Electronic Health Records (EHRs) provide centralized digital storage of pet health information, enabling quick access and efficient management by veterinarians. Blockchain Health Records offer enhanced security and transparency through decentralized data storage, reducing risks of tampering and unauthorized access. Implementing blockchain in pet health records ensures data integrity while maintaining privacy, potentially transforming the way veterinary care is delivered.
Table of Comparison
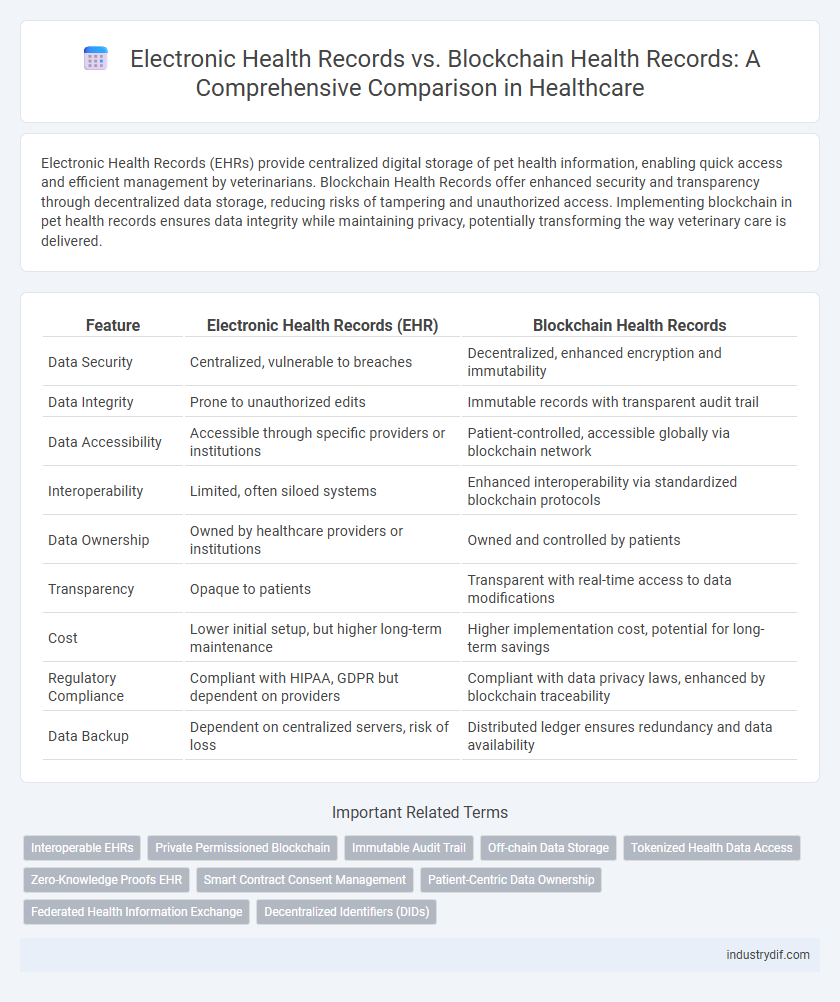
| Feature | Electronic Health Records (EHR) | Blockchain Health Records |
|---|---|---|
| Data Security | Centralized, vulnerable to breaches | Decentralized, enhanced encryption and immutability |
| Data Integrity | Prone to unauthorized edits | Immutable records with transparent audit trail |
| Data Accessibility | Accessible through specific providers or institutions | Patient-controlled, accessible globally via blockchain network |
| Interoperability | Limited, often siloed systems | Enhanced interoperability via standardized blockchain protocols |
| Data Ownership | Owned by healthcare providers or institutions | Owned and controlled by patients |
| Transparency | Opaque to patients | Transparent with real-time access to data modifications |
| Cost | Lower initial setup, but higher long-term maintenance | Higher implementation cost, potential for long-term savings |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliant with HIPAA, GDPR but dependent on providers | Compliant with data privacy laws, enhanced by blockchain traceability |
| Data Backup | Dependent on centralized servers, risk of loss | Distributed ledger ensures redundancy and data availability |
Overview of Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are digital versions of patients' medical histories, diagnoses, treatments, and test results stored in centralized databases accessible by authorized healthcare providers. EHRs streamline clinical workflows, improve care coordination, and enable real-time data sharing within healthcare institutions but often face challenges related to interoperability, data security, and patient privacy. Emerging blockchain health records aim to address these limitations by offering decentralized data management, enhanced security through encryption, and improved patient control over personal health information.
Introduction to Blockchain Health Records
Blockchain health records utilize decentralized ledger technology to enhance the security, interoperability, and patient control over medical data. Unlike traditional electronic health records (EHRs) stored in centralized databases, blockchain enables tamper-proof, transparent, and real-time access to health information across multiple providers. This advanced approach addresses critical challenges such as data breaches and fragmented patient histories by ensuring integrity and consent-based sharing of sensitive medical records.
Data Security in EHRs vs Blockchain
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) traditionally rely on centralized databases, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access, which compromises patient privacy. Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized ledger technology, providing enhanced data security through cryptographic hashing, immutability, and distributed consensus, reducing risks of tampering and unauthorized alterations. This decentralized approach ensures more robust protection of sensitive patient information compared to conventional EHR systems.
Patient Data Ownership and Control
Electronic Health Records (EHR) store patient data on centralized servers managed by healthcare providers, limiting direct patient control over access and sharing permissions. Blockchain Health Records leverage decentralized ledgers, enabling patients to own and manage their medical information securely with cryptographic keys, enhancing transparency and reducing risks of unauthorized data access. This shift empowers patient data sovereignty, improving data interoperability while maintaining privacy and auditability through immutable blockchain technology.
Interoperability Between Healthcare Systems
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) often face interoperability challenges due to diverse data formats and proprietary systems, limiting seamless information exchange between healthcare providers. Blockchain Health Records introduce decentralized ledgers that enable standardized data sharing and enhanced security, promoting real-time interoperability across different healthcare systems. This technology ensures patient data integrity and accessibility, facilitating coordinated care and reducing medical errors.
Privacy and Consent Management
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) store patient data on centralized servers, posing risks of unauthorized access and data breaches due to single points of failure. Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized ledgers, enhancing privacy through cryptographic encryption and enabling patients to control consent granularly via smart contracts. This distributed approach ensures immutable audit trails, empowering individuals with transparent, real-time access management over their sensitive medical information.
Auditability and Data Integrity
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) provide centralized data management but face challenges in auditability due to potential single points of failure and unauthorized access risks. Blockchain Health Records enhance data integrity through decentralized, immutable ledgers that enable transparent, tamper-proof audit trails for each transaction. This ensures consistent verification of patient information, fostering trust and accountability in healthcare data management.
Scalability and Implementation Challenges
Electronic Health Records (EHR) face scalability issues due to centralized data storage, which often results in bottlenecks and increased latency as patient volumes grow. Blockchain Health Records leverage decentralized architecture to enhance scalability, enabling secure, real-time data exchange across multiple providers without a single point of failure. However, implementation challenges for blockchain include high computational costs, complex interoperability standards, and regulatory compliance hurdles that slow adoption in healthcare systems.
Regulatory Compliance Considerations
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) must comply with stringent regulations like HIPAA for data privacy and security, ensuring patient information is properly protected and accessible only to authorized users. Blockchain Health Records enhance compliance by providing immutable audit trails and decentralized data control, which can reduce risks of tampering and unauthorized access while facilitating transparent patient consent management. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the integration of blockchain technologies, requiring healthcare providers to carefully assess legal standards and interoperability requirements for secure, compliant data sharing.
Future Trends in Digital Health Record Systems
Future trends in digital health record systems emphasize enhanced security and interoperability, with blockchain health records offering decentralized, tamper-proof data management compared to traditional electronic health records (EHRs). Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable predictive analytics and personalized treatment plans, improving patient outcomes. Adoption of blockchain technology in health records is expected to increase, driven by demands for data privacy, real-time access, and seamless information sharing across healthcare providers.
Related Important Terms
Interoperable EHRs
Interoperable Electronic Health Records (EHRs) enable seamless data exchange across healthcare systems, enhancing clinical decision-making and patient outcomes through standardized protocols like HL7 and FHIR. Blockchain Health Records introduce decentralized, tamper-resistant frameworks that improve data security and patient control while promoting interoperability by enabling secure sharing across diverse healthcare providers.
Private Permissioned Blockchain
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) streamline patient data management but often face challenges with security and interoperability, whereas Private Permissioned Blockchain Health Records offer enhanced data privacy, tamper-proof audit trails, and controlled access for authorized healthcare providers. Implementing a private permissioned blockchain in healthcare ensures scalable consensus mechanisms, compliance with HIPAA regulations, and improved patient data integrity across multiple institutions.
Immutable Audit Trail
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) offer structured patient data management but often lack a fully immutable audit trail, exposing vulnerabilities in data integrity and unauthorized modifications. Blockchain Health Records leverage decentralized ledger technology to create a tamper-proof, transparent, and immutable audit trail, enhancing security, trust, and compliance in healthcare data management.
Off-chain Data Storage
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) typically rely on centralized databases, which can be vulnerable to breaches and data loss, while Blockchain Health Records enhance security by storing sensitive information off-chain with cryptographic hashes on-chain to ensure data integrity and patient privacy. Off-chain data storage in blockchain systems enables scalable handling of large medical files while maintaining tamper-proof audit trails and decentralized access control.
Tokenized Health Data Access
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) typically rely on centralized databases, making data access vulnerable to breaches, whereas Blockchain Health Records use decentralized ledger technology to enable secure, transparent, and immutable tokenized health data access. Tokenized access leverages cryptographic tokens, allowing patients to control permissions granularly, enhancing privacy and interoperability across healthcare providers.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs EHR
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) enhance Electronic Health Records (EHR) by enabling secure, private sharing of patient data without revealing sensitive information, addressing data breaches and privacy concerns inherent in traditional EHR systems. Blockchain Health Records integrated with ZKPs ensure immutability, decentralized control, and verifiable access permissions, fostering trust and compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Smart Contract Consent Management
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) often face challenges in secure consent management, whereas blockchain health records leverage smart contract consent management to ensure immutable, real-time patient authorization and seamless data sharing. Smart contracts automate consent verification, reduce administrative errors, and enhance patient control over sensitive health information.
Patient-Centric Data Ownership
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) traditionally store patient data within centralized healthcare systems, limiting patient control and creating vulnerabilities for data breaches. Blockchain Health Records offer decentralized, secure platforms that empower patients with full ownership and real-time access to their medical information, enhancing privacy and interoperability across providers.
Federated Health Information Exchange
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) enable centralized patient data storage, while Blockchain Health Records utilize decentralized ledgers for secure, tamper-proof logging of medical information. Federated Health Information Exchange leverages blockchain technology to allow multiple healthcare entities to share verified patient data seamlessly without compromising privacy or data ownership.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) in blockchain health records enhance patient privacy and data security by enabling self-sovereign identity management, contrasting with traditional Electronic Health Records (EHRs) that rely on centralized data storage vulnerable to breaches. Implementing DIDs allows seamless interoperability and real-time verification of health credentials across multiple providers without compromising patient control over personal information.
Electronic Health Records vs Blockchain Health Records Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com