Dietitian services focus on personalized nutrition plans based on individual health needs, ensuring pets receive balanced diets tailored to their lifestyle and medical conditions. Nutrigenomics explores how a pet's genes influence their response to different nutrients, offering insights that can optimize diet for improved health outcomes. Combining these approaches can enhance pet wellness by integrating genetic information with expert dietary guidance.
Table of Comparison
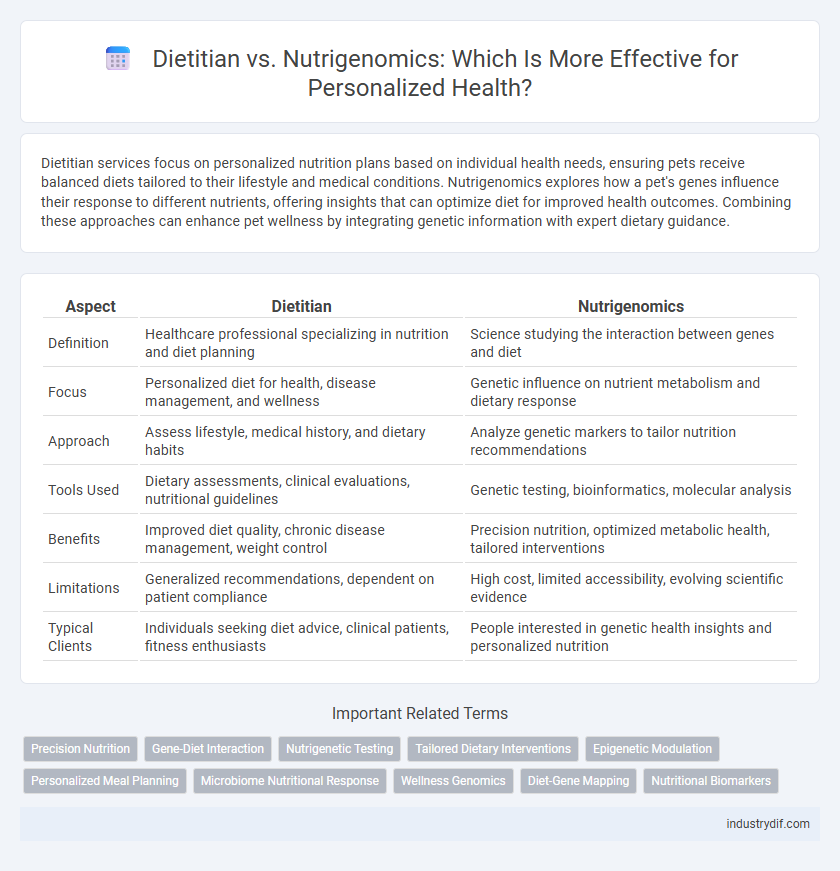
| Aspect | Dietitian | Nutrigenomics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Healthcare professional specializing in nutrition and diet planning | Science studying the interaction between genes and diet |
| Focus | Personalized diet for health, disease management, and wellness | Genetic influence on nutrient metabolism and dietary response |
| Approach | Assess lifestyle, medical history, and dietary habits | Analyze genetic markers to tailor nutrition recommendations |
| Tools Used | Dietary assessments, clinical evaluations, nutritional guidelines | Genetic testing, bioinformatics, molecular analysis |
| Benefits | Improved diet quality, chronic disease management, weight control | Precision nutrition, optimized metabolic health, tailored interventions |
| Limitations | Generalized recommendations, dependent on patient compliance | High cost, limited accessibility, evolving scientific evidence |
| Typical Clients | Individuals seeking diet advice, clinical patients, fitness enthusiasts | People interested in genetic health insights and personalized nutrition |
Introduction to Dietitian and Nutrigenomics
Dietitians are healthcare professionals specializing in human nutrition, assessing dietary needs, and creating personalized meal plans to promote overall health and manage medical conditions. Nutrigenomics studies the interaction between genes and nutrients, aiming to tailor diets based on individual genetic profiles to optimize health outcomes. Integrating dietitian expertise with nutrigenomics advances personalized nutrition strategies for disease prevention and wellness.
Defining the Role of a Dietitian
A dietitian specializes in creating personalized nutrition plans grounded in clinical evidence to improve overall health and manage medical conditions. Nutrigenomics studies how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and dietary responses, aiming to tailor diets at the molecular level. The dietitian's role involves applying scientific knowledge to develop practical dietary interventions, integrating emerging nutrigenomic insights to optimize patient outcomes.
What is Nutrigenomics?
Nutrigenomics is the scientific study of how individual genetic variations affect a person's response to nutrients and dietary components, enabling personalized nutrition strategies. It examines gene-diet interactions to optimize health outcomes and prevent diet-related diseases by tailoring food intake according to genetic profiles. This emerging field contrasts with traditional dietitian approaches by integrating genetic information for more precise dietary recommendations.
Education and Certification: Dietitian vs Nutrigenomics Expert
Dietitians typically hold a bachelor's or master's degree in dietetics, nutrition, or a related field, followed by supervised clinical training and passing a national registration exam to become a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN). Nutrigenomics experts often have advanced degrees in genetics, molecular biology, or nutrition science, with specialized training in interpreting genomic data and its impact on personalized nutrition. Certification for nutrigenomics professionals may include credentials from organizations such as the American Society of Human Genetics or specific nutrigenomics certification programs, emphasizing expertise in genetic testing and dietary interventions.
Personalized Nutrition: Key Differences
Personalized nutrition based on dietitian guidance emphasizes tailored meal plans through clinical assessment and lifestyle evaluation, while nutrigenomics integrates genetic data to customize dietary recommendations for optimal gene expression and health outcomes. Dietitians analyze traditional factors such as medical history and nutrient deficiencies, whereas nutrigenomics utilizes DNA testing to identify gene-nutrient interactions for precision nutrition. Combining both approaches enhances individualized dietary strategies, improving disease prevention and overall wellness.
Scope of Practice in Health Management
Dietitians specialize in personalized nutrition counseling, meal planning, and managing clinical diets to support health and treat disease. Nutrigenomics focuses on how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and response, enabling tailored dietary recommendations based on genetic profiles. Integrating dietitian expertise with nutrigenomic data enhances precision health management by aligning nutritional interventions with genetic predispositions.
Evidence Base and Scientific Support
Dietitians apply evidence-based nutritional science to create personalized diet plans grounded in clinical research and established dietary guidelines. Nutrigenomics explores gene-diet interactions, supported by emerging studies from genomics and molecular biology, but its long-term clinical applications require further validation. Robust scientific support favors dietitians' conventional methods, while nutrigenomics holds potential pending broader empirical evidence.
Potential Benefits and Limitations
Dietitians provide personalized nutrition advice based on clinical assessment and established dietary guidelines, ensuring practical and evidence-based meal planning for improved health outcomes. Nutrigenomics explores the interaction between genes and nutrients to tailor diets that may optimize metabolic functions and reduce disease risk, though its clinical applications are still emerging and sometimes costly. Combining dietitian expertise with nutrigenomic insights can enhance dietary precision, but limitations include genetic data interpretation challenges and variable individual responses.
Practical Applications in Healthcare
Dietitians apply evidence-based nutritional principles to develop personalized diet plans that improve patient outcomes and manage chronic diseases. Nutrigenomics explores how genetic variations influence individual responses to nutrients, enabling more precise dietary recommendations tailored to genetic profiles. Integrating nutrigenomics into dietitian practice enhances healthcare by optimizing nutrition interventions for disease prevention and management.
Choosing the Best Approach for Individual Health Needs
Dietitian services offer personalized nutrition plans based on comprehensive health assessments and dietary preferences, tailored to support overall wellness and manage chronic conditions. Nutrigenomics analyzes genetic variations to predict individual responses to nutrients, enabling highly customized dietary recommendations that optimize metabolic pathways and disease prevention. Selecting the best approach depends on integrating traditional dietary expertise with genomic insights to address unique genetic makeup and lifestyle factors effectively.
Related Important Terms
Precision Nutrition
Precision nutrition advances dietetics by integrating nutrigenomics, enabling personalized dietary plans based on genetic profiles to optimize health outcomes. Dietitians leverage this genetic information to tailor nutrient recommendations, enhancing the effectiveness of nutrition interventions and disease prevention.
Gene-Diet Interaction
Dietitian-guided nutrition focuses on personalized dietary plans based on lifestyle and health status, while nutrigenomics examines gene-diet interaction to tailor nutrition at the molecular level. Understanding gene variants that influence nutrient metabolism allows nutrigenomics to optimize diet recommendations beyond traditional dietitian assessments.
Nutrigenetic Testing
Nutrigenetic testing analyzes individual genetic variations to tailor dietary recommendations that optimize health outcomes and prevent chronic diseases. While dietitians provide personalized nutrition guidance based on lifestyle and medical history, nutrigenomics integrates genetic data to create precision nutrition plans for enhanced metabolic efficiency and disease risk reduction.
Tailored Dietary Interventions
Tailored dietary interventions leverage nutrigenomics to customize nutrition plans based on an individual's genetic profile, enhancing dietitian-guided recommendations for more effective health outcomes. Dietitians integrate nutrigenomic data with clinical expertise to design personalized diets that optimize nutrient absorption, metabolic responses, and disease prevention.
Epigenetic Modulation
Dietitians tailor nutrition plans based on current health status and lifestyle, while nutrigenomics explores how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and epigenetic modulation to optimize gene expression. Epigenetic modulation through diet targets DNA methylation and histone modification, potentially preventing chronic diseases by altering gene activity without changing the genetic code.
Personalized Meal Planning
Dietitians leverage clinical expertise to create personalized meal plans based on an individual's health status, dietary preferences, and nutritional needs, ensuring balanced nutrient intake for optimal wellness. Nutrigenomics enhances this approach by analyzing genetic data to tailor nutrition recommendations that specifically influence gene expression and metabolic responses, promoting precision in dietary interventions.
Microbiome Nutritional Response
Dietitians tailor personalized nutrition plans based on clinical assessments, while nutrigenomics explores how individual genetic variations influence the microbiome's response to dietary components. Understanding the interaction between diet, genes, and the gut microbiome enables targeted interventions that optimize metabolic health and reduce disease risk.
Wellness Genomics
Wellness genomics integrates nutrigenomics by analyzing individual genetic profiles to tailor personalized diet plans, enhancing the effectiveness of dietitians' nutritional guidance. This approach leverages genetic data to optimize metabolic health, prevent chronic diseases, and promote overall wellness through customized dietary interventions.
Diet-Gene Mapping
Dietitian-led interventions tailor nutrition plans based on individual health assessments, while nutrigenomics explores diet-gene mapping to optimize dietary recommendations by analyzing genetic variations influencing nutrient metabolism. Integrating dietitian expertise with nutrigenomic insights enhances personalized nutrition strategies for improved metabolic health and disease prevention.
Nutritional Biomarkers
Nutrigenomics leverages nutritional biomarkers to personalize dietary recommendations based on an individual's genetic profile, enhancing the precision of nutritional interventions beyond traditional dietitian assessments. Unlike conventional dietitian guidance, which often relies on generalized dietary guidelines, nutrigenomics utilizes molecular data from biomarkers to optimize nutrient intake for disease prevention and health promotion.
Dietitian vs Nutrigenomics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com