Ready-to-eat pet food offers convenience and immediate nutrition, ideal for busy pet owners seeking quick meal solutions. Cultured meat, on the other hand, provides a sustainable and ethical alternative by producing protein through cell cultivation, reducing the environmental impact of traditional farming. Both options deliver high-quality nutrition tailored to pets' dietary needs, with cultured meat emerging as a promising innovation in pet food sustainability.
Table of Comparison
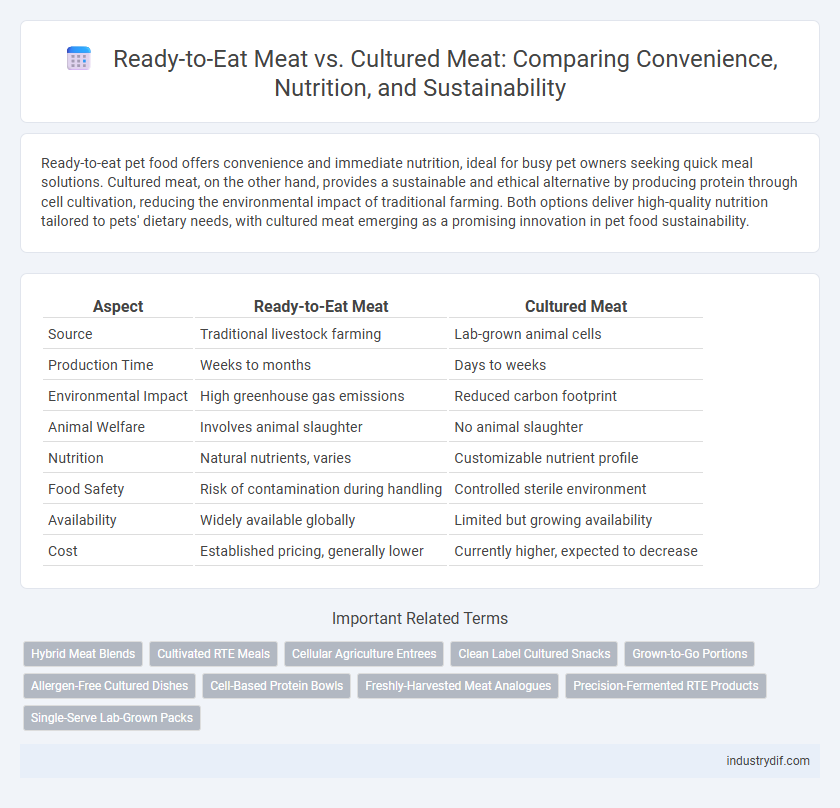
| Aspect | Ready-to-Eat Meat | Cultured Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Traditional livestock farming | Lab-grown animal cells |
| Production Time | Weeks to months | Days to weeks |
| Environmental Impact | High greenhouse gas emissions | Reduced carbon footprint |
| Animal Welfare | Involves animal slaughter | No animal slaughter |
| Nutrition | Natural nutrients, varies | Customizable nutrient profile |
| Food Safety | Risk of contamination during handling | Controlled sterile environment |
| Availability | Widely available globally | Limited but growing availability |
| Cost | Established pricing, generally lower | Currently higher, expected to decrease |
Introduction to Ready-to-Eat and Cultured Meat
Ready-to-Eat (RTE) foods are pre-prepared meals or ingredients requiring minimal to no cooking before consumption, offering convenience and time savings for busy consumers. Cultured meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, aiming to provide a sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional meat. Both innovations address food security challenges, with RTE foods catering to immediate consumption needs and cultured meat targeting long-term environmental and animal welfare concerns.
Defining Ready-to-Eat Meat Products
Ready-to-eat meat products are fully cooked and packaged meats that require no further preparation before consumption, offering convenience and immediate usability. These products range from deli slices and cured sausages to pre-cooked bacon and meat-based sandwiches, designed to maintain safety and flavor without additional cooking. Unlike cultured meat, which is lab-grown from animal cells, ready-to-eat meats are derived from traditional animal processing methods and undergo preservation techniques such as curing, smoking, or refrigeration to ensure shelf stability.
What Is Cultured Meat?
Cultured meat, also known as lab-grown meat, is produced by cultivating animal cells directly in controlled environments, eliminating the need to raise and slaughter animals. This technology leverages tissue engineering techniques to create muscle tissue that mimics conventional meat in texture, flavor, and nutritional content. As a sustainable alternative, cultured meat has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, land usage, and water consumption associated with traditional livestock farming.
Key Production Processes Compared
Ready-to-eat meat products undergo processing methods such as cooking, curing, and packaging to ensure safety and convenience for immediate consumption. Cultured meat production involves cell cultivation from animal biopsies in bioreactors, enabling muscle tissue growth without slaughtering animals. Key differences lie in ready-to-eat relying on traditional slaughter and preservation, while cultured meat emphasizes cellular agriculture and tissue engineering techniques.
Nutritional Profile: Ready-to-Eat vs Cultured Meat
Ready-to-eat meat products typically contain higher levels of sodium, preservatives, and saturated fats, which can impact cardiovascular health over time. Cultured meat offers a customizable nutritional profile, allowing for the enhancement of beneficial nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids and reduced levels of harmful compounds. This precision in cultivation can result in a product with improved protein quality, lower cholesterol, and a healthier fat composition compared to conventional ready-to-eat meats.
Food Safety and Quality Standards
Ready-to-eat foods undergo rigorous food safety inspections and must meet strict quality standards to prevent contamination and spoilage, ensuring consumer protection. Cultured meat production involves controlled laboratory environments with stringent monitoring protocols to minimize microbial risks and maintain consistent product quality. Both sectors rely on advanced hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) systems to uphold food safety and optimize nutritional value.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Ready-to-eat meat typically involves conventional livestock farming, which generates significant greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption. Cultured meat production drastically reduces environmental impacts by using less land and water while emitting fewer greenhouse gases through controlled cellular agriculture processes. Life cycle assessments indicate cultured meat could cut carbon footprints by up to 80% compared to traditional meat production.
Consumer Acceptance and Market Trends
Consumer acceptance of cultured meat is steadily increasing due to growing awareness of its environmental benefits and ethical considerations compared to traditional ready-to-eat meat products. Market trends indicate a rising demand for sustainable protein sources, with cultured meat startups attracting significant investment and collaborations from major food corporations. Ready-to-eat meals continue to dominate convenience-driven markets, but cultured meat's potential to revolutionize the sector hinges on scaling production and reducing costs to meet consumer expectations.
Regulatory Challenges and Frameworks
Regulatory challenges for ready-to-eat foods primarily focus on food safety standards, labeling accuracy, and contamination prevention to protect consumer health. Cultured meat faces emerging regulatory frameworks that require rigorous evaluation of cell sources, production methods, and long-term health impacts before market approval. Harmonizing global regulations remains critical to ensure consistent safety protocols and consumer acceptance across different regions.
Future Outlook: Innovations in Meat Industry
Ready-to-eat meals and cultured meat represent pivotal innovations shaping the future of the meat industry, driving convenience and sustainability. Cultured meat production leverages cellular agriculture technology, enabling scalable, ethical, and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional livestock farming. Rapid advancements in bioreactors, scaffold materials, and growth media formulations are expected to reduce costs and improve texture, positioning cultured meat as a competitive option alongside ready-to-eat products in global food markets.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Meat Blends
Hybrid meat blends combine ready-to-eat convenience with the sustainability of cultured meat, offering a practical solution to reduce environmental impact while meeting consumer demand for familiar flavors and textures. These innovative products blend traditional animal proteins with lab-grown cells, enhancing nutritional profiles and supporting a transition toward more ethical food systems.
Cultivated RTE Meals
Cultivated ready-to-eat (RTE) meals leverage lab-grown meat derived from animal cells, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional ready-to-eat options by reducing environmental impact and eliminating the need for animal slaughter. These meals, rich in proteins and nutrients, provide consistent quality and safety, making them a promising innovation in the food technology sector.
Cellular Agriculture Entrees
Ready-to-eat meals derived from cellular agriculture represent a significant innovation in cultured meat, offering convenience with lab-grown proteins that replicate traditional meat's texture and flavor without animal slaughter. These cultured meat entrees harness stem cell technology to cultivate muscle tissue, ensuring sustainable production with reduced environmental impact and enhanced food safety compared to conventional meat products.
Clean Label Cultured Snacks
Clean label cultured snacks combine the benefits of ready-to-eat convenience with sustainable, lab-grown meat, offering consumers transparent ingredients and reduced environmental impact. These innovative snacks prioritize natural sourcing and minimal processing, appealing to health-conscious and eco-friendly markets seeking high-protein, preservative-free options.
Grown-to-Go Portions
Ready-to-eat meals offer convenience with pre-cooked, portion-controlled servings that require minimal preparation, while cultured meat provides sustainable, lab-grown protein segments designed for freshness and environmental impact reduction. Grown-to-go portions from cultured meat ensure consistent quality and nutrition, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking eco-friendly alternatives to traditional ready-to-eat options.
Allergen-Free Cultured Dishes
Allergen-free cultured meat offers a revolutionary alternative to traditional ready-to-eat foods by eliminating common allergens such as soy, gluten, and dairy, making it safe for consumers with food sensitivities. These cultured dishes, produced through cellular agriculture, provide a controlled environment that ensures purity and consistent allergen-free labeling, enhancing food safety and expanding dietary options.
Cell-Based Protein Bowls
Ready-to-eat cell-based protein bowls offer a sustainable and nutrient-dense alternative to traditional meat dishes, utilizing cultured meat derived from animal cells without the need for livestock farming. These innovative meals reduce environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and water usage while providing easily accessible, high-quality protein sources for health-conscious consumers.
Freshly-Harvested Meat Analogues
Ready-to-eat meat analogues provide convenient, shelf-stable options without sacrificing taste, utilizing plant-based proteins and advanced texturization technologies to mimic traditional meat. Freshly-harvested cultured meat offers higher nutritional fidelity and sustainability benefits by growing animal cells directly, minimizing environmental impact compared to conventional livestock farming.
Precision-Fermented RTE Products
Precision-fermented ready-to-eat (RTE) products leverage microbial fermentation to produce high-quality proteins and flavors that mimic traditional meat, offering sustainable and scalable alternatives to cultured meat. These innovations reduce resource use and environmental impact while delivering consistent taste and nutritional profiles tailored for health-conscious consumers.
Single-Serve Lab-Grown Packs
Single-serve lab-grown meat packs offer a sustainable alternative to traditional ready-to-eat meals by providing clean, cultured protein with reduced environmental impact and no antibiotics. These portion-controlled servings cater to consumers seeking convenient, ethical, and nutrient-rich options in the evolving landscape of protein consumption.
Ready-to-Eat vs Cultured Meat Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com