Food waste in pet food manufacturing leads to significant environmental and economic losses, while upcycled food transforms surplus or imperfect ingredients into nutritious pet meals, reducing landfill contributions. Upcycled pet food maintains high-quality standards and supports sustainability by diverting ingredients that would otherwise be discarded. This innovative approach appeals to eco-conscious consumers seeking to minimize their pets' carbon footprint without compromising nutrition.
Table of Comparison
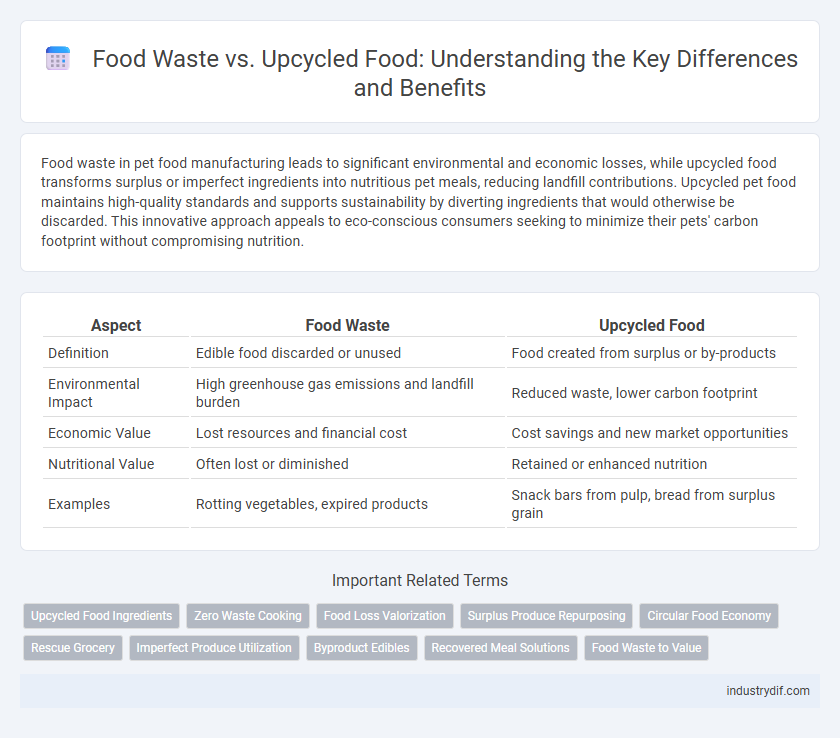
| Aspect | Food Waste | Upcycled Food |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Edible food discarded or unused | Food created from surplus or by-products |
| Environmental Impact | High greenhouse gas emissions and landfill burden | Reduced waste, lower carbon footprint |
| Economic Value | Lost resources and financial cost | Cost savings and new market opportunities |
| Nutritional Value | Often lost or diminished | Retained or enhanced nutrition |
| Examples | Rotting vegetables, expired products | Snack bars from pulp, bread from surplus grain |
Understanding Food Waste: Causes and Impacts
Food waste results from losses during production, processing, distribution, and consumption, with consumer behavior and supply chain inefficiencies as primary causes. Globally, approximately 1.3 billion tons of food are wasted annually, contributing to 8-10% of greenhouse gas emissions and significant economic losses. Addressing food waste is critical to reducing environmental impact and improving food security by minimizing resource depletion and landfill overflows.
Defining Upcycled Food: Innovations and Examples
Upcycled food refers to products created by repurposing ingredients that would otherwise be discarded, reducing food waste through innovative culinary techniques. Examples include snacks made from spent grains from breweries, fruit pulps from juice production, and surplus vegetables transformed into soups or sauces. This sustainable approach addresses environmental concerns by diverting edible ingredients from landfills and contributing to a circular food economy.
The Environmental Cost of Food Waste
Food waste generates approximately 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to climate change through methane released from decomposing organic matter in landfills. Upcycled food reduces this environmental impact by diverting ingredients that would otherwise be discarded, promoting resource efficiency and lowering carbon footprints. Implementing upcycled food practices conserves water, energy, and reduces soil degradation associated with conventional food production.
Upcycled Food: Reducing Waste through Innovation
Upcycled food transforms surplus ingredients and by-products into nutritious and delicious products, significantly reducing food waste and conserving resources. Innovative techniques in upcycled food production not only minimize landfill contributions but also lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with food disposal. Embracing upcycled food supports circular economy principles and offers sustainable solutions for global food security challenges.
Circular Economy in the Food Industry
Food waste represents a significant loss of resources and environmental impact in the food industry, while upcycled food transforms by-products and surplus ingredients into valuable products, promoting resource efficiency. Circular economy models in the food sector prioritize reducing waste by creating closed-loop systems that extend the lifecycle of food materials through processes like upcycling, composting, and redistribution. This approach enhances sustainability by minimizing landfill contributions, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and supporting economic growth through innovative food product development.
Regulatory Frameworks for Food Waste and Upcycling
Regulatory frameworks for food waste and upcycled food are evolving to promote sustainability and reduce environmental impact. Governments implement policies such as the EU Waste Framework Directive, which sets targets for waste reduction, and the U.S. FDA guidelines that ensure safety standards for upcycled ingredients in food products. These regulations encourage innovation in food upcycling by providing clear compliance criteria while minimizing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Consumer Perceptions: Food Waste vs Upcycled Products
Consumers often perceive food waste negatively due to concerns about hygiene, safety, and quality, which creates a barrier to accepting upcycled food products. Upcycled foods, made from by-products or surplus ingredients, are increasingly recognized for their environmental benefits, but awareness remains limited. Positive consumer education about sustainability and transparency in labeling can significantly improve acceptance and trust in upcycled food products.
Economic Benefits of Upcycled Food Solutions
Upcycled food solutions significantly reduce food waste by transforming edible by-products into marketable products, creating new revenue streams for producers and businesses. This approach lowers disposal costs and maximizes resource efficiency, increasing overall profitability within the food industry. Investment in upcycled food technologies also stimulates job creation and encourages sustainable supply chains, fostering long-term economic growth.
Challenges in Scaling Upcycled Food Initiatives
Scaling upcycled food initiatives faces significant challenges including inconsistent supply of surplus ingredients, regulatory hurdles related to food safety, and consumer skepticism about repurposed products. Establishing reliable sourcing channels from food waste streams such as surplus produce, byproducts, and imperfect goods requires coordination across the supply chain. Overcoming misconceptions through transparent marketing and ensuring compliance with food standards are critical to mainstream adoption of upcycled food products.
Future Trends: Transforming Food Waste into Opportunity
Advancements in food technology and sustainability are driving the future trend of converting food waste into upcycled food products, reducing environmental impact and promoting circular economy practices. Innovative startups and established companies are investing in upcycling processes that transform by-products and surplus ingredients into nutritious, value-added food items. Increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly and resource-efficient products further accelerates the growth and acceptance of upcycled food in global markets.
Related Important Terms
Upcycled Food Ingredients
Upcycled food ingredients transform surplus food materials into nutritious, sustainable products, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to traditional food waste disposal. Utilizing by-products such as fruit peels, vegetable pulp, and spent grains enhances resource efficiency and supports circular economy initiatives in the food industry.
Zero Waste Cooking
Zero waste cooking minimizes food waste by transforming leftovers and scraps into nutritious meals, enhancing sustainability and reducing landfill impact. Upcycled food utilizes ingredients diverted from waste streams, promoting resource efficiency and supporting circular food systems.
Food Loss Valorization
Food loss valorization transforms discarded food products into valuable ingredients, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability. Upcycled food leverages this process by creatively repurposing edible scraps into nutritious, marketable products that minimize food waste.
Surplus Produce Repurposing
Surplus produce repurposing transforms excess fruits and vegetables into nutritious upcycled food products, significantly reducing food waste in the supply chain. This process not only minimizes environmental impact but also creates value-added ingredients for sustainable food production.
Circular Food Economy
Food waste accounts for approximately one-third of all food produced globally, representing a significant loss of resources and environmental strain; upcycled food transforms by-products and surplus ingredients into nutritious products, reducing landfill impact and conserving energy. Circular food economy models emphasize closing resource loops by promoting upcycling initiatives, minimizing waste, and enhancing sustainability within the food production system.
Rescue Grocery
Rescue Grocery significantly reduces food waste by sourcing surplus, near-expiry, and cosmetically imperfect products to create upcycled food items that retain high nutritional value. This innovative approach transforms potential waste into affordable, sustainable groceries, minimizing environmental impact and promoting circular food systems.
Imperfect Produce Utilization
Imperfect produce utilization transforms cosmetically flawed fruits and vegetables, often discarded as food waste, into nutritious upcycled food products, reducing landfill contributions and saving resources. Leveraging these undervalued ingredients enhances sustainability by maximizing food recovery and minimizing economic losses in the supply chain.
Byproduct Edibles
Byproduct edibles transform food waste into valuable ingredients, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability within the food industry. Utilizing vegetable peels, fruit pulp, and spent grains enhances nutrition while minimizing landfill contributions and resource waste.
Recovered Meal Solutions
Recovered meal solutions transform food waste into nutritious dishes by repurposing surplus ingredients from production and retail. These upcycled foods reduce landfill impact and conserve resources while providing sustainable, high-quality meal options for consumers.
Food Waste to Value
Transforming food waste into upcycled food products reduces environmental impact by diverting surplus ingredients from landfills and creating valuable, nutritious options. This sustainable practice enhances resource efficiency, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and supports a circular food economy by converting discarded food into high-quality, marketable goods.
Food Waste vs Upcycled Food Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com