Blockbuster cinema captivates audiences with high production values, star-studded casts, and extensive marketing campaigns that guarantee widespread appeal and box office success. In contrast, microbudget cinema relies on innovative storytelling, intimate character development, and grassroots promotion to connect deeply with niche audiences and achieve critical acclaim. Both formats offer unique entertainment experiences, balancing spectacle with creativity to meet diverse viewer preferences.
Table of Comparison
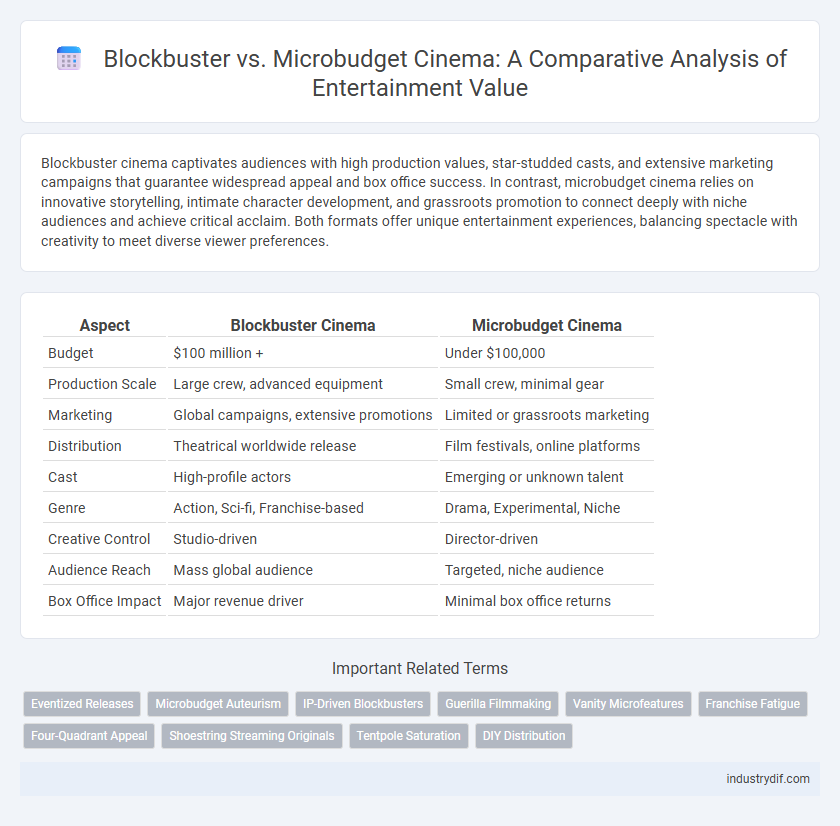
| Aspect | Blockbuster Cinema | Microbudget Cinema |
|---|---|---|
| Budget | $100 million + | Under $100,000 |
| Production Scale | Large crew, advanced equipment | Small crew, minimal gear |
| Marketing | Global campaigns, extensive promotions | Limited or grassroots marketing |
| Distribution | Theatrical worldwide release | Film festivals, online platforms |
| Cast | High-profile actors | Emerging or unknown talent |
| Genre | Action, Sci-fi, Franchise-based | Drama, Experimental, Niche |
| Creative Control | Studio-driven | Director-driven |
| Audience Reach | Mass global audience | Targeted, niche audience |
| Box Office Impact | Major revenue driver | Minimal box office returns |
Defining Blockbuster and Microbudget Cinema
Blockbuster cinema typically features high production budgets exceeding $100 million, extensive marketing campaigns, and wide theatrical releases targeting global audiences. Microbudget cinema operates on significantly lower budgets, often under $100,000, emphasizing creative storytelling, intimate settings, and limited distribution channels such as film festivals or streaming platforms. These contrasting approaches reflect divergent priorities in filmmaking, with blockbusters prioritizing spectacle and mass appeal, while microbudget films focus on artistic expression and niche markets.
Historical Evolution of Film Budgets
The historical evolution of film budgets highlights a stark contrast between blockbuster and microbudget cinema, where blockbusters often command budgets exceeding $100 million to secure A-list talent and cutting-edge special effects, driving global box office revenues. In contrast, microbudget films typically operate under $100,000, relying on minimal crew, unknown actors, and innovative storytelling to achieve critical acclaim and festival success. This budget disparity reflects broader industry trends, including technological advancements and shifting distribution models, which have democratized filmmaking while amplifying blockbuster spectacle.
Production Scale: Big Studios vs Indie Filmmakers
Blockbuster films typically involve massive production scales with budgets often exceeding $100 million, supported by major studios like Warner Bros. and Disney, ensuring access to cutting-edge technology, extensive sets, and A-list talent. Microbudget cinema, driven by indie filmmakers, operates with budgets usually under $1 million, relying on resourcefulness, minimal crews, and unconventional locations to create authentic storytelling experiences. The stark contrast in production scale highlights differences in creative freedom, marketing reach, and distribution power between big studios and independent creators.
Funding Sources and Financial Models
Blockbuster films rely heavily on major studio funding, international distribution deals, and extensive marketing budgets to maximize box office returns and ancillary revenue streams. Microbudget cinema typically secures funding through independent investors, crowdfunding platforms, and grants, emphasizing low-cost production and niche audience targeting to ensure financial viability. The contrasting financial models reflect the scale of investment and risk, with blockbusters aiming for high profitability through mass appeal, while microbudget films focus on creative flexibility and cost-effective storytelling.
Marketing Strategies: Wide Release vs Grassroots
Blockbuster films leverage wide release marketing strategies by targeting mass audiences through expansive advertising campaigns, mainstream media partnerships, and global distribution channels, maximizing visibility and box office revenue. In contrast, microbudget cinema employs grassroots marketing tactics, such as social media engagement, community screenings, and influencer collaborations, fostering intimate audience connections and organic word-of-mouth promotion. These divergent approaches reflect each model's financial scale and audience reach, with blockbusters emphasizing broad exposure and microbudget films prioritizing niche market penetration.
Audience Reach and Demographic Differences
Blockbuster films typically target a broad, global audience with high production budgets enabling extensive marketing campaigns and wide theatrical releases, attracting diverse age groups and demographics. Microbudget cinema often appeals to niche audiences, including indie film enthusiasts and younger viewers seeking unique, experimental storytelling, resulting in limited theatrical runs or direct streaming distribution. Audience reach for blockbusters can exceed hundreds of millions worldwide, while microbudget films rely on grassroots promotion and film festivals to connect with specialized demographics.
Creative Control and Artistic Freedom
Blockbuster films often face constraints from major studios prioritizing commercial success, limiting directors' creative control and pushing formulaic storytelling. Microbudget cinema thrives on artistic freedom, allowing filmmakers to explore unconventional narratives and innovative techniques without financial pressures. This independence fosters unique, culturally rich content that often challenges mainstream industry norms.
Risk Management in Film Investments
Blockbuster films demand massive capital investments, posing high financial risks but offering potential for significant box office returns and global brand expansion. Microbudget cinema minimizes initial expenditure, reducing financial exposure and allowing filmmakers to experiment with innovative storytelling techniques without aiming for mass-market appeal. Strategic risk management in film investments balances these approaches by diversifying portfolios, leveraging data analytics for audience targeting, and securing distribution deals to mitigate potential losses.
Impact on Film Innovation and Storytelling
Blockbuster films, with their substantial budgets, often prioritize visual spectacle and franchise potential, sometimes limiting narrative risks and innovative storytelling approaches. Microbudget cinema fosters creative freedom, allowing filmmakers to experiment with unconventional narratives and fresh perspectives that challenge mainstream norms. The contrast between these two models significantly shapes the evolution of film innovation and storytelling diversity in the entertainment industry.
Future Trends in Film Production Economics
Blockbuster films continue to dominate global box office revenues with budgets often exceeding $200 million, leveraging advanced visual effects and star power to guarantee wide audience appeal. Microbudget cinema, operating with under $100,000, gains competitive advantage through innovative storytelling, digital distribution platforms, and agile production techniques that lower costs and increase niche market reach. Future trends suggest a hybrid model where streaming services invest heavily in diverse content production, balancing high-budget spectacles with cost-effective independent projects to optimize profitability in evolving entertainment economics.
Related Important Terms
Eventized Releases
Blockbuster films dominate eventized releases by generating massive box office revenues through global marketing campaigns, high production values, and star-studded casts that create anticipation and cultural moments. In contrast, microbudget cinema leverages limited theatrical runs, film festivals, and digital platforms to build niche audiences and long-tail engagement without the need for widespread event-driven hype.
Microbudget Auteurism
Microbudget auteurism in cinema champions creative control and intimate storytelling by filmmakers working with limited financial resources, often under $100,000, enabling unique artistic expression unbound by mainstream studio demands. This approach contrasts sharply with blockbuster productions, which prioritize large-scale budgets, special effects, and mass appeal, making microbudget films a vital space for innovation and personal vision in entertainment.
IP-Driven Blockbusters
IP-driven blockbusters dominate the entertainment industry by leveraging established franchises and recognizable characters to maximize global box office revenue and brand loyalty. These high-budget productions often feature cutting-edge visual effects and star-studded casts, contrasting with microbudget cinema's emphasis on innovative storytelling and niche audience appeal.
Guerilla Filmmaking
Guerilla filmmaking exemplifies microbudget cinema by relying on low-cost, improvised production tactics that contrast sharply with the high budgets and controlled environments of blockbuster films. This approach leverages spontaneous locations, minimal crews, and natural lighting to create authentic storytelling while bypassing traditional studio constraints.
Vanity Microfeatures
Vanity microfeatures in microbudget cinema often emphasize personal storytelling and experimental aesthetics, contrasting sharply with blockbuster films that prioritize high production values and mass appeal through extensive visual effects and star power. These microfeatures capitalize on limited resources to create intimate narratives, leveraging authenticity and niche audiences to carve out unique spaces within the entertainment industry.
Franchise Fatigue
Blockbuster franchises often experience franchise fatigue as repetitive plotlines and formulaic characters diminish audience engagement, whereas microbudget cinema thrives on innovative storytelling and niche appeal, sustaining viewer interest with fresh, original content. The saturation of franchise films in mainstream media leads to diminishing returns, while microbudget productions leverage limited resources to create authentic, diverse narratives that resonate more deeply with discerning audiences.
Four-Quadrant Appeal
Blockbuster films leverage Four-Quadrant Appeal by targeting audiences across gender and age groups, combining action, humor, romance, and family-friendly elements to maximize box office revenue. Microbudget cinema often focuses on niche storytelling and character-driven plots, appealing primarily to specific demographics rather than aiming for broad, mass-market engagement.
Shoestring Streaming Originals
Shoestring streaming originals leverage microbudget cinema techniques to deliver innovative storytelling and niche content that contrasts sharply with the high-cost spectacle and star power typical of blockbuster films. These low-budget productions capitalize on targeted distribution through streaming platforms, maximizing audience reach while minimizing expenses and fostering creative freedom.
Tentpole Saturation
Blockbuster films dominate the entertainment industry with their massive budgets and extensive tentpole releases, leading to tentpole saturation where audiences face an overload of formulaic, high-cost productions. Microbudget cinema thrives as a counterpoint, offering unique storytelling and innovation that appeal to niche markets underserved by the tentpole-driven mainstream.
DIY Distribution
Microbudget cinema leverages DIY distribution strategies such as digital platforms, social media marketing, and community screenings to bypass traditional theatrical releases dominated by blockbuster studios. This grassroots approach allows independent filmmakers to retain creative control, target niche audiences, and maximize revenue without the constraints of large-scale distribution networks.
Blockbuster vs Microbudget Cinema Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com