providing immersive, real-time interactions that mimic physical classroom dynamics. This technology offers spatial audio, 3D visualizations, and interactive environments, optimizing collaborative learning and reducing geographical barriers in education.
Spatial Content Delivery
Physical classrooms provide tangible spatial experiences through direct interaction with real-world objects and environments, enhancing kinesthetic learning and immediate spatial awareness. Virtual reality classrooms deliver immersive 3D spatial content that allows students to explore complex concepts and environments beyond physical limitations, improving engagement and retention through experiential learning.
Presence Coefficient
The Presence Coefficient, a key metric in educational environments, measures the extent to which learners feel immersed and engaged within a classroom setting. Virtual Reality Classrooms consistently demonstrate higher Presence Coefficients compared to Physical Classrooms, enhancing student interaction, spatial awareness, and cognitive retention through simulated environments.
Avatar-Centric Instruction
Avatar-centric instruction in virtual reality classrooms enables immersive, interactive learning experiences that enhance student engagement and retention more effectively than physical classrooms. This approach leverages customizable digital avatars to foster personalized communication and active participation, bridging the gap between real-world presence and virtual interaction.
3D Learning Artifacts
Physical classrooms provide tangible 3D learning artifacts that enhance spatial understanding and tactile engagement, facilitating hands-on experiments and real-time collaboration. Virtual reality classrooms simulate these 3D artifacts digitally, offering immersive interactive models that enable students to explore complex concepts and manipulate objects within a controlled virtual environment.
Virtual Campus Twin
Virtual Campus Twin technology enables immersive learning experiences by replicating physical classroom dynamics within a virtual reality environment, enhancing student engagement and accessibility. This advanced simulation supports collaborative interaction and real-time feedback, bridging gaps between traditional education and digital innovation.
Mixed-Reality Assessment
Mixed-reality assessments in education leverage both physical classroom environments and virtual reality to provide immersive, interactive evaluations that adapt to student responses in real time. This technology enhances traditional testing by integrating sensory feedback and contextual simulations, improving engagement and offering precise data on student performance and competencies.
Haptic Classroom Simulation
Haptic classroom simulation in virtual reality offers immersive tactile feedback that enhances kinesthetic learning, allowing students to physically interact with digital objects and environments in ways impossible in traditional physical classrooms. This technology bridges sensory engagement gaps by simulating real-world touch and manipulation, which can improve comprehension and retention in STEM subjects and skill-based training.
Physical Classroom vs Virtual Reality Classroom Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com