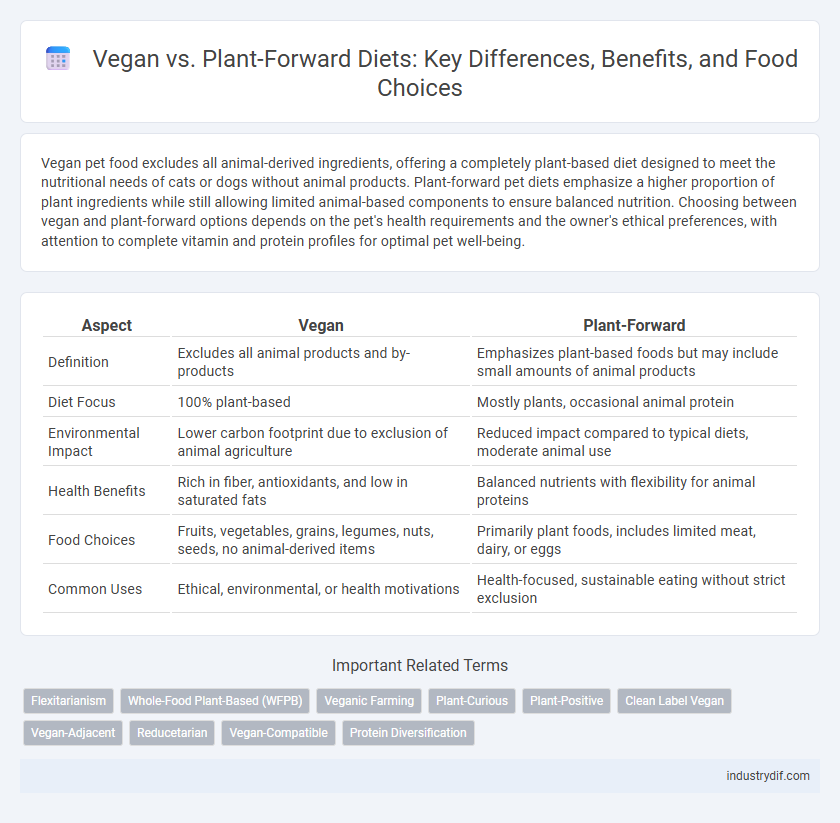
Vegan pet food excludes all animal-derived ingredients, offering a completely plant-based diet designed to meet the nutritional needs of cats or dogs without animal products. Plant-forward pet diets emphasize a higher proportion of plant ingredients while still allowing limited animal-based components to ensure balanced nutrition. Choosing between vegan and plant-forward options depends on the pet's health requirements and the owner's ethical preferences, with attention to complete vitamin and protein profiles for optimal pet well-being.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Vegan | Plant-Forward |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excludes all animal products and by-products | Emphasizes plant-based foods but may include small amounts of animal products |
| Diet Focus | 100% plant-based | Mostly plants, occasional animal protein |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to exclusion of animal agriculture | Reduced impact compared to typical diets, moderate animal use |
| Health Benefits | Rich in fiber, antioxidants, and low in saturated fats | Balanced nutrients with flexibility for animal proteins |
| Food Choices | Fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, no animal-derived items | Primarily plant foods, includes limited meat, dairy, or eggs |
| Common Uses | Ethical, environmental, or health motivations | Health-focused, sustainable eating without strict exclusion |
Defining Vegan and Plant-Forward Diets
A vegan diet excludes all animal products, emphasizing plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and legumes. Plant-forward diets prioritize plant foods while allowing limited consumption of animal products like dairy, eggs, or seafood. This approach promotes sustainability and flexibility, appealing to a broader audience seeking health benefits without full animal exclusion.
Core Principles: Veganism vs Plant-Forward Eating
Veganism centers on eliminating all animal products from the diet, emphasizing ethical and environmental considerations alongside health benefits. Plant-forward eating prioritizes plant-based foods but allows flexibility, including small amounts of animal products for balance and sustainability. Core principles of veganism strictly avoid animal-derived ingredients, while plant-forward approaches encourage maximum plant consumption without complete exclusion of animal items.
Ingredient Sourcing and Selection
Vegan diets exclude all animal products, relying on plant-based ingredients such as legumes, grains, nuts, and vegetables, often emphasizing organic and non-GMO sourcing for ethical and environmental benefits. Plant-forward approaches prioritize plant-based foods but may include small amounts of animal products, focusing on seasonally sourced, locally grown, and minimally processed ingredients to enhance sustainability and flavor. Both methods stress ingredient quality, but veganism demands strict exclusion, while plant-forward offers more flexibility in sourcing and selection.
Nutritional Profiles and Health Impacts
Vegan diets eliminate all animal products, offering high fiber, antioxidants, and plant-based proteins that support heart health and reduce inflammation. Plant-forward diets emphasize plant foods but may include moderate amounts of animal products, providing more flexibility in nutrient intake such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids. Both approaches promote lower risks of chronic diseases, but plant-forward diets may offer better nutrient balance and easier adherence for some individuals.
Environmental Sustainability Considerations
Vegan diets eliminate all animal products, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions, water use, and land degradation compared to conventional diets. Plant-forward diets emphasize increasing plant-based foods while allowing moderate animal product consumption, balancing nutritional needs and sustainability goals. Studies show plant-forward approaches can offer similar environmental benefits as veganism, with greater dietary flexibility supporting broader adoption and long-term ecological impact reduction.
Culinary Innovations and Menu Solutions
Vegan cuisine excludes all animal products, driving culinary innovations through creative use of legumes, grains, and plant-based proteins to replicate traditional textures and flavors. Plant-forward menus emphasize vegetables as the main component while allowing limited animal ingredients, fostering versatile dishes that enhance nutritional balance and sustainability. Chefs innovate with techniques like fermentation, jackfruit as meat substitute, and plant-based dairy alternatives to create appealing, nutrient-rich menu solutions that attract diverse diners.
Consumer Demand and Market Trends
Consumer demand for vegan products has surged significantly, driven by increasing awareness of animal welfare and environmental impact. Plant-forward diets, which prioritize vegetables and whole foods while allowing some animal products, are gaining broader market appeal due to their flexibility and health benefits. Market trends indicate rapid growth in plant-based meat alternatives and dairy substitutes, reflecting a shift toward sustainable and health-conscious eating habits.
Challenges for Foodservice Operators
Foodservice operators face significant challenges when integrating vegan and plant-forward menus due to the need for sourcing diverse, high-quality plant-based ingredients that meet varying dietary preferences and nutritional requirements. Menu development must balance flavor innovation with cost control while ensuring allergen management and cross-contamination prevention in busy kitchens. Training staff on plant-based culinary techniques and educating customers about the benefits and options of vegan versus plant-forward dining further complicates operational workflows.
Labeling, Certification, and Compliance
Vegan labeling requires strict adherence to certifications that confirm no animal products or by-products are used, ensuring compliance with standards like the Vegan Society Trademark. Plant-forward labeling allows inclusion of limited animal-derived ingredients, necessitating clear disclosure and adherence to guidelines such as the Plant-Based Food Association's definitions. Certification bodies provide verification, helping consumers differentiate between strictly vegan products and those emphasizing a plant-forward approach for transparency and trust.
Future Outlook in the Food Industry
The future outlook in the food industry highlights a significant shift towards vegan and plant-forward diets driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainability, health benefits, and ethical considerations. Innovations in plant-based protein alternatives and advancements in food technology are accelerating the adoption of these diets across global markets. As regulatory frameworks and corporate sustainability goals evolve, the plant-forward approach is poised to complement veganism, fostering a diversified and inclusive food ecosystem.
Related Important Terms
Flexitarianism
Flexitarianism emphasizes a primarily plant-based diet while allowing occasional consumption of animal products, bridging the gap between strict veganism and more traditional eating patterns. This approach promotes flexibility and sustainability by reducing meat intake without complete elimination, appealing to those seeking health benefits and environmental impact reduction.
Whole-Food Plant-Based (WFPB)
Whole-Food Plant-Based (WFPB) diets emphasize minimally processed plant foods such as vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, contrasting with vegan diets that exclude animal products but may include processed foods. WFPB focuses on nutrient density and health benefits by prioritizing whole grains and legumes over refined oils and sugars often found in less strict vegan diets.
Veganic Farming
Veganic farming eliminates synthetic chemicals and animal inputs, promoting sustainable soil health while supporting plant-forward diets that emphasize whole, nutrient-dense vegetables. This method aligns with vegan principles by avoiding animal exploitation, making it a foundational practice for truly ethical and eco-friendly food production.
Plant-Curious
Plant-curious eaters explore plant-forward diets by incorporating more vegetables, legumes, and whole grains without fully committing to veganism, balancing taste and nutrition. This flexible approach encourages gradual shifts toward sustainable eating patterns, appealing to those seeking health benefits and environmental impact reduction while still enjoying occasional animal products.
Plant-Positive
Plant-Positive eating emphasizes a variety of whole, nutrient-dense plants without strictly excluding animal products, promoting environmental sustainability and improved health outcomes. This approach contrasts with veganism by allowing flexible dietary choices while encouraging increased consumption of vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains.
Clean Label Vegan
Clean label vegan products emphasize minimal processing, transparent ingredient lists, and free-from artificial additives, appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking purity in plant-based foods. Plant-forward diets prioritize whole, nutrient-dense vegetables and grains while allowing flexibility beyond strict veganism, supporting sustainable and clean eating habits.
Vegan-Adjacent
Vegan-adjacent diets emphasize plant-based foods while occasionally incorporating minimal animal products, bridging the gap between strict veganism and more flexible eating habits. This approach supports sustainability and health benefits by prioritizing whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables without fully excluding dairy or eggs.
Reducetarian
Reducetarian diets emphasize reducing meat consumption rather than eliminating it entirely, bridging the gap between vegan and plant-forward lifestyles by encouraging more plant-based meals while allowing occasional animal products. This flexible approach supports sustainable eating habits and environmental benefits without requiring strict adherence to veganism, appealing to a broader audience seeking health and ecological improvements.
Vegan-Compatible
Vegan-compatible foods exclude all animal products, strictly adhering to plant-based ingredients, while plant-forward diets emphasize plant-based foods but may include modest amounts of animal products. Choosing vegan-compatible options ensures alignment with ethical, environmental, and health considerations by eliminating dairy, eggs, and meat entirely.
Protein Diversification
Protein diversification in vegan diets relies on combining legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains to meet essential amino acid requirements, emphasizing plant-based sources free from animal products. Plant-forward diets incorporate a broader spectrum of protein options, including moderate amounts of animal-based foods, enhancing nutrient variety and supporting balanced protein intake.
Vegan vs Plant-forward Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com