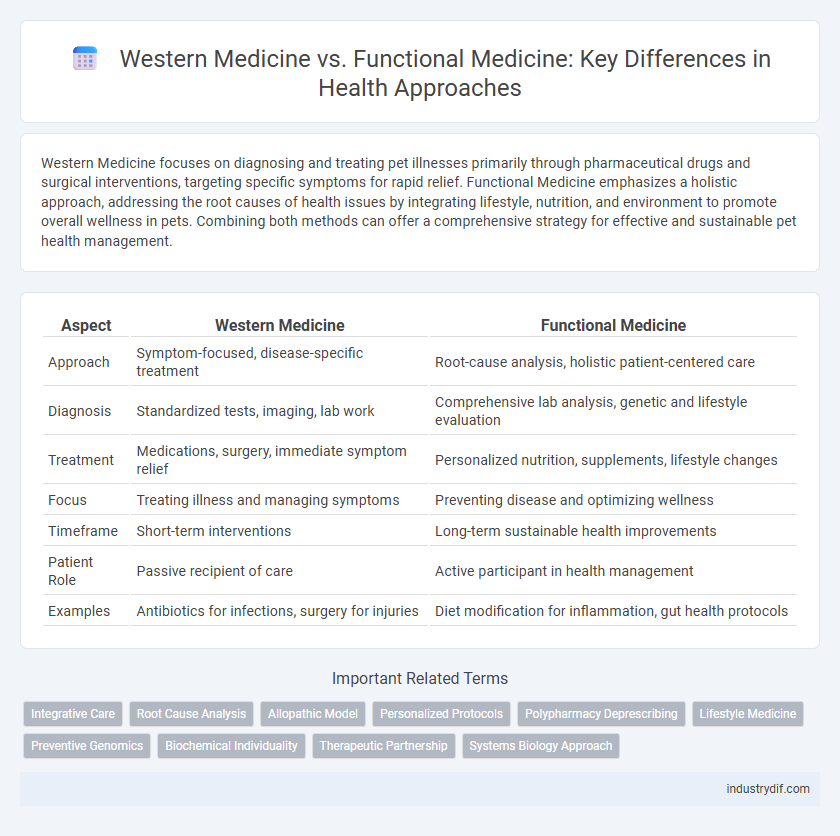
Western Medicine focuses on diagnosing and treating pet illnesses primarily through pharmaceutical drugs and surgical interventions, targeting specific symptoms for rapid relief. Functional Medicine emphasizes a holistic approach, addressing the root causes of health issues by integrating lifestyle, nutrition, and environment to promote overall wellness in pets. Combining both methods can offer a comprehensive strategy for effective and sustainable pet health management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Western Medicine | Functional Medicine |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Symptom-focused, disease-specific treatment | Root-cause analysis, holistic patient-centered care |
| Diagnosis | Standardized tests, imaging, lab work | Comprehensive lab analysis, genetic and lifestyle evaluation |
| Treatment | Medications, surgery, immediate symptom relief | Personalized nutrition, supplements, lifestyle changes |
| Focus | Treating illness and managing symptoms | Preventing disease and optimizing wellness |
| Timeframe | Short-term interventions | Long-term sustainable health improvements |
| Patient Role | Passive recipient of care | Active participant in health management |
| Examples | Antibiotics for infections, surgery for injuries | Diet modification for inflammation, gut health protocols |
Defining Western Medicine and Functional Medicine
Western medicine focuses on diagnosing and treating symptoms typically using pharmaceutical drugs, surgeries, and evidence-based clinical practices. Functional medicine prioritizes identifying and addressing root causes of diseases through personalized care, lifestyle changes, and integrative approaches. Both systems aim to improve health outcomes but differ significantly in methodology and patient engagement.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Western medicine, rooted in ancient Greek and Roman practices, evolved through scientific advancements during the Renaissance and the Industrial Revolution, emphasizing symptom treatment and disease pathology. Functional medicine, emerging in the late 20th century, integrates systems biology and personalized care to address underlying causes and promote holistic well-being. Both paradigms continue to influence modern healthcare, with functional medicine gaining recognition for its patient-centered, preventive approach.
Core Principles and Philosophies
Western Medicine centers on diagnosing and treating specific symptoms or diseases using evidence-based protocols, pharmaceuticals, and surgeries, emphasizing acute and emergency care. Functional Medicine prioritizes identifying root causes and individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, promoting personalized, holistic healing through nutrition, detoxification, and system-wide balance. Both approaches aim to improve health outcomes, but Functional Medicine offers a more integrative model targeting long-term wellness beyond symptom management.
Diagnostic Approaches and Tools
Western medicine relies heavily on standardized diagnostic tools such as blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsies to identify specific diseases and symptoms. Functional medicine employs comprehensive assessments including detailed patient histories, genetic testing, and advanced lab analyses to uncover root causes and system imbalances. Both approaches utilize technology-driven diagnostics, but functional medicine emphasizes personalized evaluation to guide tailored treatment plans.
Treatment Strategies and Modalities
Western Medicine primarily utilizes standardized pharmaceutical treatments and surgical interventions targeting specific symptoms or diseases, emphasizing rapid and evidence-based symptom relief. Functional Medicine adopts a holistic approach by addressing the root causes of illness through personalized treatment plans that integrate nutrition, lifestyle modifications, and advanced diagnostic testing. Both modalities leverage technology and clinical expertise, but Functional Medicine prioritizes patient-centered care and systemic balance over isolated symptom suppression.
Role of Patient-Provider Relationship
The patient-provider relationship in Western Medicine often centers on diagnosing symptoms and prescribing standardized treatments, which may limit personalized care. Functional Medicine emphasizes a collaborative partnership, where providers spend more time understanding the patient's lifestyle, genetics, and environment to tailor interventions. Enhanced communication and shared decision-making in Functional Medicine contribute to improved patient adherence and long-term health outcomes.
Chronic Disease Management
Western medicine primarily relies on symptom-targeted treatments and pharmaceuticals to manage chronic diseases, offering standardized protocols based on clinical trials and evidence-based guidelines. Functional medicine emphasizes individualized care by addressing underlying root causes through comprehensive patient history, lifestyle factors, and biochemical imbalances. Integrating functional medicine approaches with Western medical practices can enhance chronic disease management by promoting personalized interventions and preventative strategies.
Integration with Alternative Therapies
Western Medicine primarily emphasizes evidence-based treatments targeting specific symptoms or diseases, while Functional Medicine adopts a holistic approach, integrating alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and nutritional counseling to address root causes and improve overall health. Combining the precision of Western Medicine with the personalized, patient-centered strategies of Functional Medicine facilitates comprehensive care and supports long-term wellness. This integration enhances treatment efficacy by leveraging the strengths of both conventional diagnostics and complementary healing modalities.
Evidence-Based Outcomes and Research
Western medicine relies heavily on randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses to validate treatment efficacy, emphasizing symptom management and acute care. Functional medicine prioritizes personalized treatment plans by integrating genomic, biochemical, and lifestyle data, aiming to address root causes rather than isolated symptoms. Both approaches contribute valuable evidence-based outcomes, with functional medicine increasingly supported by emerging research in systems biology and integrative health sciences.
Future Trends in Healthcare Collaboration
Western Medicine and Functional Medicine are increasingly converging through integrated healthcare models that emphasize personalized treatment plans combining symptom management and root cause analysis. Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and genomics are driving collaboration by enabling data-driven insights and precision medicine approaches that enhance patient outcomes. Future healthcare trends indicate a growing emphasis on interdisciplinary partnerships, leveraging both evidence-based protocols from Western Medicine and holistic, patient-centered strategies from Functional Medicine.
Related Important Terms
Integrative Care
Western medicine emphasizes symptom management through standardized treatments and pharmaceutical interventions, while functional medicine prioritizes identifying and addressing root causes of disease with personalized care plans. Integrative care combines both approaches, utilizing evidence-based medical practices and holistic patient-centered strategies to optimize overall health and well-being.
Root Cause Analysis
Western Medicine primarily addresses symptoms through standardized treatments, while Functional Medicine emphasizes root cause analysis by exploring genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors to create personalized care plans that promote long-term health. Functional Medicine practitioners utilize extensive diagnostic testing and patient history to identify and treat underlying imbalances, aiming to restore optimal function rather than merely suppress symptoms.
Allopathic Model
The Allopathic Model in Western Medicine prioritizes symptom suppression and disease management through pharmaceuticals and surgery, emphasizing standardized protocols and evidence-based treatments. This approach contrasts with Functional Medicine's focus on identifying root causes and personalized care by evaluating lifestyle, genetics, and environmental factors.
Personalized Protocols
Western Medicine primarily relies on standardized treatment protocols based on broad population studies, while Functional Medicine emphasizes personalized protocols tailored to an individual's unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. By integrating comprehensive diagnostics and holistic assessments, Functional Medicine aims to address root causes rather than just symptoms, enhancing patient outcomes through customized care plans.
Polypharmacy Deprescribing
Polypharmacy deprescribing in Western medicine targets reducing unnecessary medications to minimize adverse drug reactions and improve patient outcomes, particularly in elderly populations. Functional medicine emphasizes personalized deprescribing protocols that consider underlying causes and holistic patient health, aiming to restore balance while optimizing medication use.
Lifestyle Medicine
Western Medicine primarily emphasizes symptom management and acute care using pharmaceuticals and surgical interventions, while Functional Medicine targets the root causes of disease by integrating personalized lifestyle modifications such as nutrition, exercise, and stress management. Lifestyle Medicine, a core component of Functional Medicine, utilizes evidence-based approaches like plant-rich diets, physical activity, sleep optimization, and mindfulness to prevent, treat, and often reverse chronic conditions.
Preventive Genomics
Preventive genomics in functional medicine utilizes detailed genetic profiling to identify disease risks and tailor personalized prevention strategies, contrasting with Western medicine's traditional focus on symptom-based treatment. This precision approach enables early interventions that improve long-term health outcomes by addressing genetic predispositions before clinical symptoms emerge.
Biochemical Individuality
Western Medicine often employs standardized treatments based on broad population averages, while Functional Medicine emphasizes biochemical individuality by tailoring interventions to each patient's unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This personalized approach aims to optimize health outcomes through customized nutrition, targeted supplementation, and individualized detoxification protocols.
Therapeutic Partnership
Therapeutic partnership in Western Medicine often emphasizes a clinician-directed approach where diagnosis and treatment are primarily physician-driven, whereas Functional Medicine prioritizes a collaborative relationship that actively involves patients in understanding root causes and personalized care plans. This patient-centered model in Functional Medicine enhances engagement, promotes holistic healing, and addresses complex chronic conditions through integrative strategies.
Systems Biology Approach
Western Medicine primarily targets symptom management through standardized treatments, while Functional Medicine employs a Systems Biology Approach to identify and address root causes by examining complex interactions within biological systems. This holistic methodology integrates genetics, biochemistry, and lifestyle factors to promote personalized prevention and healing.
Western Medicine vs Functional Medicine Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com