Food trucks offer a mobile dining experience with direct customer interaction, allowing for immediate feedback and unique presentation. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively through delivery services, optimizing efficiency and reducing overhead by eliminating the need for a physical storefront. Both models provide innovative solutions for food businesses but cater to different market demands and operational strategies.
Table of Comparison
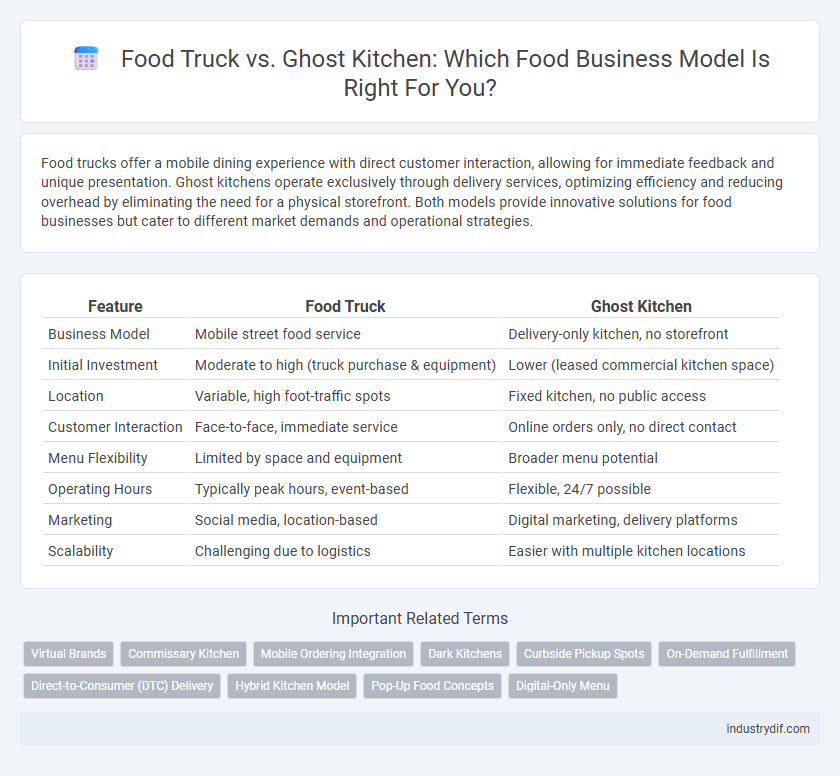
| Feature | Food Truck | Ghost Kitchen |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Mobile street food service | Delivery-only kitchen, no storefront |
| Initial Investment | Moderate to high (truck purchase & equipment) | Lower (leased commercial kitchen space) |
| Location | Variable, high foot-traffic spots | Fixed kitchen, no public access |
| Customer Interaction | Face-to-face, immediate service | Online orders only, no direct contact |
| Menu Flexibility | Limited by space and equipment | Broader menu potential |
| Operating Hours | Typically peak hours, event-based | Flexible, 24/7 possible |
| Marketing | Social media, location-based | Digital marketing, delivery platforms |
| Scalability | Challenging due to logistics | Easier with multiple kitchen locations |
Definition: Food Truck vs Ghost Kitchen
A food truck is a mobile kitchen that prepares and serves food directly to customers at various locations, offering a dynamic dining experience with immediate service. A ghost kitchen, also known as a virtual or dark kitchen, operates exclusively for delivery and takeout, with no physical storefront or dine-in option, relying heavily on online orders and third-party delivery platforms. Both concepts cater to the growing demand for convenient, accessible food, but differ fundamentally in service model and customer interaction.
Business Model Comparison
Food trucks operate with a mobile, street-level sales model that minimizes overhead by eliminating the need for a fixed location, allowing direct customer interaction and immediate sales. Ghost kitchens rely on a delivery-only model, leveraging digital ordering platforms to reduce costs associated with front-of-house operations and expand reach without the limitations of physical storefronts. Both models capitalize on low operational expenses but differ in customer engagement and scalability, with food trucks emphasizing mobility and brand visibility, while ghost kitchens prioritize efficiency and market penetration through online services.
Startup Costs and Investment
Food trucks require a startup investment typically ranging from $50,000 to $150,000, including vehicle purchase, kitchen equipment, and permits. Ghost kitchens demand lower initial costs, often between $10,000 and $50,000, mainly covering commercial kitchen rental, staffing, and technology setup. Investors prefer ghost kitchens for scalable, lower-risk operations, while food trucks offer mobile branding but higher upfront expenses.
Equipment and Space Requirements
Food trucks require compact, multi-functional equipment and limited space optimized for mobility, with built-in cooking appliances and storage designed to fit within a confined vehicle layout. Ghost kitchens operate in larger commercial spaces, equipped with industrial-grade ovens, refrigeration units, and preparation areas that support high-volume order fulfillment without customer seating or front-of-house amenities. The spatial setup in ghost kitchens allows for more extensive equipment arrays and streamlined workflows tailored for delivery-only food service models.
Menu Flexibility and Offerings
Food trucks offer limited menu flexibility due to constrained kitchen space, often focusing on a few signature dishes to maintain quality and speed. Ghost kitchens operate without customer-facing venues, enabling expansive and diverse menu offerings tailored to multiple brands or cuisines simultaneously. This operational model allows ghost kitchens to rapidly adapt menus based on market trends and customer preferences.
Licensing and Regulatory Challenges
Food trucks face stringent licensing requirements including mobile food vendor permits, health inspections, and zoning restrictions that vary significantly by city and state. Ghost kitchens, operating exclusively online without a physical storefront, encounter regulatory challenges primarily related to commercial kitchen certification, food safety compliance, and third-party delivery partnerships. Navigating these regulatory frameworks demands comprehensive understanding of local health codes, fire safety standards, and business licenses to ensure lawful and efficient operation.
Location and Market Reach
Food trucks capitalize on prime, high-traffic locations such as festivals, city centers, and business districts to attract a dynamic, on-the-go customer base. Ghost kitchens operate without a physical storefront, strategically positioning themselves in low-rent, delivery-friendly areas to maximize online market reach through multiple platforms. The location flexibility of ghost kitchens allows them to serve broader geographic areas compared to food trucks, which are limited by their physical mobility and local foot traffic.
Operational Logistics
Food trucks require mobile operations with real-time route planning, on-site cooking, and direct customer interaction, often facing challenges like limited storage and fluctuating permits. Ghost kitchens operate from fixed commercial spaces optimized for delivery, leveraging centralized inventory, streamlined food prep workflows, and sophisticated order management systems to handle high order volumes efficiently. Both models emphasize speed and flexibility, but ghost kitchens benefit from reduced overhead and scalability within controlled environments.
Branding and Customer Engagement
Food trucks offer a dynamic platform for branding through visually striking vehicle designs and direct customer interactions at diverse locations, fostering strong, personal engagement. Ghost kitchens rely heavily on digital branding strategies, utilizing social media and delivery apps to build customer loyalty without physical presence. Both models emphasize tailored marketing, but food trucks excel in experiential brand presence while ghost kitchens prioritize online visibility and convenience.
Revenue Potential and Growth Trends
Food trucks offer lower startup costs and flexible locations, generating steady local revenue with moderate growth potential. Ghost kitchens leverage online delivery channels and reduced overhead, enabling rapid scalability and higher profit margins driven by expanding demand for contactless dining. Industry reports indicate ghost kitchens could capture a growing market share, with revenue growth projected at over 20% annually compared to 5-10% for traditional food trucks.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Brands
Virtual brands operating through ghost kitchens reduce overhead costs by eliminating the need for physical storefronts, allowing food trucks to focus on mobility and direct customer engagement. Ghost kitchens leverage online ordering platforms and optimized delivery logistics, while food trucks capitalize on location flexibility and street presence to build brand recognition.
Commissary Kitchen
Food trucks and ghost kitchens both rely on commissary kitchens to meet health regulations and streamline operations, providing shared commercial kitchen spaces equipped with essential appliances and storage. Commissary kitchens reduce overhead costs by offering flexible rental options, centralized food prep, and waste management, which benefits mobile vendors and delivery-only brands alike.
Mobile Ordering Integration
Food trucks leverage mobile ordering integration to streamline on-the-go sales and reduce wait times by allowing customers to order ahead via apps, enhancing convenience and customer engagement at various locations. Ghost kitchens utilize mobile ordering platforms to efficiently manage delivery-only operations, optimizing menu updates and order flow without the need for physical dine-in space, driving faster service and broader market reach.
Dark Kitchens
Dark kitchens, also known as ghost kitchens, operate exclusively through online orders without a physical storefront, optimizing operational costs and allowing multiple virtual restaurant brands to share a single commercial space. This model leverages advanced delivery logistics and digital marketing strategies to capture growing demand for convenient, contactless food delivery services.
Curbside Pickup Spots
Food trucks offer mobile curbside pickup spots that attract customers through convenience and location flexibility, ideal for busy urban areas. Ghost kitchens rely on fixed locations without storefronts, primarily serving online orders with designated curbside pickup zones to streamline delivery and minimize wait times.
On-Demand Fulfillment
Food trucks offer flexible, on-demand fulfillment through mobile setups that bring fresh meals directly to high-traffic locations, adapting quickly to customer flow and event schedules. Ghost kitchens leverage optimized delivery logistics and multiple virtual brands operating from a centralized kitchen to efficiently fulfill online orders, reducing overhead and expanding reach without physical storefronts.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Delivery
Food trucks provide an on-the-go, location-based dining experience while leveraging DTC delivery apps to reach nearby customers quickly; ghost kitchens operate exclusively through online orders, optimizing delivery logistics and menu scalability without physical storefront constraints. Both models capitalize on digital platforms to enhance direct consumer engagement, but ghost kitchens excel at reducing overhead and expanding market reach through dedicated delivery services.
Hybrid Kitchen Model
The hybrid kitchen model combines the mobility of a food truck with the scalability of a ghost kitchen, enabling operators to serve diverse menus while reducing overhead costs and expanding delivery reach. This approach leverages centralized kitchen facilities for efficient food preparation alongside mobile units to capture on-site customer engagement, optimizing operational flexibility in the competitive food service industry.
Pop-Up Food Concepts
Pop-up food concepts leverage the mobility of food trucks to reach diverse locations and customer bases, offering direct interaction and brand visibility. Ghost kitchens utilize virtual-only spaces to minimize overhead and maximize delivery efficiency, focusing on online orders without physical storefront constraints.
Digital-Only Menu
Food trucks utilize a digital-only menu to streamline ordering and offer real-time customization, enhancing mobile customer engagement. Ghost kitchens rely entirely on digital platforms for menu display and order processing, optimizing delivery efficiency without a physical storefront.
Food truck vs Ghost kitchen Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com