Health records are traditionally stored in centralized databases, making them vulnerable to data breaches and limited in accessibility across healthcare providers. Blockchain health data ensures secure, immutable, and decentralized storage, enabling real-time access while maintaining patient privacy. This technology enhances transparency and accuracy in medical histories, supporting improved health management and interoperability.
Table of Comparison
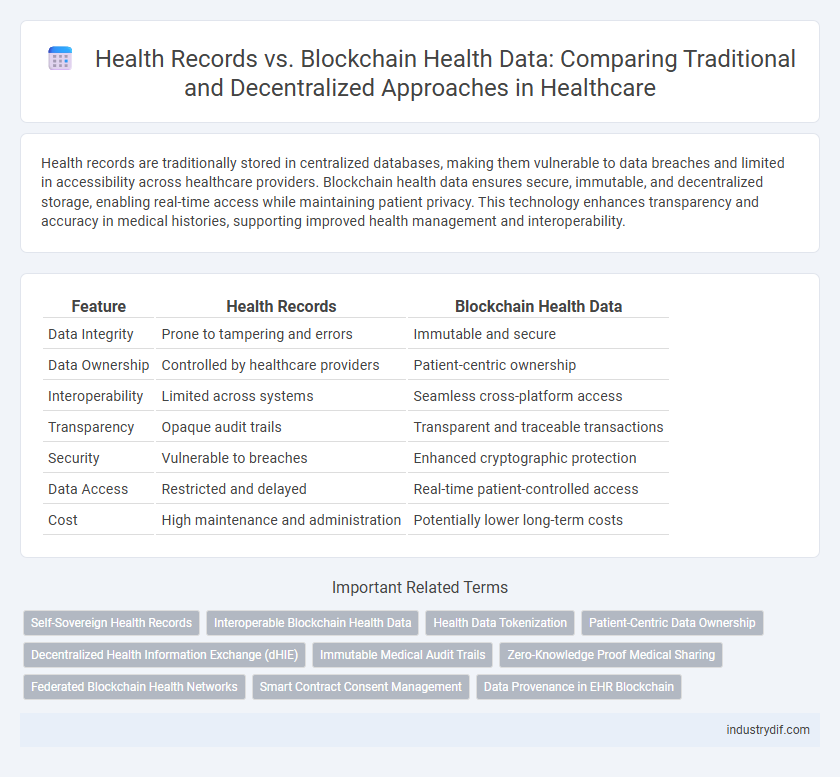
| Feature | Health Records | Blockchain Health Data |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integrity | Prone to tampering and errors | Immutable and secure |
| Data Ownership | Controlled by healthcare providers | Patient-centric ownership |
| Interoperability | Limited across systems | Seamless cross-platform access |
| Transparency | Opaque audit trails | Transparent and traceable transactions |
| Security | Vulnerable to breaches | Enhanced cryptographic protection |
| Data Access | Restricted and delayed | Real-time patient-controlled access |
| Cost | High maintenance and administration | Potentially lower long-term costs |
Understanding Traditional Health Records
Traditional health records are typically stored in centralized databases managed by healthcare providers, resulting in limited patient access and potential security vulnerabilities. These paper-based or digital files often suffer from fragmentation and inconsistency across different medical institutions, leading to difficulties in comprehensive patient care coordination. Understanding these limitations highlights the need for innovative solutions like blockchain technology to enhance data integrity, interoperability, and patient control over health information.
Introduction to Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure method for managing health records, enhancing data integrity and patient privacy compared to traditional centralized health data systems. By utilizing cryptographic encryption and distributed ledgers, blockchain ensures tamper-proof storage and real-time access control to medical information. This innovation addresses interoperability issues and streamlines data sharing among healthcare providers, ultimately improving accuracy and efficiency in patient care management.
Key Differences Between Health Records and Blockchain Data
Health records are typically centralized, stored in Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems managed by hospitals or clinics, allowing authorized healthcare providers to access patient information. Blockchain health data operates on a decentralized ledger, offering enhanced security, immutability, and patient control over data access through cryptographic methods. Key differences include data ownership, transparency, and resistance to tampering, with blockchain enabling real-time sharing across multiple stakeholders without a single point of failure.
Security and Privacy in Health Data Management
Traditional health records often face challenges with data breaches and unauthorized access due to centralized storage systems. Blockchain health data management enhances security by utilizing decentralized, immutable ledgers that encrypt patient information and provide transparent access controls. This technology ensures privacy through cryptographic protocols, reducing risks of tampering and enabling patients to maintain ownership of their health data.
Data Ownership: Patients vs Institutions
Traditional health records are typically controlled and stored by healthcare institutions, limiting patient access and ownership over their personal medical data. Blockchain health data systems decentralize storage, giving patients direct control and secure access to their health information through encrypted digital wallets. This shift enhances transparency, data integrity, and patient empowerment by enabling individuals to manage permissions and share records with trusted providers as needed.
Interoperability of Health Information Systems
Health records traditionally suffer from limited interoperability due to disparate electronic health record (EHR) systems that hinder seamless data exchange among providers. Blockchain technology enhances interoperability by creating a decentralized, secure ledger that standardizes data sharing protocols and enables real-time access to unified patient information across multiple health information systems. This improved interoperability supports coordinated care, reduces errors, and facilitates patient-centric health management with greater data integrity and transparency.
Blockchain’s Role in Reducing Healthcare Fraud
Blockchain technology enhances healthcare data security by providing an immutable ledger for health records, significantly reducing the risk of fraud. Traditional health records are vulnerable to tampering and unauthorized access, whereas blockchain's decentralized system ensures data integrity and traceability. This transparency and security framework helps prevent identity theft, billing fraud, and false insurance claims, leading to more trustworthy healthcare transactions.
Challenges in Implementing Blockchain Health Data
Implementing blockchain technology for health data faces significant challenges including interoperability issues between disparate electronic health record (EHR) systems and the high computational costs associated with maintaining decentralized ledgers. Ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA remains complex due to the immutable nature of blockchain, which conflicts with rights like data erasure. Scalability concerns and limited user adoption also hinder widespread integration of blockchain solutions in healthcare infrastructure.
Regulatory Compliance for Digital Health Records
Health records must adhere to stringent regulatory compliance frameworks such as HIPAA and GDPR to ensure patient privacy and data security. Blockchain health data solutions offer enhanced transparency and immutable audit trails, facilitating compliance by enabling real-time verification of data integrity and access controls. Integrating blockchain technology with existing digital health records improves regulatory adherence by providing decentralized data governance aligned with international standards.
Future Trends in Blockchain-Based Health Records
Future trends in blockchain-based health records emphasize enhanced data security, interoperability, and patient control over personal health information. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures immutable, tamper-proof records accessible across various healthcare providers, improving accuracy and reducing errors. Integration with AI and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is expected to boost predictive analytics and personalized treatment plans.
Related Important Terms
Self-Sovereign Health Records
Self-sovereign health records empower patients by granting full control over their medical data, ensuring privacy and interoperability without reliance on centralized databases. Blockchain health data enhances security and transparency through decentralized ledger technology, allowing seamless and tamper-proof access to personalized health information.
Interoperable Blockchain Health Data
Interoperable blockchain health data enhances traditional health records by enabling secure, transparent, and seamless sharing of patient information across different healthcare systems and providers. This decentralized approach improves data integrity, reduces errors, and facilitates real-time access to comprehensive health histories, promoting better patient outcomes and coordinated care.
Health Data Tokenization
Health data tokenization encrypts patient information into secure digital tokens, enhancing privacy and enabling controlled access compared to traditional health records. Blockchain health data systems leverage tokenization to ensure immutable, transparent, and decentralized management of sensitive medical information, reducing risks of data breaches and improving interoperability across healthcare providers.
Patient-Centric Data Ownership
Patient-centric data ownership in health records emphasizes individual control over personal medical information, enhancing privacy and consent management. Blockchain health data technology secures patient records through decentralized ledgers, enabling transparent, immutable access while empowering patients to directly manage and share their health information.
Decentralized Health Information Exchange (dHIE)
Decentralized Health Information Exchange (dHIE) leverages blockchain technology to create secure, tamper-proof health records accessible across multiple providers while maintaining patient control over data sharing. This contrasts with traditional centralized health records systems that often suffer from data silos, limited interoperability, and higher vulnerability to breaches.
Immutable Medical Audit Trails
Traditional health records often suffer from data tampering risks and lack transparent audit trails, compromising patient safety and compliance. Blockchain health data ensures immutable medical audit trails by securely recording all transactions in a decentralized ledger, enhancing data integrity, traceability, and trustworthiness in healthcare management.
Zero-Knowledge Proof Medical Sharing
Traditional health records often face issues with data breaches and unauthorized access, whereas blockchain health data using Zero-Knowledge Proofs enables secure, verifiable sharing of medical information without revealing sensitive patient details. This cryptographic technique ensures patient privacy while allowing healthcare providers to authenticate data accuracy and compliance with health data regulations.
Federated Blockchain Health Networks
Federated blockchain health networks enhance traditional health records by enabling decentralized, secure data sharing among authorized institutions while maintaining patient privacy and data integrity. This approach reduces data silos and interoperability issues, improving clinical collaboration and accelerating personalized medicine advancements.
Smart Contract Consent Management
Traditional health records face challenges of data fragmentation and unauthorized access, while blockchain health data leverages smart contract consent management to provide patients with secure, transparent, and automated control over their medical information. This approach enhances interoperability and ensures real-time consent enforcement, reducing data breaches and improving compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
Data Provenance in EHR Blockchain
Data provenance in EHR blockchain ensures the integrity and traceability of health records by creating an immutable, timestamped audit trail that verifies every modification and access event. This decentralized approach prevents data tampering and enhances patient trust by providing transparent and secure tracking of the origin and history of electronic health information.
Health records vs Blockchain health data Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com