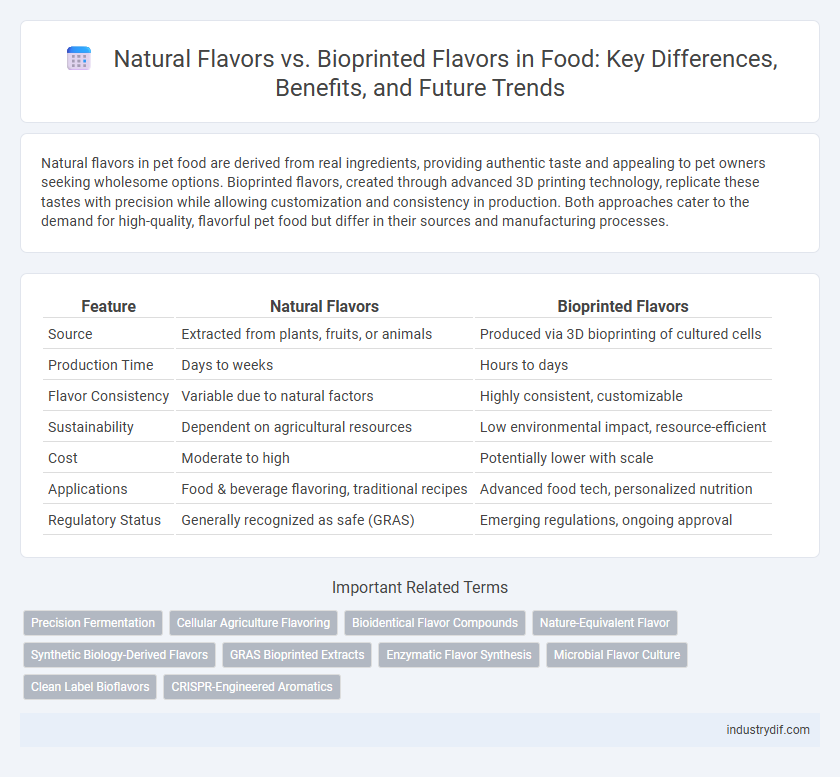
Natural flavors in pet food are derived from real ingredients, providing authentic taste and appealing to pet owners seeking wholesome options. Bioprinted flavors, created through advanced 3D printing technology, replicate these tastes with precision while allowing customization and consistency in production. Both approaches cater to the demand for high-quality, flavorful pet food but differ in their sources and manufacturing processes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Natural Flavors | Bioprinted Flavors |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from plants, fruits, or animals | Produced via 3D bioprinting of cultured cells |
| Production Time | Days to weeks | Hours to days |
| Flavor Consistency | Variable due to natural factors | Highly consistent, customizable |
| Sustainability | Dependent on agricultural resources | Low environmental impact, resource-efficient |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Potentially lower with scale |
| Applications | Food & beverage flavoring, traditional recipes | Advanced food tech, personalized nutrition |
| Regulatory Status | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) | Emerging regulations, ongoing approval |
Understanding Natural Flavors: Definition and Sources
Natural flavors are complex compounds derived from natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, spices, herbs, and animal products, used to enhance the taste and aroma of food. They are extracted through methods like distillation, solvent extraction, and cold pressing to capture the essence of the original ingredient without synthetic additives. Understanding these sources is essential to appreciating the natural flavor profiles that contribute to authentic and diverse culinary experiences.
The Science Behind Bioprinted Flavors
Bioprinted flavors utilize advanced 3D printing technology to replicate natural flavor compounds at the molecular level, ensuring precise control over taste profiles and consistency. This process involves layering cells or enzymes to synthesize complex flavor molecules without extraction from traditional natural sources. Unlike conventional natural flavors derived through chemical extraction, bioprinted flavors offer sustainable production with reduced environmental impact and enhanced scalability.
Extraction and Production Methods: Natural vs Bioprinting
Natural flavors are typically extracted from plants, fruits, or animal sources using methods such as steam distillation, solvent extraction, or cold pressing, preserving their inherent aromatic compounds. Bioprinted flavors involve layering cultured cells or biomolecules using 3D bioprinting technology, allowing precise control over flavor profiles and sustainability. These production methods differ significantly, with natural extraction relying on raw materials and bioprinting creating flavors through synthetic biology and tissue engineering.
Ingredient Transparency and Labeling
Natural flavors are derived from plant or animal sources and must be clearly labeled on ingredient lists to ensure consumer transparency. Bioprinted flavors, produced through cellular agriculture and biotechnology, offer precise flavor replication but often face challenges in standardized labeling due to their novel production methods. Clear disclosure of flavor origins and ingredient composition is essential for informed consumer choices and regulatory compliance in the food industry.
Flavor Consistency and Customization
Natural flavors offer authentic taste profiles but often vary due to seasonal and agricultural differences, leading to inconsistent flavor intensity. Bioprinted flavors utilize advanced biotechnology to replicate precise molecular compositions, ensuring consistent flavor quality across batches. This technology also enables extensive customization, allowing manufacturers to tailor flavor profiles to specific consumer preferences or dietary needs with high accuracy.
Health and Safety Considerations
Natural flavors are derived from plant or animal sources and typically undergo minimal processing, offering a profile with fewer synthetic additives and generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status by regulatory agencies. Bioprinted flavors, created using cellular agriculture and 3D printing technology, allow for precise control over ingredient composition, reducing allergens and contaminants but require thorough evaluation for long-term health impacts and regulatory approval. Both approaches demand rigorous safety testing to ensure they do not introduce harmful compounds or negatively affect consumer health.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Comparison
Natural flavors are derived from plant and animal sources using traditional extraction methods, which can involve extensive water and land use, leading to habitat disruption and higher carbon emissions. Bioprinted flavors are produced through cellular agriculture techniques that utilize microorganisms or cultured cells, significantly reducing resource consumption, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions. Consequently, bioprinted flavors offer a more sustainable alternative by minimizing environmental footprint and promoting resource-efficient production processes.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Natural flavors, derived from plant and animal sources, continue to dominate consumer preference due to their perceived authenticity and safety, driving significant market demand in the food industry. Bioprinted flavors, created through advanced biotechnology and 3D printing techniques, are emerging as innovative alternatives with the potential to enhance flavor customization and sustainability, attracting interest from tech-savvy and environmentally conscious consumers. Shifts in market trends reveal growing curiosity around bioprinted flavors, especially among younger demographics seeking novel culinary experiences and transparency in ingredient sourcing.
Regulatory Guidelines for Natural and Bioprinted Flavors
Regulatory guidelines for natural flavors are stringent, requiring sourcing from natural plant or animal origins and approval by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA to ensure safety and authenticity. Bioprinted flavors, emerging through advanced cellular agriculture and synthetic biology, face evolving regulations that emphasize transparency, safety assessments, and labeling to distinguish them from traditional natural flavors. Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is crucial for market acceptance and consumer trust in both natural and bioprinted flavor products.
Future Innovations in Food Flavor Technology
Natural flavors derived from plant and animal sources continue to dominate the food industry, but bioprinted flavors, created using cellular agriculture and 3D printing technologies, represent a groundbreaking frontier in flavor innovation. These bioprinted flavors enable precise control over taste profiles and sustainability, reducing reliance on traditional agriculture and enhancing food customization. Future advancements in bioprinting could revolutionize flavor complexity and environmental impact, making it a pivotal area in next-generation food flavor technology.
Related Important Terms
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation enables the production of bioprinted flavors by harnessing microorganisms to create consistent, high-purity taste compounds that mimic natural flavors. This innovative approach offers greater sustainability and scalability compared to traditional extraction methods used for natural flavors.
Cellular Agriculture Flavoring
Natural flavors are derived from traditional extraction methods using plant or animal sources, while bioprinted flavors leverage cellular agriculture to precisely cultivate flavor molecules via engineered cells, offering sustainable and customizable taste profiles. This innovative approach to flavoring reduces reliance on natural resource consumption and enables scalable production of complex, authentic flavors without environmental degradation.
Bioidentical Flavor Compounds
Bioidentical flavor compounds in bioprinted flavors are chemically identical to natural flavor molecules, offering consistent taste profiles and enhanced purity compared to traditional natural flavors extracted from plants or animals. This precision enables scalable production without relying on seasonal or geographic constraints, ensuring sustainable and customizable flavor solutions for the food industry.
Nature-Equivalent Flavor
Nature-equivalent flavors derived through bioprinting replicate the molecular profile of natural flavors using advanced biotechnology, offering consistent taste and purity without synthetic additives. These bioprinted flavors provide a sustainable alternative to traditional natural flavors by minimizing reliance on agricultural resources and reducing environmental impact.
Synthetic Biology-Derived Flavors
Synthetic biology-derived flavors utilize engineered microorganisms to produce consistent, scalable, and sustainable flavor compounds, offering precise control over taste profiles compared to traditional natural flavors extracted from plants. Bioprinted flavors, created through advanced biofabrication techniques, enable the customization of complex flavor structures at the molecular level, enhancing intensity and stability while reducing environmental impact.
GRAS Bioprinted Extracts
GRAS bioprinted extracts represent a cutting-edge innovation in natural flavor enhancement, leveraging precise cellular engineering to produce complex flavor compounds sustainably and consistently. These bioprinted flavors meet Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) standards, offering food manufacturers a reliable alternative to traditional natural extracts without compromising taste or safety.
Enzymatic Flavor Synthesis
Enzymatic flavor synthesis in bioprinted flavors offers precise control over molecular structures, enabling the creation of complex, natural-tasting profiles that closely mimic traditional flavors without synthetic additives. Natural flavors derived from enzymatic processes use specific enzymes to transform raw materials, enhancing flavor intensity and stability while maintaining clean-label appeal.
Microbial Flavor Culture
Microbial flavor culture utilizes genetically engineered microorganisms to produce bioprinted flavors, offering consistent taste profiles and sustainable alternatives to natural flavors derived from plants and animals. This biotechnological approach enhances flavor complexity and safety by minimizing variations caused by environmental factors inherent in traditional natural flavor extraction.
Clean Label Bioflavors
Clean label bioflavors derived through bioprinting techniques offer a sustainable and precise alternative to traditional natural flavors, ensuring consistency and reducing reliance on unpredictable agricultural sources. These bioengineered flavors maintain the authenticity of natural taste profiles while supporting transparency and consumer demand for minimally processed, additive-free ingredients.
CRISPR-Engineered Aromatics
CRISPR-engineered aromatics enable precise genetic modifications to enhance natural flavor compounds, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional natural flavors derived from plants. Bioprinted flavors leverage this technology by accurately replicating complex aromatic profiles, ensuring consistent taste while reducing environmental impact and resource consumption.
Natural Flavors vs Bioprinted Flavors Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com