Vegan pet food eliminates all animal products, promoting ethical and environmental benefits by reducing the reliance on animal agriculture. Climatarian pet diets prioritize low-carbon ingredients, balancing animal and plant sources to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and support sustainable farming. Choosing between vegan and climatarian options depends on pet nutritional needs and environmental impact preferences.
Table of Comparison
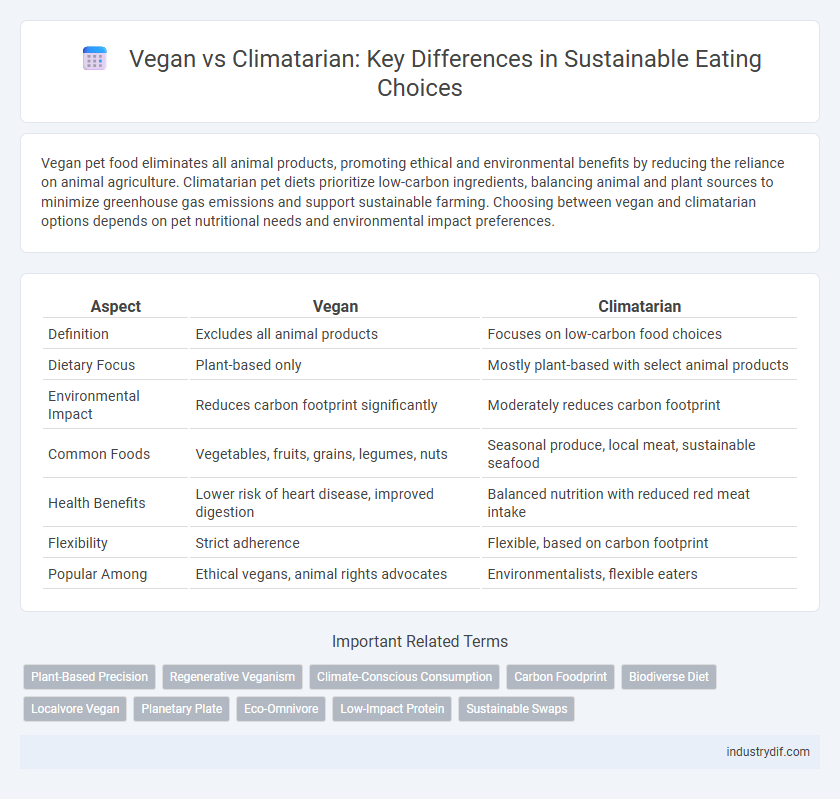
| Aspect | Vegan | Climatarian |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excludes all animal products | Focuses on low-carbon food choices |
| Dietary Focus | Plant-based only | Mostly plant-based with select animal products |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint significantly | Moderately reduces carbon footprint |
| Common Foods | Vegetables, fruits, grains, legumes, nuts | Seasonal produce, local meat, sustainable seafood |
| Health Benefits | Lower risk of heart disease, improved digestion | Balanced nutrition with reduced red meat intake |
| Flexibility | Strict adherence | Flexible, based on carbon footprint |
| Popular Among | Ethical vegans, animal rights advocates | Environmentalists, flexible eaters |
Defining Vegan and Climatarian Diets
A vegan diet excludes all animal products, emphasizing plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, nuts, and seeds to promote animal welfare and environmental sustainability. A climatarian diet focuses on reducing carbon footprints by selecting foods with low greenhouse gas emissions, often prioritizing seasonal, local, and minimally processed plant-based options but may include sustainable animal products. Both diets aim to mitigate climate change impacts through conscious food choices but differ in strictness regarding animal product consumption.
Core Principles of Veganism
Veganism centers on abstaining from all animal products to promote animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and personal health. Core principles include avoiding meat, dairy, eggs, and honey, while emphasizing plant-based foods rich in nutrients and fiber. This dietary choice significantly reduces carbon footprints, conserves water, and minimizes land use compared to animal-based diets.
Core Principles of Climatarianism
Climatarianism centers on reducing one's carbon footprint through mindful food choices, emphasizing seasonal, local, and plant-based ingredients to minimize environmental impact. Unlike strict veganism, climatarian diets allow for moderate consumption of sustainably sourced animal products and advocate for waste reduction and energy-efficient cooking methods. This approach promotes a balanced diet aligned with climate-conscious practices without completely eliminating animal-derived foods.
Key Differences Between Vegan and Climatarian
Vegans eliminate all animal products from their diet to promote animal welfare and health, while climatarians focus on reducing their carbon footprint by choosing foods with lower environmental impact, which may include some animal products. The vegan diet strictly adheres to plant-based consumption, avoiding dairy, eggs, and meat, whereas climatarians emphasize seasonal, local, and sustainably sourced foods to minimize greenhouse gas emissions. Key differences lie in ethical commitment and environmental strategy, with vegans driven by animal ethics and climatarians by climate impact reduction.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Vegan diets eliminate all animal products, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to omnivorous diets. Climatarian eating focuses on choosing foods with a low carbon footprint, such as seasonal, local, and minimally processed items, which can include some sustainably sourced animal products. Studies indicate that while veganism generally yields the lowest environmental impact, adopting climatarian principles offers a flexible, scalable approach to decrease food-related emissions and resource use.
Nutritional Considerations for Each Diet
Vegan diets emphasize plant-based foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants but require careful attention to nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids to prevent deficiencies. Climatarian diets focus on reducing food-related carbon footprints by prioritizing seasonal, local, and sustainably sourced foods, which can include moderate animal products that provide complete proteins and essential nutrients. Both dietary approaches benefit from balanced meal planning to ensure adequate intake of protein, micronutrients, and healthy fats tailored to individual health requirements.
Industry Trends: Vegan and Climatarian Products
Vegan products continue to dominate the plant-based food market, driven by rising consumer demand for animal-free alternatives and sustainability. Climatarian products emphasize low carbon footprints and regenerative sourcing, gaining traction through transparent labeling and eco-conscious certifications. Both trends influence food industry innovation, with manufacturers expanding offerings in plant-based proteins, fermented foods, and climate-friendly packaging.
Supply Chain Challenges for Both Diets
Vegan and climatarian diets face distinct supply chain challenges rooted in sourcing sustainability and ingredient availability. Vegan supply chains require consistent access to diverse plant-based proteins and alternative ingredients, which can be limited by regional agricultural practices and seasonal variability. Climatarian diets demand integration of low-carbon food sourcing and transparent carbon footprint tracking, complicating logistics and increasing reliance on innovative supply chain technologies.
Consumer Adoption and Market Demand
Consumer adoption of vegan diets has surged due to growing awareness of animal welfare and health benefits, driving a robust market demand for plant-based products globally. Climatarian eating, emphasizing low-carbon food choices, is gaining traction among environmentally conscious consumers, influencing food industry trends towards sustainable sourcing. Market data reveals that while vegan products dominate in volume, climatarian preferences are expanding rapidly, signaling a shift in consumer behavior towards integrated environmental and ethical food considerations.
Future Outlook: Veganism vs Climatarianism in the Food Industry
The future of the food industry is increasingly shaped by veganism and climatarianism, with veganism driving innovation in plant-based proteins and meat alternatives that reduce animal agriculture's environmental impact. Climatarianism emphasizes a broader dietary approach, prioritizing seasonal, locally sourced, and low-carbon footprint foods, which appeals to consumers seeking sustainable but less restrictive options. Market projections predict rapid growth in both sectors, with climatarianism gaining traction among flexitarians and veganism expanding due to rising ethical and health consciousness worldwide.
Related Important Terms
Plant-Based Precision
Plant-based precision emphasizes tailored vegan and climatarian diets that maximize nutritional value while minimizing environmental impact, leveraging ingredient selection for optimized health and sustainability. These approaches prioritize whole, minimally processed plant foods, balancing carbon footprint reduction with diverse nutrient intake for climate-conscious eating.
Regenerative Veganism
Regenerative veganism combines a plant-based diet with agricultural practices that restore soil health, enhance biodiversity, and sequester carbon, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional veganism and climatarian eating. This approach prioritizes ecosystem resilience and climate change mitigation by avoiding animal products while actively supporting regenerative farming techniques.
Climate-Conscious Consumption
Vegan diets eliminate all animal products, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and resource use, while climatarian diets emphasize locally sourced, seasonal, and low-impact foods, balancing environmental concerns with dietary flexibility. Both approaches prioritize climate-conscious consumption by minimizing carbon footprints through sustainable food choices and reducing reliance on industrial agriculture.
Carbon Foodprint
Vegan diets significantly reduce carbon foodprints by eliminating animal agriculture, which contributes to nearly 60% of global greenhouse gas emissions from food production. Climatarian diets prioritize locally sourced, seasonal foods to minimize transportation and waste, achieving a balanced approach to lowering carbon footprints while allowing limited animal products.
Biodiverse Diet
A biodiverse diet emphasizes consuming a variety of plant-based foods that support ecosystem health, aligning closely with vegan principles that exclude animal products for ethical and environmental reasons. Climatarian diets prioritize seasonal, locally sourced foods with minimal carbon footprints, often integrating small amounts of sustainably sourced animal products to balance biodiversity and climate impact.
Localvore Vegan
Localvore vegans prioritize consuming plant-based foods sourced from local farms and markets to minimize carbon emissions and support sustainable agriculture. This approach reduces food miles and promotes seasonal, nutrient-rich produce, distinguishing it from broader climatarian diets that emphasize climate impact across all food types.
Planetary Plate
The Planetary Plate framework emphasizes plant-based diets with moderate animal product consumption, aligning closely with climatarian principles that prioritize low-carbon food choices. Vegan diets eliminate animal products entirely, offering significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions but may require careful nutrient planning to maintain balance on the Planetary Plate.
Eco-Omnivore
Eco-Omnivores balance plant-based and sustainably sourced animal foods to minimize environmental impact, bridging the gap between strict vegans and flexitarian climatarian diets. Emphasizing local, seasonal, and low-impact products, this approach reduces carbon footprint while supporting biodiversity and ethical food systems.
Low-Impact Protein
Vegan diets prioritize plant-based proteins such as legumes, nuts, and grains, which typically have a lower carbon footprint compared to animal-based sources, making them a crucial choice for reducing environmental impact. Climatarian diets emphasize consuming locally sourced, seasonal foods, including low-impact proteins like sustainably farmed fish and poultry, balancing environmental concerns with dietary flexibility.
Sustainable Swaps
Choosing vegan options significantly reduces carbon footprints by eliminating animal agriculture emissions, while climatarian diets prioritize locally sourced, seasonal produce to minimize transportation-related pollution; sustainable swaps like plant-based milk or regenerative-farmed grains support both approaches by lowering greenhouse gases and conserving biodiversity. Incorporating legumes, nuts, and whole grains replaces resource-intensive meats, aligning with sustainable food practices that mitigate climate change and promote ecological balance.
Vegan vs Climatarian Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com