Hospitals offer comprehensive care with a wide range of specialists and advanced diagnostics, ideal for complex pet health issues. Microhospitals provide focused, immediate care for pets with less severe conditions, ensuring quicker treatment and personalized attention. Selecting between a hospital and microhospital depends on the urgency and complexity of your pet's medical needs.
Table of Comparison
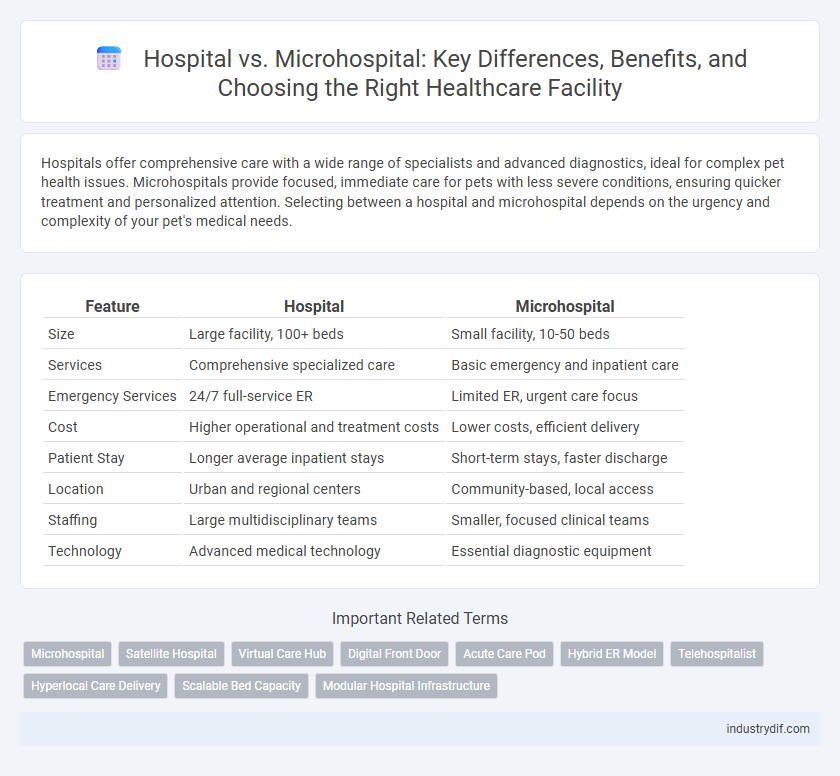
| Feature | Hospital | Microhospital |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large facility, 100+ beds | Small facility, 10-50 beds |
| Services | Comprehensive specialized care | Basic emergency and inpatient care |
| Emergency Services | 24/7 full-service ER | Limited ER, urgent care focus |
| Cost | Higher operational and treatment costs | Lower costs, efficient delivery |
| Patient Stay | Longer average inpatient stays | Short-term stays, faster discharge |
| Location | Urban and regional centers | Community-based, local access |
| Staffing | Large multidisciplinary teams | Smaller, focused clinical teams |
| Technology | Advanced medical technology | Essential diagnostic equipment |
Defining Hospitals and Microhospitals
Hospitals are large healthcare facilities providing a wide range of medical services, including emergency care, surgeries, specialized treatments, and inpatient stays. Microhospitals are smaller, community-focused facilities designed to offer essential acute care services such as emergency treatment, diagnostic testing, and limited inpatient care within a compact setting. Both serve critical healthcare roles, but microhospitals emphasize accessibility and efficiency for localized patient populations.
Key Differences Between Hospitals and Microhospitals
Hospitals typically offer extensive medical services, including specialized departments and emergency care, while microhospitals focus on providing essential inpatient and outpatient services within a smaller facility, often serving local communities. Microhospitals usually have 10 to 50 beds, enabling quicker patient turnover and personalized care, whereas traditional hospitals can exceed hundreds of beds and accommodate complex surgeries and intensive care units. Cost efficiency and accessibility differentiate microhospitals from larger hospitals, making them suitable for areas with limited healthcare infrastructure.
Services Offered: Hospitals vs Microhospitals
Hospitals provide a comprehensive range of services, including emergency care, specialized surgeries, intensive care units, and advanced diagnostic imaging. Microhospitals focus on delivering essential outpatient services, minor surgical procedures, basic emergency care, and primary care services within a smaller, community-based setting. The difference in service scope makes hospitals suitable for complex medical conditions, while microhospitals emphasize accessibility and quick, efficient care for less severe health issues.
Patient Care and Experience
Microhospitals offer a more personalized patient care experience with shorter wait times and easier access to specialized services compared to traditional hospitals. These facilities typically feature advanced technology and a streamlined staff structure, enhancing both the efficiency and quality of care. Patients benefit from a community-centered approach in microhospitals, fostering improved satisfaction and quicker recovery outcomes.
Cost Comparison: Hospitals and Microhospitals
Microhospitals typically incur lower operational costs compared to traditional hospitals due to their smaller size and specialized services, leading to reduced overhead expenses. Hospitals often face higher fixed and variable costs, including extensive staffing, complex infrastructure, and advanced medical equipment maintenance. Patients may encounter more affordable treatment options and shorter wait times at microhospitals, making them a cost-effective alternative for non-emergency and outpatient care.
Staffing Models in Hospitals vs Microhospitals
Hospitals typically employ a traditional staffing model featuring specialized physicians, registered nurses, and a wide range of allied health professionals to support extensive inpatient and outpatient services. Microhospitals use a streamlined staffing approach with a smaller team of cross-trained professionals, including advanced practice providers and critical care nurses, enabling efficient delivery of urgent and routine care within a 24-hour facility. This lean model reduces overhead while maintaining high-quality patient outcomes in a community-focused setting.
Location and Accessibility
Hospitals are typically located in urban centers or large towns, offering comprehensive medical services but can be less accessible for patients in rural or suburban areas. Microhospitals, smaller facilities usually situated in neighborhood or suburban locations, provide convenient access to emergency care and essential services without the need to travel long distances. Their strategic placement enhances healthcare accessibility by reducing travel time and easing patient load on larger hospitals.
Regulatory and Accreditation Standards
Hospitals and microhospitals adhere to stringent regulatory and accreditation standards established by bodies such as The Joint Commission and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to ensure patient safety and quality care. Hospitals typically undergo comprehensive evaluation across various departments due to their larger scale, while microhospitals, despite their smaller size, must meet equivalent standards in emergency care, inpatient services, and outpatient procedures. Both facility types implement protocols aligned with state and federal regulations, including licensure requirements, patient rights, and infection control standards, to maintain accreditation and operational legitimacy.
Ideal Use Cases for Hospitals vs Microhospitals
Hospitals are ideal for complex medical cases requiring specialized care, extensive surgical facilities, and comprehensive inpatient services, supporting critical and multi-disciplinary treatments. Microhospitals suit community-based care with urgent but low-acuity conditions, offering convenient access to emergency services, basic diagnostics, and short-term observation without the scale of full hospitals. Choosing between the two depends on patient needs, with hospitals focusing on high-acuity, long-term care and microhospitals optimizing rapid, local treatment for common emergencies and minor procedures.
Future Trends in Hospital and Microhospital Development
Future trends in hospital and microhospital development emphasize the integration of advanced telemedicine technologies and AI-driven diagnostics to enhance patient outcomes and operational efficiency. Microhospitals are expected to expand their role in providing localized, cost-effective care with rapid access to emergency services and outpatient procedures. Large hospitals continue investing in personalized medicine and smart infrastructure to accommodate complex treatments and growing healthcare demands.
Related Important Terms
Microhospital
Microhospitals offer a compact, patient-centered alternative to traditional hospitals by providing essential inpatient services, emergency care, and specialized treatments within a smaller footprint, enabling quicker access and personalized care in community settings. These facilities enhance healthcare efficiency by reducing congestion in larger hospitals while maintaining high-quality standards and advanced medical technology.
Satellite Hospital
Satellite hospitals, a subset of microhospitals, provide localized healthcare services with a full range of emergency and outpatient care similar to traditional hospitals but on a smaller scale, optimizing accessibility and reducing patient travel time. Unlike large hospitals, satellite hospitals emphasize rapid, community-based treatment, integrating advanced medical technology and specialized staff to deliver efficient, cost-effective care within suburban or rural settings.
Virtual Care Hub
A Virtual Care Hub in a microhospital integrates telemedicine technology to deliver specialized health services efficiently within a compact setting, offering faster patient access and personalized care compared to traditional hospitals. This model enhances remote monitoring, improves patient outcomes, and reduces the strain on larger hospital facilities by managing chronic conditions and emergency cases via virtual consultations.
Digital Front Door
Hospitals leverage comprehensive digital front door platforms to streamline patient intake, virtual consultations, and real-time health data integration, enhancing access and care coordination. Microhospitals prioritize agile digital front doors with simplified telehealth interfaces and rapid scheduling features, optimizing convenience and tailored local care delivery.
Acute Care Pod
Acute Care Pods in microhospitals provide targeted, high-quality treatment for urgent medical conditions, enabling faster patient recovery through specialized, streamlined care units. Hospitals typically offer broader services but may lack the microhospital's efficiency in rapid acute care delivery within compact, technology-driven environments.
Hybrid ER Model
The hybrid ER model integrates advanced imaging technologies and treatment capabilities within a microhospital setting, enabling rapid diagnosis and immediate intervention for critical patients. This approach enhances patient outcomes by combining the comprehensive services of a traditional hospital with the efficiency and accessibility of a microhospital.
Telehospitalist
Telehospitalists enhance patient care in both hospitals and microhospitals by providing remote, real-time clinical expertise, improving response times and outcomes. Microhospitals utilize telehospitalists to extend specialty services and reduce onsite staffing needs, optimizing resource allocation while maintaining high-quality care.
Hyperlocal Care Delivery
Microhospitals offer hyperlocal care delivery by providing essential medical services within a smaller, community-focused setting, reducing patient travel time and enhancing access to urgent care. Unlike traditional hospitals, microhospitals emphasize personalized treatment and rapid response for common emergencies, improving overall patient outcomes in their immediate neighborhoods.
Scalable Bed Capacity
Microhospitals offer scalable bed capacity by providing flexible, smaller-scale inpatient units that can be expanded or modified based on community demand, contrasting with traditional hospitals where bed capacity is often fixed and requires significant capital investment to increase. This adaptability in microhospitals supports efficient resource allocation and rapid response to patient volume fluctuations, enhancing overall healthcare delivery.
Modular Hospital Infrastructure
Microhospitals leverage modular hospital infrastructure to enable rapid deployment, cost-efficiency, and scalable patient care compared to traditional hospitals. Modular designs streamline construction timelines by up to 50%, optimizing space utilization while maintaining compliance with healthcare regulations and quality standards.
Hospital vs Microhospital Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com