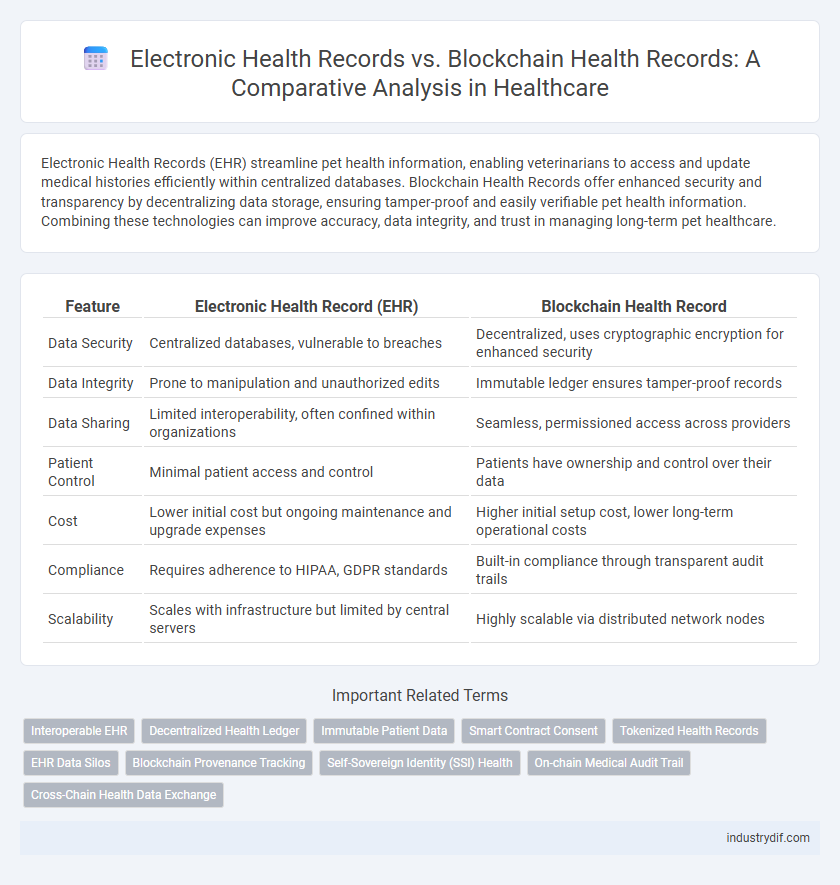
Electronic Health Records (EHR) streamline pet health information, enabling veterinarians to access and update medical histories efficiently within centralized databases. Blockchain Health Records offer enhanced security and transparency by decentralizing data storage, ensuring tamper-proof and easily verifiable pet health information. Combining these technologies can improve accuracy, data integrity, and trust in managing long-term pet healthcare.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electronic Health Record (EHR) | Blockchain Health Record |
|---|---|---|
| Data Security | Centralized databases, vulnerable to breaches | Decentralized, uses cryptographic encryption for enhanced security |
| Data Integrity | Prone to manipulation and unauthorized edits | Immutable ledger ensures tamper-proof records |
| Data Sharing | Limited interoperability, often confined within organizations | Seamless, permissioned access across providers |
| Patient Control | Minimal patient access and control | Patients have ownership and control over their data |
| Cost | Lower initial cost but ongoing maintenance and upgrade expenses | Higher initial setup cost, lower long-term operational costs |
| Compliance | Requires adherence to HIPAA, GDPR standards | Built-in compliance through transparent audit trails |
| Scalability | Scales with infrastructure but limited by central servers | Highly scalable via distributed network nodes |
Introduction to Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Electronic Health Records (EHR) are digital versions of patients' paper charts, designed to streamline data storage, retrieval, and sharing across healthcare providers. EHR systems facilitate real-time access to patient medical histories, lab results, and treatment plans, improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. These records adhere to standardized formats and regulations like HIPAA to ensure data security and interoperability within the healthcare ecosystem.
Understanding Blockchain Health Records (BHR)
Blockchain Health Records (BHR) utilize decentralized ledger technology to enhance data security, interoperability, and patient control over medical information compared to traditional Electronic Health Records (EHR). BHR systems enable immutable and transparent access logs, reducing the risk of data tampering and unauthorized access. This emerging approach facilitates more efficient data sharing among healthcare providers while maintaining privacy and compliance with health regulations.
Key Differences Between EHR and BHR
Electronic Health Records (EHR) store patient data in centralized digital databases managed by healthcare providers, enabling easy access and updating of medical history, but raising concerns about data security and interoperability. Blockchain Health Records (BHR) use decentralized ledger technology to provide enhanced data security, patient control over records, and immutable audit trails, reducing risks of tampering and unauthorized access. Key differences include data ownership, with BHR promoting patient empowerment, and consensus mechanisms ensuring trust without relying on a central authority, contrasting with traditional EHR systems.
Data Security: EHR vs Blockchain Health Records
Electronic Health Records (EHR) rely on centralized databases vulnerable to hacking and unauthorized access, often requiring complex protocols for data protection. Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized ledger technology, enhancing data security through immutable, cryptographically secured entries that ensure transparency and tamper-resistance. Patient data on blockchain systems benefits from improved privacy controls and encrypted transactions, reducing risks associated with data breaches compared to traditional EHRs.
Interoperability and Data Sharing in EHR and BHR
Electronic Health Records (EHR) streamline interoperability by enabling standardized data exchange across healthcare providers through established protocols like HL7 and FHIR. Blockchain Health Records (BHR) enhance data sharing by providing a decentralized, secure ledger that grants patients control over access permissions, promoting transparency and reducing data silos. BHR's distributed architecture addresses interoperability challenges by ensuring immutability and real-time synchronization of patient data across multiple stakeholders.
Patient Privacy and Consent Management
Electronic Health Records (EHR) store patient data in centralized databases, which can be vulnerable to breaches and unauthorized access, compromising patient privacy. Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized, encrypted ledgers that enhance security and give patients granular control over who can access their information through smart contracts for consent management. This decentralized approach reduces the risk of data tampering and ensures transparent, immutable audit trails, significantly improving patient privacy and consent enforcement compared to traditional EHR systems.
Cost Implications: Traditional EHR Systems vs Blockchain
Traditional Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems incur high costs due to centralized data storage, ongoing maintenance, and frequent security updates. Blockchain health records reduce expenses by enabling decentralized data management, minimizing the need for intermediaries, and enhancing data integrity through distributed ledger technology. Cost savings also arise from improved interoperability and reduced administrative overhead in blockchain-based health record solutions.
Scalability and Integration Challenges
Electronic Health Records (EHR) face scalability issues due to centralized database limitations and integration challenges with diverse healthcare systems and legacy software. Blockchain Health Records offer enhanced scalability through decentralized data storage and improved interoperability with standardized protocols, but require substantial computational resources and consensus mechanisms that may hinder real-time data access. Both systems demand advanced integration frameworks to ensure seamless data exchange and maintain compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
Regulatory Compliance in EHR and Blockchain-Based Records
Electronic Health Records (EHR) comply with established healthcare regulations such as HIPAA, ensuring standardized data security and patient privacy through centralized control. Blockchain-based health records enhance regulatory compliance by providing immutable audit trails and decentralized data management, which reduces fraud and unauthorized access risks. Both systems must navigate evolving legal frameworks, but blockchain offers improved transparency and secure patient consent tracking.
Future Trends in Digital Health Records
Electronic Health Records (EHR) are evolving with increasing integration of blockchain technology, enhancing data security, interoperability, and patient consent management. Blockchain Health Records offer decentralized, immutable ledgers that reduce the risk of data breaches and improve trust among healthcare providers and patients. Future trends indicate widespread adoption of hybrid systems combining EHR convenience with blockchain's transparency to drive personalized and efficient healthcare delivery.
Related Important Terms
Interoperable EHR
Interoperable Electronic Health Records (EHR) enable seamless data exchange across healthcare systems, enhancing patient care through integrated medical histories and real-time updates. Blockchain Health Records introduce a decentralized framework that improves data security, patient control, and immutable audit trails, addressing interoperability challenges by ensuring transparent, tamper-proof access to health information.
Decentralized Health Ledger
Electronic Health Records (EHR) typically rely on centralized databases vulnerable to single points of failure, whereas Blockchain Health Records utilize a decentralized health ledger that enhances data security, patient control, and interoperability across multiple healthcare providers. This decentralized architecture ensures immutable, transparent access to patient information, reducing fraud and improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical data exchange.
Immutable Patient Data
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) provide centralized storage but remain vulnerable to unauthorized alterations, compromising data integrity. Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized ledgers with cryptographic security, ensuring immutable patient data that enhances trust and traceability in healthcare systems.
Smart Contract Consent
Smart Contract Consent in Blockchain Health Records enables automated, transparent patient authorization for data access, enhancing security and compliance compared to traditional Electronic Health Records (EHRs) reliant on manual consent processes. This technology ensures real-time tracking and immutable audit trails, reducing administrative burden and improving patient control over sensitive health information.
Tokenized Health Records
Tokenized Health Records on blockchain enhance Electronic Health Records (EHR) by providing secure, immutable data exchange through cryptographic tokens that represent patient information, improving interoperability and patient control. Unlike traditional EHRs, blockchain-based health records enable real-time data verification and decentralized access, reducing fraud and enhancing privacy compliance.
EHR Data Silos
Electronic Health Records (EHR) often face data silo challenges, limiting interoperability and secure patient data sharing across providers. Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized ledgers to break down these silos, enhancing data transparency, security, and seamless access for authorized users.
Blockchain Provenance Tracking
Blockchain health records provide enhanced provenance tracking through immutable audit trails that verify data origin and modifications in real-time, ensuring higher transparency and security compared to traditional electronic health records (EHRs). This decentralized approach reduces fraud risks and enables seamless interoperability across healthcare providers while maintaining patient data integrity and privacy.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) Health
Electronic Health Records (EHR) centralize patient data within healthcare providers' systems, often limiting patient control and data interoperability. Blockchain Health Records leveraging Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) empower patients with decentralized ownership, enhancing privacy, security, and seamless data sharing across multiple health institutions.
On-chain Medical Audit Trail
Electronic Health Records (EHR) store patient data centralized, which can lead to vulnerabilities in data integrity and lack of transparent audit trails, whereas Blockchain Health Records provide a decentralized on-chain medical audit trail that ensures immutable, tamper-proof logs of access and modifications, enhancing security and compliance. The blockchain's cryptographic consensus mechanism enables real-time verification and traceability of all medical transactions, improving trust among healthcare providers and patients.
Cross-Chain Health Data Exchange
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) centralize patient data within individual healthcare systems, limiting interoperability and real-time data sharing, whereas Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized ledgers to enable secure, transparent, and tamper-proof cross-chain health data exchange. This blockchain-based approach enhances data integrity, patient control, and seamless interoperability across diverse healthcare platforms and organizations.
Electronic Health Record vs Blockchain Health Record Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com