Artisanal cheese offers rich flavors and complex textures derived from traditional aging processes and high-quality milk, appealing to cheese connoisseurs who value authenticity. Vegan cheese analogues provide plant-based alternatives made from nuts, soy, or coconut, catering to lactose-intolerant consumers and those seeking ethical options without compromising on taste. Both options deliver unique sensory experiences, with artisanal cheese excelling in natural fermentation while vegan versions innovate through ingredient blends to mimic creaminess and flavor.
Table of Comparison
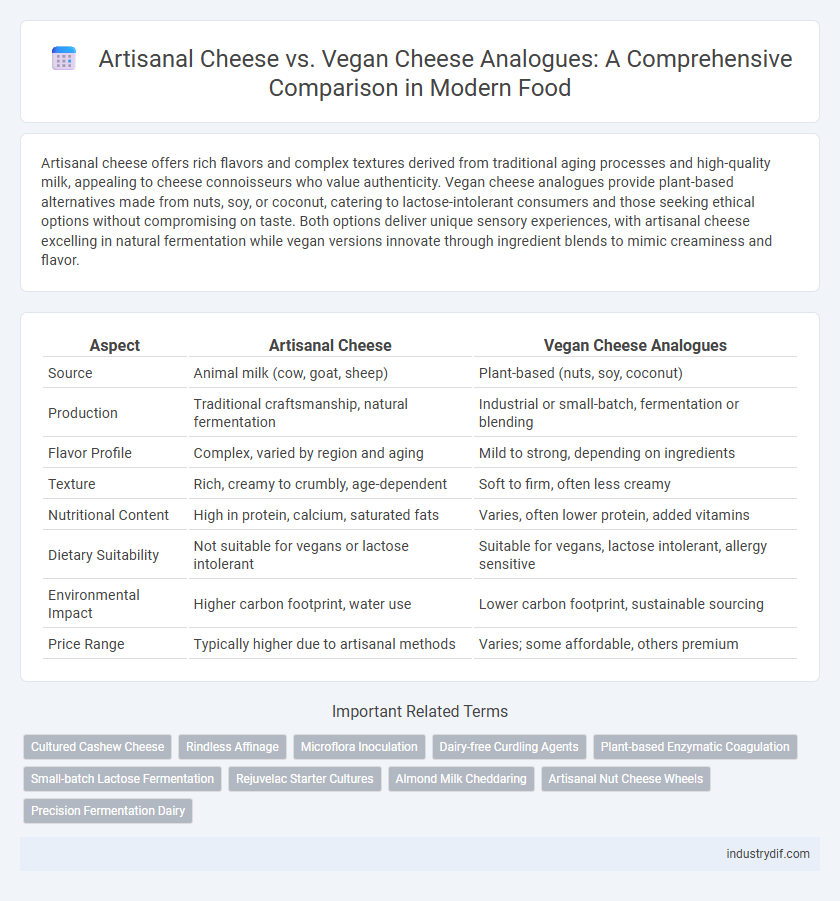
| Aspect | Artisanal Cheese | Vegan Cheese Analogues |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal milk (cow, goat, sheep) | Plant-based (nuts, soy, coconut) |
| Production | Traditional craftsmanship, natural fermentation | Industrial or small-batch, fermentation or blending |
| Flavor Profile | Complex, varied by region and aging | Mild to strong, depending on ingredients |
| Texture | Rich, creamy to crumbly, age-dependent | Soft to firm, often less creamy |
| Nutritional Content | High in protein, calcium, saturated fats | Varies, often lower protein, added vitamins |
| Dietary Suitability | Not suitable for vegans or lactose intolerant | Suitable for vegans, lactose intolerant, allergy sensitive |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint, water use | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable sourcing |
| Price Range | Typically higher due to artisanal methods | Varies; some affordable, others premium |
Defining Artisanal Cheese: Tradition and Craftsmanship
Artisanal cheese embodies tradition and craftsmanship, crafted in small batches using time-honored techniques passed down through generations. It relies on natural milk from cows, goats, or sheep, emphasizing local terroir and unique microbial cultures that contribute to complex flavors and textures. This handcrafted approach contrasts with vegan cheese analogues, which primarily use plant-based ingredients and industrial processes to mimic traditional cheese characteristics.
What Are Vegan Cheese Analogues? Ingredients and Innovation
Vegan cheese analogues are plant-based alternatives to traditional artisanal cheese, crafted from ingredients like nuts, soy, coconut oil, nutritional yeast, and cultured plant proteins. These products utilize innovative fermentation techniques and enzymatic processes to mimic the texture and flavor profiles of dairy cheese, appealing to lactose-intolerant and vegan consumers. Continuous advancements in food technology drive the development of vegan cheese analogues that increasingly replicate the complexity and richness of artisanal varieties.
Production Processes: Handcrafted vs. Plant-Based Methods
Artisanal cheese involves traditional handcrafted techniques using animal milk, fermentation, and aging processes that develop complex flavors and textures. Vegan cheese analogues are produced through plant-based methods utilizing ingredients like nuts, soy, or coconut oil, often combined with fermentation or enzymatic processes to mimic dairy characteristics. Understanding these distinct production processes highlights differences in ingredient sourcing, environmental impact, and flavor development between artisanal and vegan cheeses.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Taste and Aroma
Artisanal cheese boasts complex flavor profiles characterized by rich, tangy, and earthy notes developed through traditional fermentation and aging processes. Vegan cheese analogues often rely on plant-based ingredients like nuts and soy, offering milder, nuttier, or slightly sweet aromas that lack the depth of aged dairy counterparts. While artisanal cheeses present robust umami and creamy textures, vegan alternatives prioritize fresh, subtle flavors appealing to those seeking dairy-free options.
Nutritional Content: Dairy vs. Non-Dairy Alternatives
Artisanal cheese typically contains higher levels of protein, calcium, and vitamins A and B12 compared to vegan cheese analogues, which often rely on plant-based oils and starches, leading to lower protein content and varied micronutrient profiles. Vegan cheese alternatives may be fortified with nutrients like calcium and vitamin B12 to mimic dairy cheese's nutritional benefits but often lack the complete amino acid profile found in animal-based cheese. Consumers focused on nutrition should consider the source and fortification of vegan cheeses, as well as potential differences in saturated fat, cholesterol, and fiber content when comparing to artisanal dairy cheeses.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Artisanal cheese production often relies on traditional agricultural practices that can support local biodiversity but may generate higher greenhouse gas emissions due to livestock. Vegan cheese analogues, typically made from plant-based ingredients like nuts or soy, generally have a lower carbon footprint and reduced water usage, contributing to more sustainable food systems. However, the environmental impact varies based on farming methods and sourcing practices for both types.
Market Trends: Consumer Preferences and Growth
Artisanal cheese continues to attract consumers seeking authentic flavors and traditional craftsmanship, driving steady market growth fueled by increasing interest in heritage and locally sourced products. Vegan cheese analogues experience rapid expansion due to rising plant-based diets, lactose intolerance awareness, and environmental concerns, with sales surging in both online and retail channels. Market analysis reveals shifting consumer preferences towards health-conscious and ethical choices, propelling innovation and diversification in both artisanal and vegan cheese segments.
Price Point and Accessibility
Artisanal cheese often commands a higher price point due to traditional production methods and limited batch sizes, making it less accessible to budget-conscious consumers. Vegan cheese analogues generally offer more affordable options and greater availability in mainstream markets, reflecting rising demand and mass production efficiencies. Price sensitivity and distribution channels significantly influence consumer choice between these two cheese categories.
Pairing and Culinary Uses
Artisanal cheese offers rich, complex flavors and creamy textures that enhance wine pairings, charcuterie boards, and gourmet dishes, complementing robust reds and crisp whites alike. Vegan cheese analogues, made from plant-based ingredients like nuts, soy, or root vegetables, provide diverse flavor profiles ideal for lactose-intolerant or vegan diets, pairing well with fresh vegetables, fruit, and light wines. Both artisanal and vegan cheeses lend themselves to culinary uses such as melting in sandwiches, grating over pasta, or serving as standalone appetizers, but artisanal cheeses often deliver a more pronounced depth, while vegan cheeses prioritize versatility and dietary inclusivity.
Challenges and Future Developments in Cheese Production
Artisanal cheese production faces challenges such as maintaining traditional methods while meeting modern food safety regulations and scaling production sustainably. Vegan cheese analogues must overcome technical hurdles in replicating the complex flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles of dairy cheese using plant-based ingredients. Future developments focus on improving ingredient innovation, fermentation techniques, and sustainable sourcing to enhance quality, flavor authenticity, and environmental impact in both cheese categories.
Related Important Terms
Cultured Cashew Cheese
Cultured cashew cheese, a popular artisanal cheese alternative, offers a creamy texture and rich probiotic profile derived from natural fermentation, distinguishing it from traditional vegan cheese analogues made primarily from processed plant oils and starches. This cultured variant leverages the natural fats and proteins in cashews to replicate the depth of flavor and mouthfeel commonly associated with aged dairy cheeses, appealing to both plant-based and health-conscious consumers.
Rindless Affinage
Artisanal cheese, known for its complex flavors developed through traditional affinage methods, contrasts with vegan cheese analogues that often lack natural rind formation due to plant-based ingredients and rindless aging processes. Rindless affinage in vegan cheeses impacts texture and flavor maturation, resulting in a distinct sensory profile compared to the rich, aged crusts characteristic of artisanal cheeses.
Microflora Inoculation
Artisanal cheese relies on natural microflora inoculation from raw milk and the aging environment, fostering complex microbial communities that develop unique flavors and textures. Vegan cheese analogues often utilize selected bacterial cultures or fermentation processes with plant-based substrates to mimic traditional cheese microflora, though the diversity and metabolic activity tend to be more controlled and limited.
Dairy-free Curdling Agents
Dairy-free curdling agents used in artisanal vegan cheese analogues often include plant-based enzymes like microbial rennet derived from fungi or bacteria, which replicate traditional dairy fermentation processes without animal involvement. These agents contribute to texture and flavor development, offering a sustainable and allergen-friendly alternative to dairy-based rennet in cheese production.
Plant-based Enzymatic Coagulation
Artisanal cheese relies on animal rennet for enzymatic coagulation, while vegan cheese analogues utilize plant-based enzymes such as microbial coagulants derived from fig latex or thistle extract to achieve curd formation. This plant-based enzymatic coagulation process ensures dairy-free cheese products maintain texture and flavor profiles similar to traditional artisanal cheeses, meeting demand for lactose-free and vegan-friendly options.
Small-batch Lactose Fermentation
Small-batch artisanal cheese uses traditional lactose fermentation processes with specific bacterial cultures to develop complex flavors and textures unique to handcrafted production. Vegan cheese analogues rely on plant-based ingredients and often utilize fermentation with alternative microbes or enzymes, lacking lactose but aiming to replicate the creamy consistency and umami profile of dairy cheeses.
Rejuvelac Starter Cultures
Rejuvelac starter cultures enhance the fermentation process in artisanal cheese, promoting complex flavors and beneficial probiotics that improve texture and health benefits. In vegan cheese analogues, rejuvelac serves as a natural fermenting agent, creating tangy profiles while supporting dairy-free diets with plant-based nutrition and gut-friendly microbes.
Almond Milk Cheddaring
Artisanal cheese, crafted through traditional fermentation and aging processes, offers complex flavors and textures that reflect regional terroir, while vegan cheese analogues, particularly almond milk cheddaring, rely on plant-based ingredients and innovative techniques to mimic the creamy, sharp profile of cheddar without dairy. Almond milk cheddaring involves enzymatic fermentation and natural flavor enhancers to achieve authentic taste and meltability, appealing to lactose-intolerant consumers and those seeking sustainable, ethical alternatives.
Artisanal Nut Cheese Wheels
Artisanal nut cheese wheels offer a unique blend of rich, creamy textures and complex flavors derived from carefully fermented nuts like cashews and almonds, distinguishing them from typical vegan cheese analogues that often rely on processed ingredients. These handcrafted cheeses emphasize traditional aging methods and natural probiotics, resulting in a product prized for its depth and authenticity in the growing plant-based cheese market.
Precision Fermentation Dairy
Artisanal cheese, crafted through traditional methods using animal milk and natural microbial cultures, offers complex flavors and textures that reflect regional terroirs, while vegan cheese analogues produced via precision fermentation dairy leverage genetically engineered microbes to biosynthesize milk proteins, enabling lactose-free, sustainable alternatives with improved nutritional profiles. Precision fermentation dairy technologies provide scalable production of casein and whey proteins, allowing vegan cheeses to mimic the meltability and mouthfeel of artisanal dairy cheeses, contributing to reduced environmental impact and animal welfare benefits.
Artisanal cheese vs Vegan cheese analogues Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com