Nutritionists tailor pet diets based on general health needs and lifestyle factors, focusing on balanced nutrient intake to improve overall well-being. Nutrigenomics explores how a pet's genetic makeup interacts with specific nutrients, allowing for highly personalized dietary recommendations that optimize health at the molecular level. Combining nutritionist expertise with nutrigenomic insights can lead to more effective, individualized nutrition plans that support long-term pet health.
Table of Comparison
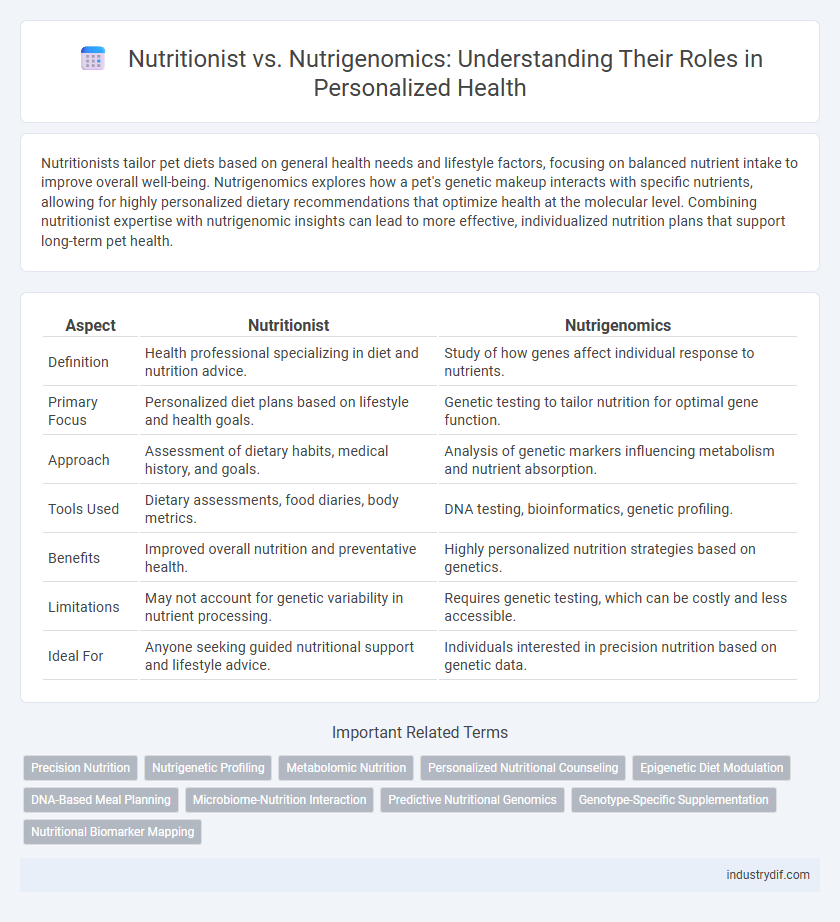
| Aspect | Nutritionist | Nutrigenomics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Health professional specializing in diet and nutrition advice. | Study of how genes affect individual response to nutrients. |
| Primary Focus | Personalized diet plans based on lifestyle and health goals. | Genetic testing to tailor nutrition for optimal gene function. |
| Approach | Assessment of dietary habits, medical history, and goals. | Analysis of genetic markers influencing metabolism and nutrient absorption. |
| Tools Used | Dietary assessments, food diaries, body metrics. | DNA testing, bioinformatics, genetic profiling. |
| Benefits | Improved overall nutrition and preventative health. | Highly personalized nutrition strategies based on genetics. |
| Limitations | May not account for genetic variability in nutrient processing. | Requires genetic testing, which can be costly and less accessible. |
| Ideal For | Anyone seeking guided nutritional support and lifestyle advice. | Individuals interested in precision nutrition based on genetic data. |
Introduction to Nutritionist vs Nutrigenomics
A nutritionist provides personalized dietary advice based on general health principles and individual needs, focusing on optimizing overall wellness through balanced nutrition. Nutrigenomics explores the interaction between genes and diet, using genetic information to tailor nutritional strategies for disease prevention and health improvement. Understanding the differences between a nutritionist's role and nutrigenomics enables more precise and effective dietary planning.
Defining the Role of a Nutritionist
A nutritionist specializes in assessing individual dietary needs and creating personalized nutrition plans based on clinical evidence and lifestyle factors. Unlike nutrigenomics, which explores how genes influence nutrient metabolism and health outcomes, a nutritionist applies practical knowledge to guide food choices and promote overall wellness. By integrating scientific research with client-centered counseling, nutritionists play a crucial role in preventing and managing chronic diseases through tailored nutrition strategies.
What is Nutrigenomics?
Nutrigenomics is the scientific study of how individual genetic variations affect the body's response to nutrients and dietary components, enabling personalized nutrition strategies for disease prevention and health optimization. Unlike traditional nutritionists who provide generalized dietary advice, nutrigenomics integrates genomic data to tailor dietary recommendations that promote optimal gene expression and metabolic health. This emerging field combines genetics, molecular biology, and nutrition science to revolutionize personalized dietary interventions based on an individual's unique genetic profile.
Key Differences Between Nutritionists and Nutrigenomics Experts
Nutritionists focus on general dietary guidance and personalized meal plans to improve overall health and manage chronic conditions, relying on traditional nutrition science and evidence-based practices. Nutrigenomics experts specialize in analyzing how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and dietary responses, using genomic data to tailor nutrition recommendations at a molecular level. Key differences lie in their methodologies: nutritionists apply broad nutritional principles, while nutrigenomics experts leverage genetic testing to customize interventions for precision health outcomes.
Assessments and Diagnostic Approaches
Nutritionists primarily rely on dietary assessments, food diaries, and biochemical tests to evaluate nutrient intake and overall health status. Nutrigenomics incorporates advanced genetic testing and molecular diagnostics to analyze how individual DNA variations influence nutrient metabolism and disease risk. Combining these diagnostic approaches enhances personalized nutrition strategies for optimized health outcomes.
Personalized Nutrition: Traditional vs Genetic-Based
Personalized nutrition incorporates both traditional nutritionist approaches and nutrigenomics, with the latter leveraging genetic-based data to tailor diet plans according to an individual's DNA profile. Traditional nutritionists analyze dietary habits, lifestyle, and health status to recommend personalized meal plans, while nutrigenomics focuses on how specific genes influence nutrient metabolism and disease risk. Integrating genetic insights enables a more precise customization of nutrition strategies, improving health outcomes beyond conventional methods.
Education and Certification Requirements
Nutritionists typically require a bachelor's degree in nutrition, dietetics, or a related field, often followed by certification such as the Certified Nutrition Specialist (CNS) credential. Nutrigenomics professionals usually hold advanced degrees in genetics, molecular biology, or nutrition science, with specialized training or certification in nutrigenomics to interpret gene-diet interactions. Both career paths demand rigorous education and continuous professional development to ensure expertise in personalized nutrition and genetic influences on health.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Approach
Nutritionists provide personalized dietary guidance based on individual health status and lifestyle, promoting balanced nutrition and addressing general health concerns, but they may lack the ability to tailor recommendations at the genetic level. Nutrigenomics analyzes genetic variations to understand how individuals respond to nutrients, enabling highly customized dietary plans that can optimize health outcomes and prevent disease; however, this approach requires advanced testing and may not be accessible or fully validated for all populations. Combining traditional nutritional advice with nutrigenomic insights offers a comprehensive strategy for personalized health management, balancing broad expertise with genetic precision.
How to Choose the Right Nutrition Professional
Selecting the right nutrition professional depends on your health goals and needs; a nutritionist offers personalized dietary advice based on general nutrition principles, while a nutrigenomics specialist integrates genetic data to tailor nutrition plans for optimal health outcomes. Evaluating credentials, such as registered dietitian status or expertise in genetic testing, ensures credible guidance. Consider your budget, health conditions, and interest in genetic insights when deciding between traditional nutrition counseling and advanced nutrigenomic analysis.
Future Trends in Nutrition and Genomic Science
Future trends in nutrition emphasize the integration of nutrigenomics, which tailors dietary recommendations based on an individual's genetic makeup, enhancing personalized nutrition plans. Nutritionists are increasingly utilizing genomic data to develop precise diet strategies that prevent chronic diseases and improve overall health outcomes. Advances in genomic science promise to revolutionize traditional nutrition by enabling targeted interventions and optimizing nutrient absorption at a molecular level.
Related Important Terms
Precision Nutrition
Nutritionists provide personalized dietary guidance based on general health assessments, while nutrigenomics uses genetic information to tailor nutrition plans at a molecular level, enabling precision nutrition. By integrating genetic data with lifestyle factors, nutrigenomics optimizes nutrient intake and enhances disease prevention strategies beyond traditional nutrition counseling.
Nutrigenetic Profiling
Nutrigenetic profiling analyzes individual genetic variations affecting nutrient metabolism to create personalized diet plans, unlike traditional nutritionists who rely on general dietary guidelines. This advanced approach enhances precision nutrition by tailoring recommendations based on unique genetic markers influencing nutrient absorption and chronic disease risk.
Metabolomic Nutrition
Metabolomic nutrition bridges the gap between traditional nutritionist practices and nutrigenomics by analyzing metabolites to tailor dietary recommendations based on an individual's unique metabolic profile. This approach enhances personalized nutrition strategies, optimizing health outcomes through precise metabolic pathway insights rather than generalized dietary guidelines.
Personalized Nutritional Counseling
Personalized nutritional counseling integrates insights from nutrigenomics, enabling nutritionists to tailor diet plans based on an individual's genetic profile for optimized health outcomes. This approach enhances traditional nutrition guidance by addressing unique metabolic responses and nutrient interactions at the molecular level.
Epigenetic Diet Modulation
Nutritionists provide personalized dietary guidance based on general health needs, while nutrigenomics explores how individual genetic variations influence response to nutrients, enabling epigenetic diet modulation to optimize gene expression and prevent chronic diseases. Epigenetic diet modulation utilizes specific nutrients to trigger beneficial changes in DNA methylation and histone modification, supporting metabolic health and reducing inflammation.
DNA-Based Meal Planning
Nutritionists design personalized meal plans based on individual dietary needs and lifestyle, while nutrigenomics leverages DNA analysis to develop precision nutrition strategies that optimize health outcomes by targeting genetic variations. DNA-based meal planning integrates genetic information to customize nutrient intake, enhancing metabolic functions and reducing risks for chronic diseases through tailored dietary interventions.
Microbiome-Nutrition Interaction
Nutritionists provide personalized dietary advice based on general health and lifestyle factors, while nutrigenomics explores how individual genetic variations influence nutrient metabolism and dietary responses. Research on microbiome-nutrition interaction reveals that gut microbiota composition modulates nutrient absorption and metabolic pathways, emphasizing the importance of integrating microbiome profiles in precision nutrition strategies.
Predictive Nutritional Genomics
Predictive Nutritional Genomics leverages individual genetic profiles to tailor dietary recommendations, enhancing personalized nutrition beyond traditional nutritionist approaches that generally focus on generalized dietary guidelines. This cutting-edge field enables precise prediction of nutrient metabolism and disease risk, optimizing preventive health strategies at the molecular level.
Genotype-Specific Supplementation
Genotype-specific supplementation leverages nutrigenomics to tailor dietary recommendations based on an individual's genetic makeup, enhancing nutrient absorption and metabolic response. Unlike traditional nutritionists who provide generalized advice, nutrigenomics offers precision targeting of supplements to optimize health outcomes according to specific gene variants.
Nutritional Biomarker Mapping
Nutritional biomarker mapping enhances the precision of nutrigenomics by identifying specific genetic markers that influence nutrient metabolism and dietary response, enabling personalized nutrition strategies beyond traditional nutritionist advice. This approach leverages genetic, proteomic, and metabolomic data to tailor interventions that optimize health outcomes based on individual molecular profiles.
Nutritionist vs Nutrigenomics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com