Feature films offer a linear storytelling experience with a fixed narrative, allowing audiences to immerse themselves in a carefully crafted plot and cinematic visuals. Interactive narratives provide a dynamic experience where viewers influence the story's outcome, enhancing engagement through decision-making and personalized paths. This blend of storytelling and interactivity transforms passive viewers into active participants, redefining entertainment in the digital age.
Table of Comparison
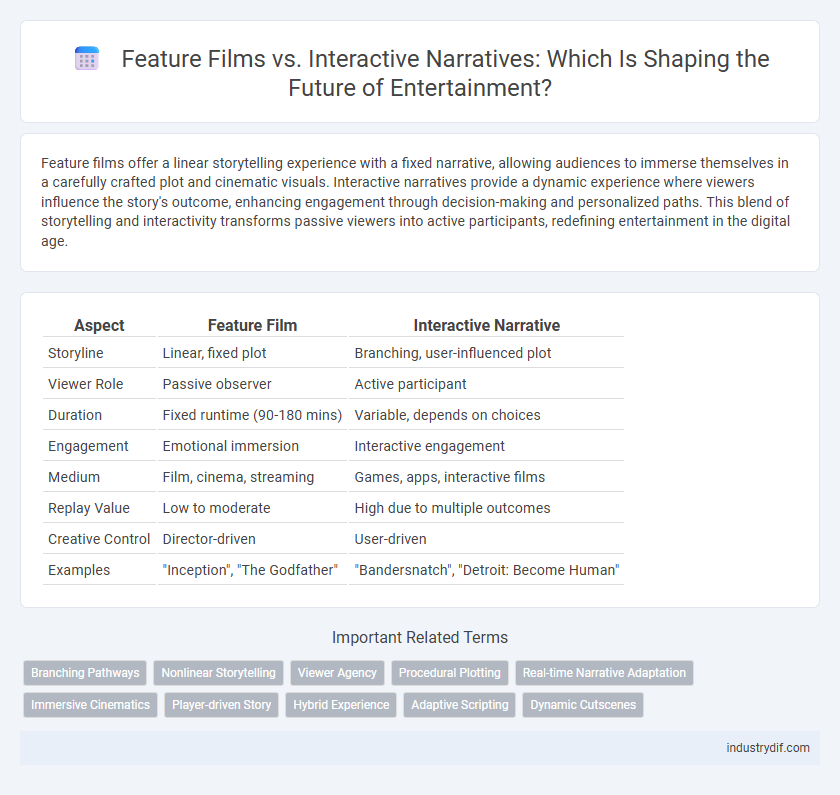
| Aspect | Feature Film | Interactive Narrative |
|---|---|---|
| Storyline | Linear, fixed plot | Branching, user-influenced plot |
| Viewer Role | Passive observer | Active participant |
| Duration | Fixed runtime (90-180 mins) | Variable, depends on choices |
| Engagement | Emotional immersion | Interactive engagement |
| Medium | Film, cinema, streaming | Games, apps, interactive films |
| Replay Value | Low to moderate | High due to multiple outcomes |
| Creative Control | Director-driven | User-driven |
| Examples | "Inception", "The Godfather" | "Bandersnatch", "Detroit: Become Human" |
Defining Feature Film and Interactive Narrative
Feature films are traditionally linear, pre-scripted visual stories presented in theaters or on streaming platforms, delivering a fixed narrative crafted by directors and screenwriters. Interactive narratives engage audiences by allowing them to influence story outcomes through choices and actions, blending storytelling with gameplay elements across digital mediums like video games and immersive experiences. Both formats prioritize emotional engagement but differ fundamentally in user agency and narrative structure.
Historical Evolution of Both Formats
Feature films originated in the late 19th century with pioneers like Georges Melies, evolving into a dominant storytelling medium through technological advancements such as synchronized sound and color cinematography. Interactive narratives emerged later, gaining momentum with the rise of digital technology and video games in the late 20th century, allowing audiences to influence story outcomes dynamically. Both formats have transformed storytelling by integrating immersive techniques, with feature films emphasizing linear, director-driven narratives and interactive narratives prioritizing user agency and branching storylines.
Narrative Structure: Linear vs Nonlinear
Feature films typically follow a linear narrative structure, presenting a clear beginning, middle, and end to guide the audience through a cohesive story arc. Interactive narratives employ a nonlinear structure, allowing viewers to influence the storyline through choices that create multiple branching paths and alternate endings. This shift from linear to nonlinear storytelling enhances user engagement by offering personalized experiences and increased narrative complexity.
Audience Engagement and Participation
Feature films offer a curated, passive viewing experience that emphasizes visual storytelling and emotional resonance, drawing audiences into a predefined narrative arc. Interactive narratives empower viewers with control over plot progression and character decisions, increasing engagement through active participation and personalized story outcomes. The contrasting dynamics between these formats highlight evolving audience preferences toward immersive, choice-driven entertainment experiences.
Creative Control: Director vs Player
Feature films grant directors comprehensive creative control over narrative structure, visual style, and pacing, ensuring a cohesive storytelling experience. Interactive narratives shift creative agency to players, allowing personalized choices to shape plot outcomes and character development. This dynamic interplay between director-driven vision and player-driven exploration redefines audience engagement in entertainment.
Technological Innovations Shaping Each Medium
Feature films utilize advanced CGI, motion capture, and high-resolution imaging to create immersive visual storytelling experiences, while interactive narratives integrate real-time rendering, branching storylines, and AI-driven character interactions to engage users dynamically. Emerging technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) further blur the lines by enabling interactive films and experiential narratives that respond to audience choices. Machine learning algorithms enhance personalization, making interactive storytelling more adaptive and deeply engaging compared to traditional linear feature films.
Production Process and Budget Considerations
Feature film production typically involves a linear storytelling approach with a fixed script, requiring significant investment in sets, costumes, and post-production over a defined timeline. Interactive narratives demand flexible development workflows to accommodate branching storylines, increasing complexity in scripting, programming, and user testing, which can elevate production costs. Budget allocation for interactive narratives often prioritizes technology integration and user experience design, contrasting with the feature film focus on visual effects and traditional cinematography.
Distribution Channels and Accessibility
Feature films are primarily distributed through traditional channels such as cinemas, streaming platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime, and physical media including Blu-ray and DVDs, offering wide accessibility to global audiences. Interactive narratives leverage digital distribution on specialized apps, video game consoles, and web-based platforms, enhancing user engagement but often requiring specific devices or internet connectivity. While feature films provide broad ease of access and passive consumption, interactive narratives demand proactive participation, influencing their reach and audience interaction.
Monetization Models in Entertainment
Feature films primarily rely on box office sales, streaming rights, and merchandising for monetization, generating substantial upfront revenue and long-term royalties. Interactive narratives incorporate microtransactions, subscription models, and episodic content sales to create ongoing revenue streams by engaging users in immersive experiences. Combining these models allows entertainment companies to optimize profitability by leveraging both traditional and digital consumption patterns.
Future Trends: Convergence and Divergence
Feature films and interactive narratives are evolving with emerging technologies, blending cinematic storytelling with user-driven experiences to create hybrid entertainment forms. Advances in AI and virtual reality enable deeper immersion and personalized plot developments, while traditional films maintain their appeal through curated, high-production-value narratives. This convergence fosters innovative storytelling methods, whereas divergence preserves distinct audience preferences and consumption patterns across linear and interactive media.
Related Important Terms
Branching Pathways
Feature films deliver a linear storytelling experience with predetermined plot development and fixed endings, providing audiences with a cohesive and cinematic narrative. In contrast, interactive narratives employ branching pathways, allowing viewers to make choices that influence character decisions, plot outcomes, and multiple possible endings, increasing engagement and personalization.
Nonlinear Storytelling
Feature films deliver a fixed, linear narrative crafted to elicit specific emotional responses, while interactive narratives employ nonlinear storytelling techniques that allow audiences to influence plot progression and character outcomes. This dynamic engagement enhances immersion by offering multiple story paths, branching scenarios, and personalized experiences beyond traditional cinematic constraints.
Viewer Agency
Feature films present a predetermined storyline with limited viewer influence, emphasizing a fixed narrative arc and controlled emotional impact. Interactive narratives provide dynamic storytelling where viewer choices directly alter plot outcomes, enhancing immersion and personal engagement.
Procedural Plotting
Feature films utilize procedural plotting by following a predetermined, linear sequence of events crafted by screenwriters to ensure a cohesive narrative arc and emotional impact. Interactive narratives employ procedural plotting algorithms that dynamically adjust the storyline based on user choices, creating personalized and branching experiences within the entertainment medium.
Real-time Narrative Adaptation
Feature films deliver carefully crafted, linear storytelling with a fixed narrative arc, while interactive narratives leverage real-time narrative adaptation technologies to dynamically alter plot developments based on audience choices, enhancing engagement. Real-time narrative engines use algorithms and branching storylines to personalize viewer experiences, creating a unique and immersive form of entertainment distinct from traditional cinema.
Immersive Cinematics
Feature films deliver immersive cinematics through carefully crafted linear storytelling and high production values, engaging audiences with visually stunning scenes and emotional depth. Interactive narratives enhance immersion by allowing viewers to influence the storyline, combining cinematic quality with dynamic user-driven experiences that create personalized entertainment journeys.
Player-driven Story
Feature films present a fixed narrative crafted by writers and directors, offering audiences a passive viewing experience with predetermined plotlines and character arcs. In contrast, interactive narratives empower players to influence story outcomes through choices and actions, enabling a dynamic, player-driven story that adapts to individual decisions and enhances engagement.
Hybrid Experience
Hybrid experiences in entertainment merge the immersive storytelling of feature films with the participatory elements of interactive narratives, creating dynamic content where viewers influence the plot's direction. This blend leverages cinematic techniques alongside branching storylines, enhancing engagement through personalized and emotionally resonant journeys.
Adaptive Scripting
Feature films rely on fixed scripts and predetermined storylines, offering a curated, linear narrative experience. Interactive narratives utilize adaptive scripting to dynamically alter plot progression based on audience choices, creating personalized and immersive storytelling.
Dynamic Cutscenes
Dynamic cutscenes in feature films deliver a predetermined visual storytelling experience with high production quality and cinematic techniques, while interactive narratives use these sequences to adapt in real-time based on player choices, increasing immersion and agency. The integration of dynamic cutscenes in interactive narratives bridges traditional film storytelling with gameplay, offering a personalized emotional impact and deeper engagement.
Feature Film vs Interactive Narrative Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com