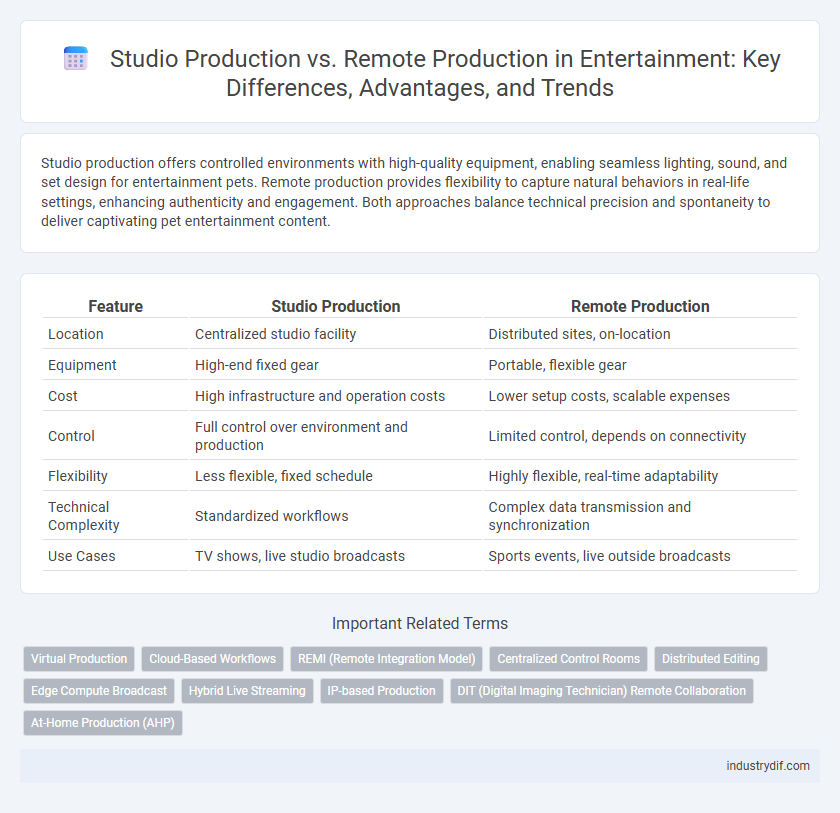
Studio production offers controlled environments with high-quality equipment, enabling seamless lighting, sound, and set design for entertainment pets. Remote production provides flexibility to capture natural behaviors in real-life settings, enhancing authenticity and engagement. Both approaches balance technical precision and spontaneity to deliver captivating pet entertainment content.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Studio Production | Remote Production |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Centralized studio facility | Distributed sites, on-location |
| Equipment | High-end fixed gear | Portable, flexible gear |
| Cost | High infrastructure and operation costs | Lower setup costs, scalable expenses |
| Control | Full control over environment and production | Limited control, depends on connectivity |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed schedule | Highly flexible, real-time adaptability |
| Technical Complexity | Standardized workflows | Complex data transmission and synchronization |
| Use Cases | TV shows, live studio broadcasts | Sports events, live outside broadcasts |
Defining Studio Production and Remote Production
Studio production refers to the process of creating television shows or films within a controlled, physical environment equipped with professional cameras, lighting, and sound equipment. Remote production involves capturing and managing live content broadcast from various locations outside the traditional studio setting, utilizing mobile units or cloud-based technologies for real-time collaboration. Both methodologies emphasize different logistical setups, with studio production prioritizing controlled environments and remote production enabling flexibility and on-site authenticity.
Key Differences Between Studio and Remote Production
Studio production offers controlled environments with fixed lighting, sound, and camera setups, ensuring consistent quality and easy coordination among crew members. Remote production relies on decentralized equipment and personnel, utilizing IP-based technologies to capture and transmit live feeds from multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and cost efficiency. Key differences include latency management, signal integration complexity, and logistical considerations for talent and technical support.
Advantages of Studio-Based Production
Studio-based production offers unparalleled control over lighting, sound, and set design, ensuring consistent high-quality visuals and audio output. It enables immediate access to advanced equipment and technical support, minimizing delays and enhancing production efficiency. The controlled environment reduces external interruptions and technical risks, providing a reliable platform for complex scenes and live broadcasts.
Benefits of Remote Production in Entertainment
Remote production in entertainment offers significant cost savings by reducing the need for on-site crews and equipment transportation. It enhances flexibility, enabling real-time collaboration across global locations and faster content delivery. This approach also improves scalability, allowing studios to manage multiple productions simultaneously while maintaining high-quality output.
Technology Powering Studio vs Remote Production
Studio production relies heavily on advanced on-site equipment such as multi-camera setups, professional lighting rigs, and sophisticated audio consoles to ensure high-quality content creation. Remote production leverages cloud-based platforms, high-speed internet, and IP-based video transmission technologies to enable real-time collaboration and seamless content delivery from distributed locations. Cutting-edge tools like 5G connectivity and AI-driven automation further enhance the efficiency and flexibility of remote production workflows compared to traditional studio setups.
Cost Considerations: Studio vs Remote Production
Studio production entails significant fixed costs including set construction, studio rental, and on-site technical staff salaries, which can substantially increase the overall budget. Remote production offers cost savings by minimizing physical infrastructure expenses and reducing travel and accommodation costs for crew and talent. However, remote setups may incur higher investment in reliable communication technology and cloud-based production tools to maintain broadcast quality.
Flexibility and Scalability in Production Models
Studio production offers controlled environments with fixed infrastructure, enabling consistent quality but limited flexibility and scalability. Remote production leverages cloud-based technologies and decentralized teams, allowing rapid scaling and adaptability to diverse locations and event sizes. This model enhances real-time collaboration and resource allocation, making it ideal for dynamic and large-scale entertainment projects.
Impact on Content Quality and Creativity
Studio production offers controlled environments with high-end equipment, enabling superior image and sound quality that enhances content richness. Remote production leverages flexibility, allowing access to diverse locations and talent, which fosters innovation and unique storytelling angles. Balancing technological capabilities with creative vision ensures optimal engagement and audience experience in both formats.
Security and Data Management in Both Approaches
Studio production offers controlled environments with robust physical security measures and centralized data management systems, reducing risks of unauthorized access and data breaches. Remote production relies heavily on secure cloud-based platforms and encrypted data transmission protocols to protect content across distributed locations. Both approaches require stringent cybersecurity practices, but remote production demands enhanced network security and real-time monitoring to safeguard sensitive production assets.
Future Trends: Studio and Remote Production Integration
Future trends in entertainment highlight the seamless integration of studio production with remote production technologies, leveraging cloud-based workflows and real-time collaboration tools to enhance content creation efficiency. Advances in 5G connectivity and AI-powered automation are enabling higher-quality live broadcasts and virtual sets without geographic constraints. This hybrid approach optimizes resource allocation, reduces costs, and expands creative possibilities for producers and audiences alike.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Production
Virtual production combines real-time CGI with live-action footage, enabling seamless integration of physical and digital elements on set, which enhances creative control and reduces post-production costs. Unlike traditional studio production, remote production leverages cloud-based workflows and decentralized teams to capture and edit content from multiple locations, increasing flexibility and scalability in entertainment projects.
Cloud-Based Workflows
Cloud-based workflows in studio production enable real-time collaboration, centralized asset management, and immediate access to high-resolution media from multiple locations, reducing latency and hardware dependency. Remote production leverages cloud infrastructure to stream live events, allowing decentralized teams to manage broadcasts efficiently while maintaining consistent quality and scalability.
REMI (Remote Integration Model)
REMI (Remote Integration Model) transforms studio production by enabling live broadcasts with minimal on-site personnel, leveraging high-bandwidth IP networks to transmit real-time audio, video, and control signals to centralized production hubs. This approach reduces costs and logistical complexities while maintaining high-quality content delivery for sports, concerts, and news events.
Centralized Control Rooms
Centralized control rooms in studio production enable seamless integration of multiple camera feeds, real-time editing, and enhanced quality control, resulting in a more polished broadcast. In remote production, centralized control rooms manage live events from distant locations, reducing onsite personnel while maintaining efficient coordination and high production standards.
Distributed Editing
Studio production centralizes all editing processes within a controlled environment, enabling real-time collaboration and immediate access to high-end equipment for seamless content creation. Remote production leverages distributed editing technologies, allowing geographically dispersed teams to work simultaneously on live or recorded footage, enhancing flexibility and reducing latency in content delivery.
Edge Compute Broadcast
Edge compute broadcast enhances remote production by processing and distributing live content closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to traditional studio production. This technology enables real-time editing, graphics insertion, and multi-camera switching at the network edge, empowering broadcasters to deliver high-quality, scalable live events without the constraints of centralized studio infrastructure.
Hybrid Live Streaming
Hybrid live streaming combines the control and quality of studio production with the flexibility and reach of remote production, enabling seamless integration of in-studio and on-location feeds. This approach leverages advanced cloud-based platforms and low-latency networks to deliver high-quality, interactive content to diverse audiences across multiple devices.
IP-based Production
IP-based production revolutionizes both studio and remote entertainment workflows by enabling seamless, high-quality content capture and distribution over standard networks. While studio production benefits from centralized control and stable environments, remote IP production offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability, supporting live events with minimal latency and cost-effective resource allocation.
DIT (Digital Imaging Technician) Remote Collaboration
DIT remote collaboration enhances studio production by enabling real-time color grading, data management, and technical adjustments across dispersed teams, streamlining workflow and reducing turnaround times. Remote production relies heavily on DIT expertise to ensure consistent image quality and seamless integration between on-site and off-site operations, optimizing resource allocation and creative control.
At-Home Production (AHP)
At-Home Production (AHP) enhances Studio Production by decentralizing workflows, leveraging cloud-based technologies to manage live broadcasts with remote crews and talent, reducing costs and increasing flexibility. Remote Production integrates high-bandwidth connections and IP-based video transmission to deliver real-time content while maintaining broadcast-quality standards outside traditional studio environments.
Studio Production vs Remote Production Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com