Processed pet food often contains meat that has been altered with additives and preservatives, impacting its nutritional quality and digestibility. Cultured meat, grown from animal cells in a controlled environment, offers a sustainable and potentially healthier alternative by eliminating the need for slaughter and reducing contaminants. Choosing cultured meat in pet food formulations could enhance protein quality while minimizing environmental impact and health risks associated with processed meats.
Table of Comparison
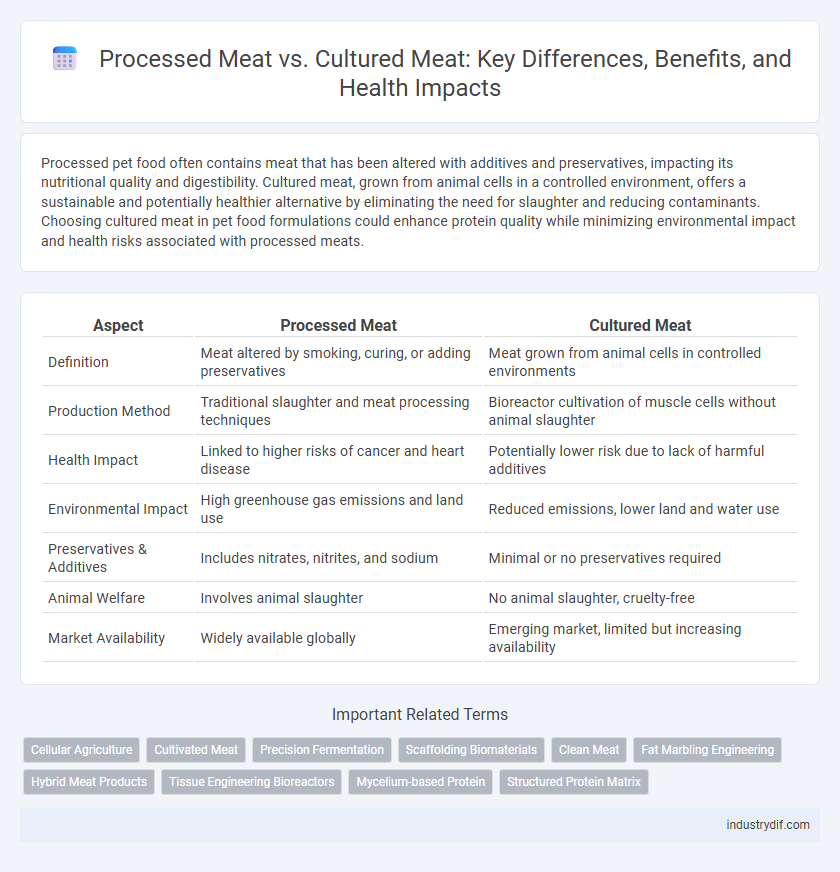
| Aspect | Processed Meat | Cultured Meat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Meat altered by smoking, curing, or adding preservatives | Meat grown from animal cells in controlled environments |
| Production Method | Traditional slaughter and meat processing techniques | Bioreactor cultivation of muscle cells without animal slaughter |
| Health Impact | Linked to higher risks of cancer and heart disease | Potentially lower risk due to lack of harmful additives |
| Environmental Impact | High greenhouse gas emissions and land use | Reduced emissions, lower land and water use |
| Preservatives & Additives | Includes nitrates, nitrites, and sodium | Minimal or no preservatives required |
| Animal Welfare | Involves animal slaughter | No animal slaughter, cruelty-free |
| Market Availability | Widely available globally | Emerging market, limited but increasing availability |
Introduction to Processed and Cultured Meat
Processed meat refers to meat that has been transformed through salting, curing, fermentation, or smoking to enhance flavor and preservation, commonly including products like sausages, bacon, and deli meats. Cultured meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, offering a sustainable alternative that mimics conventional meat without raising animals. Both types represent significant trends in the food industry, addressing concerns related to health, environmental impact, and ethical food production.
Defining Processed Meat: Composition and Methods
Processed meat consists of animal muscle meat that has been modified through methods such as salting, curing, smoking, or fermentation to enhance flavor and extend shelf life. Common ingredients often include nitrates, nitrites, salt, preservatives, and various additives that alter texture and color. This contrasts with cultured meat, which is grown directly from animal cells without the traditional processing steps applied to conventional meat products.
What is Cultured Meat? Science Behind Lab-Grown Protein
Cultured meat, also known as lab-grown meat, is produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, eliminating the need to raise and slaughter animals. This innovative process involves harvesting muscle cells, providing them with nutrients, and allowing them to multiply and differentiate into edible tissue. Advances in tissue engineering and bioreactor technology enable scalable production of cultured meat with reduced environmental impact and potential health benefits compared to traditional processed meat.
Key Differences: Production Processes
Processed meat undergoes methods such as curing, smoking, salting, or adding preservatives to extend shelf life and enhance flavor, often involving significant chemical and physical modification of the original meat. Cultured meat is produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, using tissue engineering techniques to grow muscle tissue without raising or slaughtering animals. The primary distinction lies in processed meat relying on conventional meat altered post-slaughter, while cultured meat is generated from cell cultures in vitro, offering a sustainable alternative with potentially lower environmental impact.
Nutritional Profile Comparison
Processed meat often contains higher levels of sodium, saturated fats, and preservatives, which can negatively impact cardiovascular health. Cultured meat typically offers a cleaner nutritional profile with controlled fat content and reduced harmful additives, providing a potentially healthier protein source. Research indicates cultured meat may deliver comparable levels of essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals like iron and B12, crucial for maintaining balanced nutrition.
Environmental Impact: Processed vs Cultured Meat
Cultured meat significantly reduces environmental impact compared to traditional processed meat by requiring less land, water, and energy while producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Studies show cultured meat can cut carbon emissions by up to 90% and water usage by 82% relative to conventional processed meat production. Scaling cultured meat technology supports sustainable food systems and mitigates climate change effects linked to industrial livestock farming.
Health Implications and Consumer Safety
Processed meat contains preservatives and additives linked to increased risks of heart disease and certain cancers, raising significant health concerns. Cultured meat, produced through cell cultivation without harmful chemicals, offers a safer alternative with potentially lower risks of contamination and foodborne illnesses. Advances in cultured meat technology emphasize reduced exposure to antibiotics and pathogens, enhancing consumer safety and promoting better long-term health outcomes.
Industry Trends and Market Growth
The processed meat market remains robust with consistent demand for convenience foods, driven by technological advancements in preservation and flavor enhancement. Cultured meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is experiencing rapid growth fueled by investments exceeding $1 billion and increasing consumer interest in sustainable protein alternatives. Market forecasts predict the cultured meat sector to expand at a CAGR of over 20% from 2024 to 2030, reshaping the global meat industry landscape.
Regulatory Challenges and Approvals
Regulatory challenges for processed and cultured meat center on safety assessments, labeling standards, and compliance with food laws to ensure consumer protection. Agencies like the FDA and USDA collaborate to define clear approval pathways, but variations in regulatory frameworks across countries can delay market entry. Thorough evaluation of production methods and ingredient sourcing remains critical to achieving official authorization and public acceptance.
Future Outlook: Innovation in Sustainable Meat Alternatives
Innovations in sustainable meat alternatives are rapidly advancing with cultured meat offering a promising future by significantly reducing environmental impact compared to traditional processed meat. Cultured meat production utilizes cellular agriculture techniques to create protein-rich products without the extensive land and water use associated with farming livestock. Industry leaders and startups are investing heavily in scaling cultured meat technologies, projecting a future where sustainable, lab-grown meat becomes a mainstream option for environmentally conscious consumers.
Related Important Terms
Cellular Agriculture
Cellular agriculture advances the production of cultured meat by cultivating animal cells in controlled environments, significantly reducing the environmental impact compared to traditional processed meat methods reliant on livestock farming. This technology offers scalable solutions for sustainable protein sources, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and resource consumption while maintaining the sensory and nutritional properties of conventional meat.
Cultivated Meat
Cultivated meat, produced by culturing animal cells in a controlled environment, offers a sustainable alternative to processed meat by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing land and water usage. This innovative method ensures a cleaner, antibiotic-free product with the potential to address ethical concerns and meet growing global protein demands.
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation enables the production of cultured meat by using microorganisms to convert plant-based substrates into animal proteins, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional processed meat. This technology reduces environmental impact and enhances food safety by eliminating the need for animal slaughter and minimizing chemical additives found in conventional processed meats.
Scaffolding Biomaterials
Scaffolding biomaterials in cultured meat production serve as crucial frameworks that support cell attachment, growth, and nutrient diffusion, distinguishing them from processed meat which lacks this biological structure. These biomaterials enhance the texture and safety of cultured meat by enabling precise control over tissue development, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional processed meat products.
Clean Meat
Clean meat, also known as cultured meat, is produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, eliminating the need for traditional livestock farming and reducing the environmental impact. This innovative approach offers a sustainable alternative to processed meat, providing comparable taste and texture while minimizing health risks associated with additives and preservatives commonly found in processed products.
Fat Marbling Engineering
Fat marbling engineering in cultured meat leverages precise cell culture techniques to replicate the intramuscular fat distribution found in traditional processed meat, enhancing flavor and texture profiles. Advanced bioreactors and scaffold designs promote lipid accumulation at a cellular level, offering a sustainable alternative that mimics the sensory qualities of conventionally processed marbled cuts.
Hybrid Meat Products
Hybrid meat products combine processed meat with cultured meat cells to reduce environmental impact and enhance sustainability in food production. These products offer improved texture and flavor profiles while addressing ethical concerns associated with traditional livestock farming.
Tissue Engineering Bioreactors
Tissue engineering bioreactors play a crucial role in cultured meat production by providing controlled environments that optimize cell growth, nutrient delivery, and tissue maturation, unlike traditional processed meat methods that rely on animal slaughter. These bioreactors enable scalable, sustainable, and ethical meat cultivation by mimicking physiological conditions, reducing resource use and environmental impact compared to conventional meat processing.
Mycelium-based Protein
Mycelium-based protein offers a sustainable alternative within processed and cultured meat categories by utilizing fungal mycelium to create a nutrient-rich, high-protein product with a texture similar to animal meat. This innovative protein source reduces environmental impact, requiring less land and water compared to traditional livestock and cultured meat production methods.
Structured Protein Matrix
Structured protein matrix in cultured meat replicates the texture and composition of traditional processed meat by organizing plant-based or animal cells into fibrous networks. This matrix enhances mouthfeel and nutritional profile, differentiating cultured meat from conventional processed products that often rely on additives and mechanical processing.
Processed vs Cultured Meat Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com