Processed pet foods often contain artificial additives, preservatives, and fillers that can affect your pet's health over time. Clean label foods emphasize natural, recognizable ingredients, promoting better digestion and overall wellness for pets. Choosing clean label options supports transparent sourcing and higher nutritional quality, benefiting both pets and concerned pet owners.
Table of Comparison
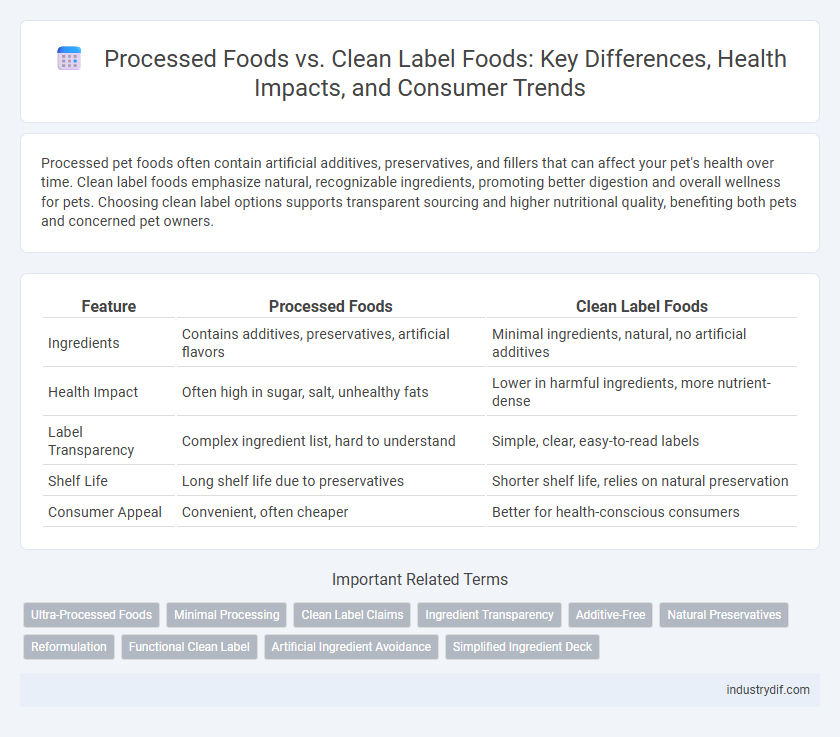
| Feature | Processed Foods | Clean Label Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Contains additives, preservatives, artificial flavors | Minimal ingredients, natural, no artificial additives |
| Health Impact | Often high in sugar, salt, unhealthy fats | Lower in harmful ingredients, more nutrient-dense |
| Label Transparency | Complex ingredient list, hard to understand | Simple, clear, easy-to-read labels |
| Shelf Life | Long shelf life due to preservatives | Shorter shelf life, relies on natural preservation |
| Consumer Appeal | Convenient, often cheaper | Better for health-conscious consumers |
Understanding Processed Foods: Definition and Types
Processed foods undergo various methods such as freezing, canning, baking, and drying to enhance shelf life and convenience, often containing additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients. Types of processed foods range from minimally processed items like washed and packaged vegetables to heavily processed products such as ready-to-eat meals, snack foods, and processed meats. Understanding the degree of processing helps consumers distinguish between nutritious options and those with potentially lower nutritional value or added chemicals.
What Are Clean Label Foods? Key Characteristics
Clean label foods are products made with natural, easily recognizable ingredients free from artificial additives, preservatives, and colorings. They emphasize transparency, simplicity, and authenticity, catering to consumer demand for healthier, minimally processed options. Key characteristics include short ingredient lists, no synthetic chemicals, and clear, honest packaging information.
Ingredient Lists: Processed vs Clean Label Foods
Processed foods often contain long ingredient lists filled with artificial additives, preservatives, and synthetic flavors designed to enhance taste and shelf life. Clean label foods prioritize transparency by using simpler, recognizable ingredients such as natural herbs, spices, and whole food components, appealing to health-conscious consumers. Ingredient lists in clean label foods emphasize minimal processing and the absence of artificial chemicals, directly impacting consumer trust and product perception.
Health Impacts: Comparing Processed and Clean Label Foods
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives, which can contribute to obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Clean label foods, characterized by natural ingredients and minimal processing, are associated with better nutritional profiles that support overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Choosing clean label options promotes better digestion, lower inflammation, and improved metabolic function compared to heavily processed alternatives.
Consumer Trends in Food Choices
Consumer trends reveal a growing preference for clean label foods, driven by increased awareness of health and ingredient transparency. Processed foods, often associated with artificial additives and preservatives, face declining demand as consumers seek natural, minimally processed alternatives. Market research indicates a surge in clean label product sales, reflecting a shift towards healthier, trust-based food choices worldwide.
Labeling Regulations and Industry Standards
Labeling regulations for processed foods typically require detailed ingredient lists and nutritional information to ensure consumer transparency, while clean label foods emphasize minimal, recognizable ingredients aligned with consumer demand for natural, additive-free products. Industry standards for processed foods often permit the use of preservatives, artificial colors, and flavors, whereas clean label standards discourage or prohibit these additives to maintain product purity. The regulatory oversight for clean label foods is evolving, reflecting increased scrutiny over ingredient sourcing, allergen declarations, and claims of organic or non-GMO status to align with health-conscious market trends.
Clean Label Movement: Drivers and Challenges
The Clean Label Movement is driven by increasing consumer demand for transparency, natural ingredients, and minimal processing in food products. Challenges include balancing product shelf-life, safety, and taste while eliminating synthetic additives and preservatives. Food manufacturers must innovate to meet clean label standards without compromising quality or affordability.
Manufacturing Processes: Conventional vs Clean Label Approaches
Manufacturing processes in conventional processed foods often involve synthetic additives, preservatives, and extensive chemical treatments to prolong shelf life and enhance flavor. Clean label approaches prioritize minimal processing, using natural ingredients and straightforward methods to maintain transparency and meet consumer demand for healthier, recognizable components. This shift reduces reliance on artificial substances, emphasizing sustainability and ingredient integrity throughout the production cycle.
Additives and Preservatives: Roles and Concerns
Processed foods often contain additives and preservatives such as sodium benzoate, artificial flavors, and colorants to enhance shelf life and taste, raising concerns about potential health risks like allergies and increased exposure to synthetic chemicals. Clean label foods prioritize natural ingredients and minimal processing, using natural preservatives like vinegar or rosemary extract to maintain freshness while addressing consumer demand for transparency and health-conscious choices. Understanding the roles and impacts of these substances is crucial for informed dietary decisions and food safety awareness.
Future of Processed and Clean Label Foods in the Industry
The future of processed foods is increasingly driven by innovation in ingredient transparency and healthier formulations that respond to consumer demand for clean label products. Advances in food technology enable the development of processed foods with reduced additives, natural preservatives, and clear labeling to enhance trust and appeal. Market trends indicate a strong shift towards clean label foods featuring recognizable ingredients and minimal processing while maintaining convenience and shelf life, reshaping industry standards and consumer expectations.
Related Important Terms
Ultra-Processed Foods
Ultra-processed foods contain artificial additives, preservatives, and high levels of sugars or unhealthy fats that negatively impact health, while clean label foods emphasize minimal processing, natural ingredients, and transparency in sourcing. Consumers increasingly prefer clean label options due to growing awareness of the risks associated with excessive consumption of ultra-processed products linked to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Minimal Processing
Minimal processing in clean label foods preserves natural ingredients and nutrients by avoiding additives, artificial flavors, and extensive refining, ensuring transparency and health benefits. Processed foods often undergo multiple stages of alteration, including high heat, chemical treatments, and preservatives, which can diminish nutritional value and introduce synthetic substances.
Clean Label Claims
Clean label foods emphasize transparency, using natural ingredients and avoiding artificial additives, preservatives, and chemicals to meet consumer demand for healthier, more trustworthy products. These foods often feature clean label claims such as non-GMO, organic, gluten-free, and no artificial colors or flavors, enhancing brand appeal and fostering consumer confidence.
Ingredient Transparency
Clean label foods emphasize ingredient transparency by using simple, recognizable components and minimal additives, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking natural options. In contrast, processed foods often contain complex additives and preservatives, making it challenging for consumers to fully understand the nutritional content and sourcing of ingredients.
Additive-Free
Additive-free clean label foods emphasize natural ingredients without artificial preservatives, colors, or flavors, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking transparency and simplicity. Processed foods often contain synthetic additives to enhance shelf life, texture, and taste but may raise concerns about long-term health effects and ingredient transparency.
Natural Preservatives
Natural preservatives such as rosemary extract, vinegar, and citrus-derived ascorbic acid are increasingly used in clean label foods to extend shelf life without synthetic additives. Processed foods often rely on artificial preservatives like sodium benzoate or BHA, which may raise consumer concerns about health and ingredient transparency.
Reformulation
Reformulation in processed foods involves reducing artificial additives, preservatives, and excessive sugars or salts to meet consumer demand for cleaner labels and healthier options. Clean label foods emphasize transparent ingredient lists and natural components, driving food manufacturers to innovate reformulation strategies that enhance nutritional profiles without compromising taste or shelf life.
Functional Clean Label
Functional clean label foods prioritize natural ingredients with clear health benefits and minimal processing, enhancing nutritional value without artificial additives or preservatives. This approach responds to increasing consumer demand for transparency, purity, and functionality in food products, contrasting with processed foods that often contain synthetic components and complex ingredient lists.
Artificial Ingredient Avoidance
Processed foods often contain artificial preservatives, colorings, and flavorings that consumers seek to avoid for health reasons, driving demand for clean label foods made with natural, minimally processed ingredients. Clean label foods prioritize transparency by excluding synthetic additives, appealing to health-conscious individuals who prioritize ingredient purity and natural sourcing.
Simplified Ingredient Deck
Processed foods typically contain long ingredient lists with additives, preservatives, and artificial flavors, making them less transparent and harder for consumers to understand. Clean label foods emphasize a simplified ingredient deck featuring recognizable, natural components, enhancing consumer trust and promoting healthier eating choices.
Processed Foods vs Clean Label Foods Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com