Plant-based pet food offers a sustainable and allergen-friendly alternative, utilizing ingredients like peas, lentils, and chickpeas to provide essential proteins and nutrients. Cultivated meat, grown from animal cells, delivers real animal protein without the environmental drawbacks of traditional livestock farming, ensuring high digestibility and natural amino acid profiles for pets. Both options address ethical and ecological concerns, presenting viable choices for pet owners seeking healthier and more sustainable diets.
Table of Comparison
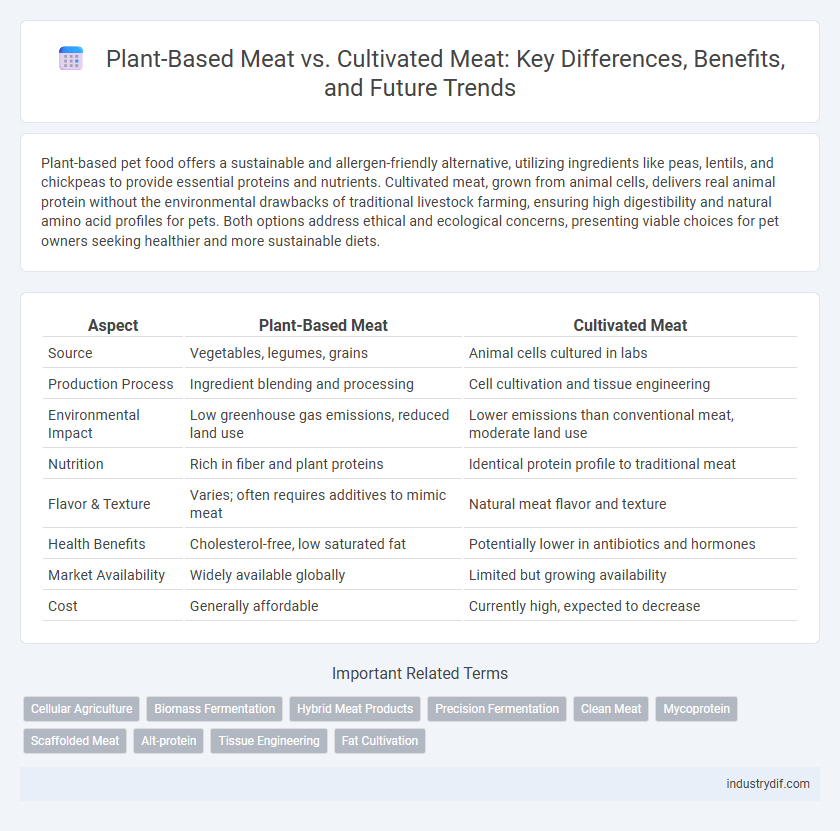
| Aspect | Plant-Based Meat | Cultivated Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Vegetables, legumes, grains | Animal cells cultured in labs |
| Production Process | Ingredient blending and processing | Cell cultivation and tissue engineering |
| Environmental Impact | Low greenhouse gas emissions, reduced land use | Lower emissions than conventional meat, moderate land use |
| Nutrition | Rich in fiber and plant proteins | Identical protein profile to traditional meat |
| Flavor & Texture | Varies; often requires additives to mimic meat | Natural meat flavor and texture |
| Health Benefits | Cholesterol-free, low saturated fat | Potentially lower in antibiotics and hormones |
| Market Availability | Widely available globally | Limited but growing availability |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Currently high, expected to decrease |
Introduction to Plant-Based and Cultivated Meat
Plant-based meat is created from vegetables, legumes, and grains designed to mimic the taste and texture of animal meat using ingredients like soy protein and pea protein. Cultivated meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is produced by culturing animal cells in a controlled environment, eliminating the need to raise and slaughter animals. Both alternatives aim to provide sustainable and ethical options to traditional meat consumption while addressing environmental and animal welfare concerns.
Key Differences Between Plant-Based and Cultivated Meat
Plant-based meat is derived from vegetables, grains, and legumes, aiming to mimic the taste and texture of traditional meat using proteins like soy or pea, whereas cultivated meat is produced by growing animal cells in bioreactors without raising animals. Plant-based products generally have a lower environmental footprint due to their reliance on crops, while cultivated meat offers the potential for real animal tissue, including muscle and fat, resulting in closer taste and nutritional profiles to conventional meat. Cultivated meat requires advanced biotechnological processes and infrastructure, making it currently more expensive than plant-based options, which benefit from established agricultural supply chains.
Ingredient Sourcing and Production Methods
Plant-based meat leverages natural ingredients such as legumes, grains, and vegetables, relying on extrusion and blending technologies to mimic the texture and flavor of animal meat. Cultivated meat is produced by harvesting animal cells and growing them in bioreactors through cellular agriculture, which requires precise culture media containing amino acids, vitamins, and growth factors. Both methods emphasize sustainability, but plant-based sourcing focuses on crop cultivation while cultivated meat depends on biotechnological processes to reduce resource usage and environmental impact.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Plant-based meat alternatives typically offer higher fiber content, vitamins such as B12 and iron derived from fortified sources, and lower saturated fats compared to cultivated meat. Cultivated meat closely mimics the nutritional profile of conventional animal meat, providing complete proteins, heme iron, and essential amino acids without antibiotics or hormones. Both options present unique nutritional benefits, making them viable solutions for health-conscious consumers seeking sustainable protein sources.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Plant-based meat production significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to both conventional and cultivated meat. Cultivated meat, produced through cellular agriculture, offers potential environmental benefits by minimizing animal agriculture's resource demands but still requires substantial energy inputs for bioreactors and growth media. Life cycle assessments highlight plant-based alternatives as currently more environmentally sustainable, though advancements in cultivated meat technology could narrow this gap over time.
Consumer Acceptance and Market Trends
Consumer acceptance of plant-based meat remains strong due to its sustainability benefits and established market presence, while cultivated meat is gaining interest for its potential to replicate traditional meat taste and texture with fewer environmental impacts. Market trends indicate rapid growth in plant-based products driven by vegan and flexitarian diets, alongside increasing investment in cultivated meat startups aiming to commercialize lab-grown protein at scale. Regulatory approvals and consumer education are critical factors shaping the future adoption and broader market penetration of cultivated meat compared to the more mature plant-based sector.
Regulatory Landscape and Food Safety
Regulatory frameworks for plant-based and cultivated meat vary significantly, with cultivated meat requiring rigorous safety assessments by agencies like the FDA and USDA before market approval to ensure consumer protection. Plant-based meat substitutes generally face less stringent regulatory hurdles due to their traditional food ingredients and established production methods. Ongoing research and evolving legislation aim to address labeling standards, allergen risks, and long-term health impacts to secure safe integration into global food systems.
Sensory Experience: Taste, Texture, and Appearance
Plant-based meats replicate the sensory experience by using ingredients like soy, pea protein, and beet juice to mimic taste, texture, and appearance, often achieving a slightly fibrous texture with a plant-derived umami flavor. Cultivated meat, derived from animal cells, delivers an authentic sensory profile closely matching traditional meat with natural muscle fibers, authentic fat content, and true meat juices enhancing juiciness and mouthfeel. The sensory difference is most notable in texture and flavor nuances, where cultivated meat offers superior genuine meat characteristics while plant-based alternatives excel in consistency and variety of flavors.
Cost Factors and Scalability
Plant-based meat products benefit from established supply chains and lower production costs, driven by scalable agricultural inputs such as soy and pea proteins. Cultivated meat faces higher initial expenses due to specialized cell culture technologies, bioreactors, and costly growth media, limiting early scalability. Advances in bioprocessing and media optimization are essential to reduce costs and expand commercial-scale production of cultivated meat alternatives.
Future Outlook for Alternative Proteins
The future outlook for alternative proteins indicates rapid growth in both plant-based and cultivated meat markets, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable and ethical food sources. Technological advancements in cellular agriculture are expected to reduce production costs and improve scalability of cultivated meat, making it more competitive with traditional animal protein. Market projections estimate the global alternative protein sector could exceed $140 billion by 2030, reflecting strong investment and innovation trends shaping the future of sustainable food systems.
Related Important Terms
Cellular Agriculture
Cellular agriculture leverages tissue engineering techniques to produce cultivated meat by growing animal cells directly, reducing reliance on traditional livestock farming and lowering environmental impact. Plant-based meat alternatives use protein extracted from plants like soy or peas to replicate meat's texture and flavor without involving animal products.
Biomass Fermentation
Biomass fermentation in plant-based meat production utilizes microbial cells such as fungi and bacteria to create protein-rich biomass that mimics animal meat texture and nutrition. Cultivated meat relies on cell culture techniques, whereas biomass fermentation offers scalable, cost-effective protein synthesis without animal cells, enhancing sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
Hybrid Meat Products
Hybrid meat products combine plant-based proteins and cultivated meat cells, offering a sustainable alternative that reduces environmental impact while maintaining familiar meat textures and flavors. This innovative approach leverages advanced cellular agriculture and plant protein technology to meet consumer demand for nutritious, ethical, and lower-carbon-footprint food options.
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation enables the production of animal-identical proteins by genetically programming microorganisms, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional animal farming within both plant-based and cultivated meat sectors. This biotechnology enhances texture, flavor, and nutritional profiles, driving innovation in clean meat production while reducing environmental impact and resource consumption.
Clean Meat
Clean meat, produced through cellular agriculture, offers a sustainable and ethical alternative to conventional animal farming by cultivating animal cells directly without raising and slaughtering livestock. This innovative method significantly reduces environmental impact, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource consumption while delivering authentic meat flavors and textures comparable to traditional meat products.
Mycoprotein
Mycoprotein, a sustainable protein source derived from fungi fermentation, offers a nutritious and environmentally friendly alternative to both plant-based and cultivated meats, providing high protein content, fiber, and essential amino acids. Its production requires significantly less land and water compared to traditional livestock farming, making it a key player in reducing the environmental impact of global protein consumption.
Scaffolded Meat
Scaffolded meat, a subset of cultivated meat, uses a 3D framework to support cell growth, enhancing texture and structural integrity similar to traditional meat. This technology enables scalable production of plant-based alternatives with improved mouthfeel and nutritional profile, addressing consumer demand for sustainable and ethical protein sources.
Alt-protein
Plant-based proteins derived from soy, peas, and other legumes offer sustainable alternatives to animal products, reducing environmental impact through lower greenhouse gas emissions and land use. Cultivated meat, produced by culturing animal cells in bioreactors, delivers real meat textures and flavors while minimizing antibiotic use and ethical concerns associated with traditional livestock farming.
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering in cultivated meat utilizes animal cells grown on scaffolds to create structured, muscle-like textures that closely mimic traditional meat, offering a sustainable alternative to plant-based proteins that lack the same fibrous complexity. By precisely controlling cell differentiation and growth conditions, cultivated meat achieves superior taste and nutritional profiles compared to conventional plant-based alternatives.
Fat Cultivation
Plant-based meat relies on vegetable oils and extracted plant fats to mimic animal fat, providing texture and juiciness without cholesterol. Cultivated meat develops fat cells directly from animal stem cells, enabling precise fat composition that enhances flavor and mouthfeel while maintaining a clean meat profile.
Plant-Based vs Cultivated Meat Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com