Medical devices are essential in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating pet health conditions with precise functionality and clinical accuracy. Wearable biosensors offer continuous real-time monitoring of pets' vital signs and activity levels, enabling early detection of potential health issues. Combining traditional medical devices with wearable biosensors enhances comprehensive health management for pets, improving outcomes through timely interventions.
Table of Comparison
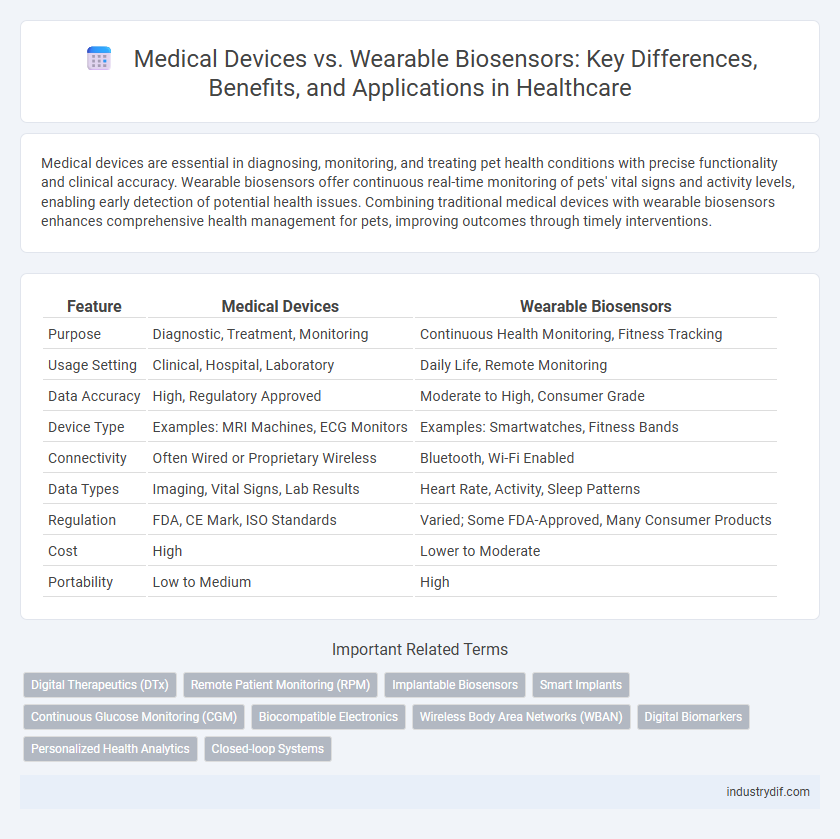
| Feature | Medical Devices | Wearable Biosensors |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Diagnostic, Treatment, Monitoring | Continuous Health Monitoring, Fitness Tracking |
| Usage Setting | Clinical, Hospital, Laboratory | Daily Life, Remote Monitoring |
| Data Accuracy | High, Regulatory Approved | Moderate to High, Consumer Grade |
| Device Type | Examples: MRI Machines, ECG Monitors | Examples: Smartwatches, Fitness Bands |
| Connectivity | Often Wired or Proprietary Wireless | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Enabled |
| Data Types | Imaging, Vital Signs, Lab Results | Heart Rate, Activity, Sleep Patterns |
| Regulation | FDA, CE Mark, ISO Standards | Varied; Some FDA-Approved, Many Consumer Products |
| Cost | High | Lower to Moderate |
| Portability | Low to Medium | High |
Overview of Medical Devices and Wearable Biosensors
Medical devices encompass a broad range of instruments, apparatuses, and machines used for diagnosing, monitoring, and treating medical conditions, including imaging systems, surgical equipment, and implantable devices. Wearable biosensors represent a specialized category within medical devices designed for continuous, real-time monitoring of physiological parameters such as heart rate, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation through form factors like smartwatches and fitness bands. The integration of advanced sensors and wireless technology in wearable biosensors facilitates non-invasive health data collection, enabling personalized healthcare management and early detection of health anomalies.
Key Differences Between Medical Devices and Wearable Biosensors
Medical devices typically refer to clinically approved instruments designed for diagnosis, treatment, or monitoring of medical conditions in controlled healthcare settings, while wearable biosensors are portable, non-invasive devices that continuously track physiological data such as heart rate, glucose levels, or activity in real-time. Medical devices often require regulatory clearance from bodies like the FDA, whereas wearable biosensors focus on user convenience, preventive care, and daily health management without constant clinical oversight. The primary difference lies in the application scope, accuracy requirements, and integration within professional medical workflows versus consumer-driven health tracking.
Technological Advancements Driving Each Sector
Medical devices leverage advanced imaging technologies and AI-driven diagnostics to enhance precision in clinical settings, enabling early disease detection and personalized treatment plans. Wearable biosensors utilize miniaturized sensors, flexible electronics, and continuous real-time data monitoring to track physiological parameters such as heart rate, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation outside traditional healthcare environments. Innovations in semiconductor materials, wireless connectivity, and cloud computing further drive the evolution of both sectors, facilitating seamless integration of health data and improving patient outcomes.
Regulatory Standards for Medical Devices vs Wearables
Medical devices are subject to stringent regulatory standards set by authorities such as the FDA and EMA, requiring extensive clinical trials and certification processes to ensure safety and efficacy. Wearable biosensors, while increasingly integrated into health monitoring, often face less rigorous and evolving regulations, focusing on data accuracy, user safety, and interoperability with healthcare systems. Regulatory frameworks for wearables prioritize real-time data transmission and user privacy, reflecting their consumer-centric design compared to traditional medical devices.
Integration with Digital Health Ecosystems
Medical devices and wearable biosensors both contribute significantly to digital health ecosystems by enabling continuous health monitoring and data collection; however, wearable biosensors offer enhanced real-time integration through wireless connectivity and seamless synchronization with mobile applications and cloud platforms. Medical devices, often designed for clinical settings, provide high-precision diagnostics but may face limitations in interoperability and ease of data sharing compared to wearable biosensors. The integration of wearable biosensors into digital health ecosystems supports personalized healthcare, remote patient monitoring, and proactive disease management by leveraging advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence for data analysis.
Data Accuracy and Reliability in Health Monitoring
Medical devices typically offer higher data accuracy and reliability in health monitoring due to rigorous calibration and clinical validation processes. Wearable biosensors provide continuous, real-time data but may experience signal noise and variability influenced by user activity and environmental factors. Integrating advanced algorithms with wearable technology can enhance data precision, narrowing the gap between traditional medical devices and biosensors in clinical applications.
Clinical Applications: Diagnostic vs Preventive Use
Medical devices primarily facilitate diagnostic applications by enabling precise detection and monitoring of diseases through tools such as imaging equipment and laboratory analyzers. Wearable biosensors focus on preventive use, continuously tracking physiological parameters like heart rate, glucose levels, and activity patterns to alert users and clinicians of early health deviations. Integration of both technologies allows for comprehensive healthcare management, combining accurate diagnostics with proactive prevention strategies.
Patient Engagement and User Experience
Medical devices and wearable biosensors both enhance patient engagement by providing real-time health monitoring, but wearable biosensors offer superior user experience through continuous, non-invasive tracking and seamless data integration with mobile apps. These biosensors empower patients with personalized feedback and proactive health management, increasing adherence to treatment plans and promoting active participation. In contrast, traditional medical devices often require clinical settings and deliver intermittent data, limiting real-time interaction and immediate user response.
Market Trends and Growth Opportunities
The global medical devices market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4%, driven by advancements in diagnostic imaging and minimally invasive surgical equipment, while wearable biosensors are experiencing a faster expansion rate with an estimated CAGR of 18.3% due to rising demand for continuous health monitoring and telemedicine applications. Technological innovations in sensor miniaturization and AI-powered data analytics enhance wearable biosensor accuracy and user engagement, creating significant growth opportunities in chronic disease management and personalized healthcare. Integration of wearable biosensors with IoT platforms is unlocking new market segments, particularly in remote patient monitoring and fitness tracking, contrasting with traditional medical devices that dominate hospital and clinical settings.
Future Outlook for Medical Devices and Wearable Biosensors
Medical devices and wearable biosensors are poised for significant growth driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, miniaturization, and IoT integration, enhancing real-time health monitoring and personalized treatment. The expansion of remote patient monitoring technologies and continuous data analytics is expected to transform chronic disease management and early diagnosis frameworks. Regulatory frameworks and data security standards will evolve to support widespread adoption while ensuring patient safety and privacy.
Related Important Terms
Digital Therapeutics (DTx)
Digital Therapeutics (DTx) leverage wearable biosensors to provide continuous, real-time health data that enhances personalized treatment plans beyond traditional medical devices, enabling targeted behavioral interventions and chronic disease management. These biosensors integrate with sophisticated software algorithms in DTx to deliver adaptive therapies, improve patient adherence, and optimize clinical outcomes through data-driven insights.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Medical devices in Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) offer precise clinical-grade measurements essential for diagnosing and managing chronic conditions, while wearable biosensors provide continuous, real-time data tracking for early detection and personalized health insights. Integration of wearable biosensors with RPM systems enhances patient engagement and enables proactive intervention, improving clinical outcomes and reducing hospital readmissions.
Implantable Biosensors
Implantable biosensors offer continuous, real-time monitoring of physiological parameters directly within the body, providing higher accuracy and early detection of anomalies compared to external medical devices. These advanced sensors enable personalized healthcare by transmitting critical data on biomarkers, glucose levels, or cardiac rhythms to medical professionals, enhancing diagnostic precision and treatment efficacy.
Smart Implants
Smart implants represent an advanced category of medical devices designed for continuous internal monitoring and therapeutic intervention, surpassing traditional wearable biosensors that primarily track external physiological parameters. These implants integrate biosensing capabilities with biocompatible materials and wireless communication, enabling precise real-time health data collection and personalized treatment within the body.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems integrate wearable biosensors that provide real-time glucose level tracking, contrasting with traditional medical devices that often require intermittent blood samples. Wearable CGM biosensors enhance diabetes management by delivering continuous, non-invasive data, enabling timely adjustments in treatment and improving glycemic control.
Biocompatible Electronics
Medical devices traditionally rely on biocompatible electronics to ensure safe integration with human tissues, minimizing immune response and enhancing patient outcomes. Wearable biosensors advance this concept by incorporating flexible, skin-conformal biocompatible materials that enable continuous, real-time health monitoring without compromising comfort or safety.
Wireless Body Area Networks (WBAN)
Medical devices integrated with Wireless Body Area Networks (WBAN) enable continuous health monitoring by collecting and transmitting physiological data through wearable biosensors, enhancing real-time diagnostic accuracy. Wearable biosensors in WBANs offer wireless connectivity and seamless data exchange with medical devices, facilitating remote patient monitoring and personalized healthcare management.
Digital Biomarkers
Medical devices traditionally measure physiological parameters within controlled clinical settings, whereas wearable biosensors continuously monitor digital biomarkers such as heart rate variability, glucose levels, and electrodermal activity in real-time, enabling personalized health insights. Digital biomarkers collected from wearable biosensors facilitate early disease detection, remote patient monitoring, and tailored therapeutic interventions, transforming healthcare delivery through enhanced data accuracy and accessibility.
Personalized Health Analytics
Medical devices provide clinical-grade diagnostics and treatment monitoring, while wearable biosensors continuously track real-time physiological data to enable personalized health analytics and proactive management of chronic conditions. Integrating wearable biosensor data with medical device outputs enhances precision medicine by delivering individualized insights for optimized health outcomes.
Closed-loop Systems
Closed-loop systems integrate medical devices with wearable biosensors to enable real-time monitoring and automated therapeutic adjustments, significantly improving treatment accuracy and patient outcomes. These systems use continuous biosignal data to trigger precise drug delivery or intervention, reducing human error and enhancing chronic disease management.
Medical Devices vs Wearable Biosensors Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com