Food safety ensures that pet food is free from harmful contaminants, pathogens, and toxins, protecting pets from illness and health risks. Food transparency involves providing clear, accurate information about ingredient sourcing, production processes, and nutritional content to help pet owners make informed choices. Both aspects are crucial for building trust and promoting the well-being of pets through reliable and wholesome nutrition.
Table of Comparison
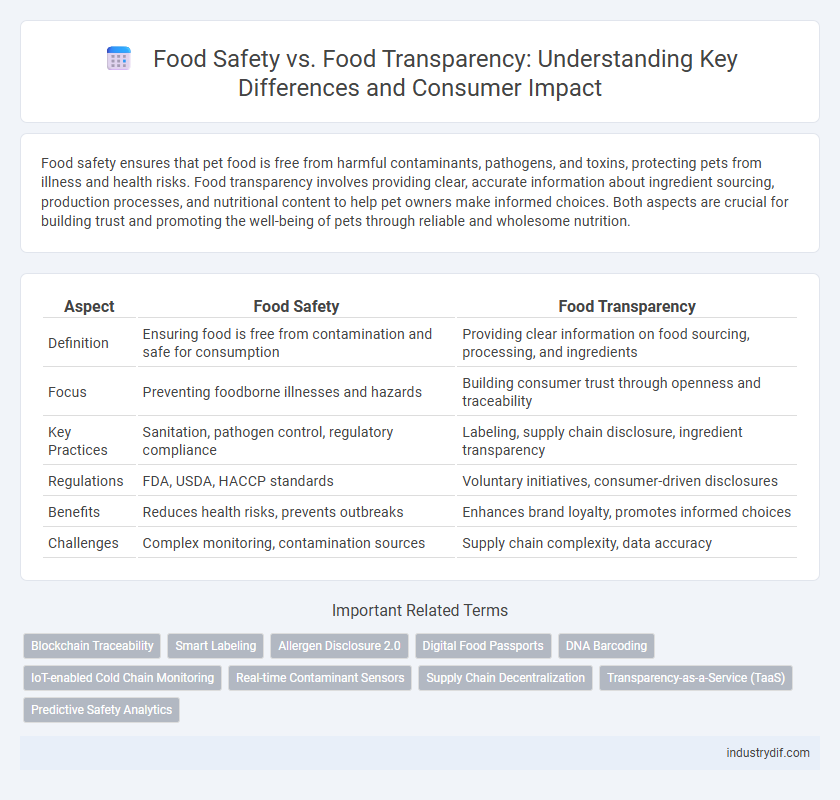
| Aspect | Food Safety | Food Transparency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensuring food is free from contamination and safe for consumption | Providing clear information on food sourcing, processing, and ingredients |
| Focus | Preventing foodborne illnesses and hazards | Building consumer trust through openness and traceability |
| Key Practices | Sanitation, pathogen control, regulatory compliance | Labeling, supply chain disclosure, ingredient transparency |
| Regulations | FDA, USDA, HACCP standards | Voluntary initiatives, consumer-driven disclosures |
| Benefits | Reduces health risks, prevents outbreaks | Enhances brand loyalty, promotes informed choices |
| Challenges | Complex monitoring, contamination sources | Supply chain complexity, data accuracy |
Understanding Food Safety: Key Definitions
Food safety involves measures to prevent contamination and ensure products are free from harmful pathogens, chemicals, and physical hazards. Key definitions include hazard analysis, critical control points (HACCP), and foodborne illness prevention protocols that maintain product integrity from farm to table. Food transparency, while related, focuses on providing clear information about sourcing, ingredients, and processing methods to build consumer trust.
What is Food Transparency? Explained
Food transparency refers to the clear and accessible disclosure of information about food products, including sourcing, ingredients, processing methods, and supply chain details. It enables consumers to make informed choices by revealing the origins, nutritional content, and ethical practices behind their food. This openness fosters trust, improves food safety standards, and ensures accountability within the food industry.
The Relationship Between Food Safety and Transparency
Food safety and food transparency are intrinsically linked, as transparent sourcing and production practices enable more effective monitoring and risk management of foodborne hazards. Enhanced transparency through traceability systems empowers consumers and regulatory bodies to identify contamination sources swiftly, reducing outbreak impacts. Comprehensive data sharing between producers, suppliers, and inspectors strengthens accountability while promoting safer food supply chains.
Regulatory Standards for Food Safety
Regulatory standards for food safety establish mandatory guidelines to prevent contamination, ensure proper handling, and maintain hygiene across the supply chain. These standards, enforced by agencies such as the FDA and USDA, require rigorous testing, labeling, and traceability to protect public health. Enhanced food transparency complements these regulations by providing consumers with accessible information about sourcing and production practices, fostering trust and accountability in the food industry.
The Role of Technology in Food Transparency
Technology enhances food transparency by enabling real-time tracking of food origins, processing, and distribution through blockchain and IoT sensors. Digital platforms and mobile apps allow consumers to access detailed information about food quality, safety certifications, and supply chain practices. This increased visibility empowers informed purchasing decisions and fosters trust between producers and consumers.
Consumer Demand: Safety vs. Transparency
Consumer demand for food safety centers on ensuring products are free from contaminants, pathogens, and harmful additives to prevent health risks. Food transparency emphasizes clear labeling, ingredient sourcing, and ethical practices to build trust and enable informed purchasing decisions. Balancing safety protocols with transparent communication drives consumer confidence and shapes purchasing trends in the modern food industry.
Challenges in Achieving Complete Food Safety
Achieving complete food safety faces challenges such as contamination risks at various supply chain stages and inconsistent regulatory standards across regions. Transparency demands detailed traceability and open communication, which often conflict with proprietary processes and cost constraints. Balancing rigorous safety protocols with transparent practices requires advanced technologies like blockchain and real-time monitoring systems to ensure accountability and consumer trust.
Barriers to Full Food Transparency
Barriers to full food transparency include complex global supply chains, where tracing the origin and handling of food products becomes challenging due to multiple intermediaries and lack of standardized data sharing protocols. Limited technology adoption and inconsistencies in regulatory frameworks across countries further hinder real-time access to accurate food safety information. Consumer mistrust often arises from opaque labeling practices and insufficient disclosure of food sourcing, processing, and safety measures.
Industry Initiatives Bridging Safety and Transparency
Industry initiatives like blockchain technology and IoT sensors are enhancing food safety while promoting transparency by providing real-time tracking of food products from farm to table. Certification programs and third-party audits ensure compliance with safety standards and publicly share quality data to build consumer trust. These integrated systems enable rapid response to contamination incidents and improve accountability across the supply chain.
Future Trends in Food Safety and Transparency
Future trends in food safety and transparency emphasize the integration of blockchain technology to enhance traceability and reduce contamination risks throughout supply chains. Advances in IoT-enabled sensors enable real-time monitoring of food quality, freshness, and pathogen detection, ensuring stricter compliance with safety standards. Consumer demand for detailed provenance information drives the adoption of digital labeling and AI-powered analytics, fostering greater accountability and trust in food products.
Related Important Terms
Blockchain Traceability
Blockchain traceability enhances food safety by providing immutable, real-time records of every step in the supply chain, enabling rapid identification and containment of contamination sources. This transparent system fosters consumer trust and regulatory compliance by ensuring that all data about food origin, handling, and quality is accessible and verifiable.
Smart Labeling
Smart labeling enhances food safety by providing real-time information on product origin, ingredients, and storage conditions, enabling consumers to make informed decisions and reduce the risk of contamination. Transparent smart labels utilize blockchain technology and QR codes to ensure traceability and authenticity, fostering trust between producers and consumers while facilitating swift responses to food safety issues.
Allergen Disclosure 2.0
Food Safety emphasizes preventing contamination and allergic reactions by adhering to strict allergen disclosure regulations, while Food Transparency promotes open communication and trust by providing detailed ingredient sourcing and cross-contact risk information; Allergen Disclosure 2.0 integrates advanced technologies like blockchain and digital labeling to enhance accuracy and real-time updates, ensuring consumers with allergies receive precise, trustworthy data. This innovation supports both regulatory compliance and consumer empowerment by facilitating rapid access to allergen information across the supply chain.
Digital Food Passports
Digital food passports enhance food safety by providing traceability and real-time data on product origin, handling, and storage conditions, reducing risks of contamination and fraud. They also improve food transparency by offering consumers detailed information on ingredients, allergen presence, and ethical sourcing, fostering trust and informed purchasing decisions.
DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding enhances food safety by accurately identifying species in food products, preventing fraud and contamination risks associated with mislabeling. This molecular technique also promotes food transparency, enabling consumers and regulators to verify ingredient authenticity and origin with precise genetic data.
IoT-enabled Cold Chain Monitoring
IoT-enabled cold chain monitoring enhances food safety by providing real-time temperature data, reducing risks of spoilage and contamination during transportation and storage. This technology also boosts food transparency by enabling traceability and accountability, allowing consumers and stakeholders to verify product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Real-time Contaminant Sensors
Real-time contaminant sensors enhance food safety by detecting hazards instantly, reducing the risk of contamination and foodborne illnesses. These sensors also promote food transparency by providing consumers and suppliers with accurate, real-time data on food quality and safety throughout the supply chain.
Supply Chain Decentralization
Supply chain decentralization enhances food transparency by enabling real-time tracking of product origins and handling processes, reducing the risk of contamination and fraud. This distributed approach improves food safety by facilitating faster identification and isolation of safety breaches within complex supply networks.
Transparency-as-a-Service (TaaS)
Transparency-as-a-Service (TaaS) revolutionizes food safety by offering real-time, blockchain-enabled traceability from farm to table, ensuring consumers access verified information about ingredients, sourcing, and handling protocols. This service empowers stakeholders to proactively manage contamination risks and comply with regulatory standards while building trust through unparalleled supply chain visibility.
Predictive Safety Analytics
Predictive safety analytics leverages big data and machine learning algorithms to identify potential food safety risks before they occur, enhancing hazard detection and prevention throughout the supply chain. Food transparency complements this approach by providing real-time visibility into product origin, handling, and quality metrics, enabling proactive decision-making and building consumer trust.
Food Safety vs Food Transparency Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com