Traditional surgery in pet healthcare involves manual techniques performed by veterinarians with direct physical contact, often resulting in longer recovery times and increased risk of infection. Robotic-assisted surgery offers enhanced precision, minimally invasive procedures, and faster healing for pets due to advanced technology and improved surgical accuracy. Choosing robotic-assisted methods can significantly improve outcomes in complex veterinary surgeries by reducing trauma and postoperative complications.
Table of Comparison
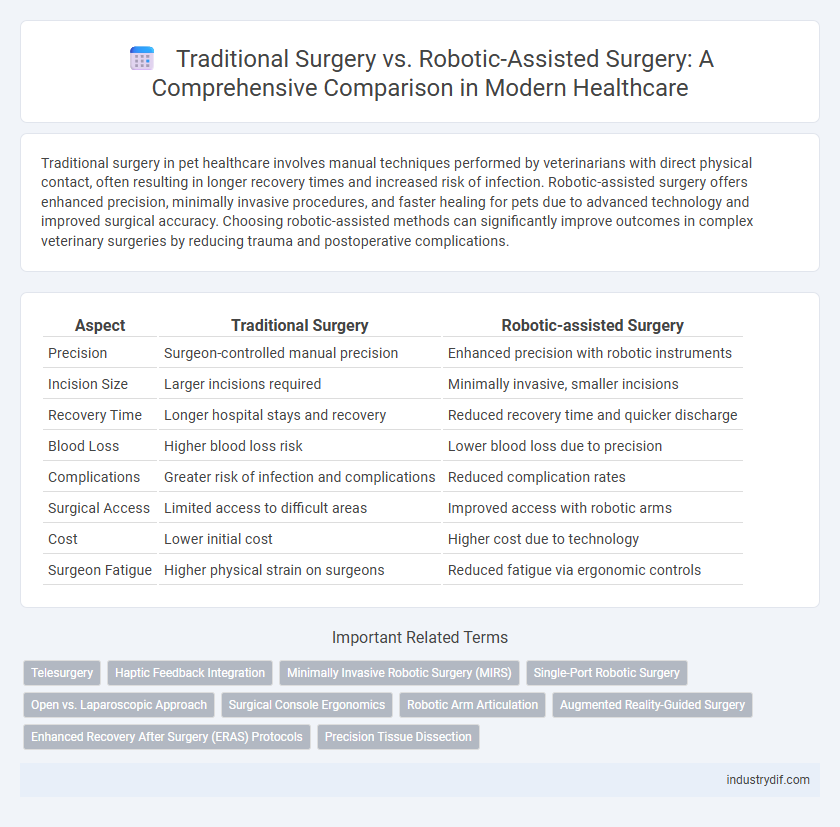
| Aspect | Traditional Surgery | Robotic-assisted Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Surgeon-controlled manual precision | Enhanced precision with robotic instruments |
| Incision Size | Larger incisions required | Minimally invasive, smaller incisions |
| Recovery Time | Longer hospital stays and recovery | Reduced recovery time and quicker discharge |
| Blood Loss | Higher blood loss risk | Lower blood loss due to precision |
| Complications | Greater risk of infection and complications | Reduced complication rates |
| Surgical Access | Limited access to difficult areas | Improved access with robotic arms |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to technology |
| Surgeon Fatigue | Higher physical strain on surgeons | Reduced fatigue via ergonomic controls |
Overview of Traditional Surgery
Traditional surgery involves manual techniques where surgeons use hands-on methods to perform operations, often requiring large incisions for direct access to the target area. This approach typically results in longer recovery times, increased risk of infection, and greater postoperative pain compared to minimally invasive methods. Despite advancements, traditional surgery remains essential for complex cases where robotic assistance may not be feasible.
Introduction to Robotic-assisted Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery utilizes advanced robotic systems to enhance precision, flexibility, and control during surgical procedures, minimizing human error compared to traditional methods. This technology employs high-definition 3D visualization and robotic arms controlled by surgeons through a console, improving accuracy and reducing invasiveness. Clinical studies demonstrate faster patient recovery, reduced blood loss, and lower complication rates with robotic-assisted surgeries across various specialties such as urology, gynecology, and cardiothoracic surgery.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Robotic-assisted Surgery
Traditional surgery involves manual incisions and direct visual guidance by the surgeon, often resulting in larger cuts and longer recovery times. Robotic-assisted surgery utilizes advanced robotic systems to enhance precision through smaller incisions, providing surgeons with a 3D high-definition view and greater dexterity. This technology often leads to reduced blood loss, minimized scarring, and faster patient recovery compared to traditional methods.
Advantages of Traditional Surgical Approaches
Traditional surgical approaches offer the advantage of direct tactile feedback and visual cues, allowing surgeons to navigate complex anatomical structures with precision. These methods have a well-established track record, supported by decades of clinical outcomes, making them reliable choices in emergency and intricate procedures. Furthermore, traditional surgery often requires less expensive equipment, reducing costs and increasing accessibility in resource-limited healthcare settings.
Benefits of Robotic-assisted Surgical Techniques
Robotic-assisted surgical techniques enhance precision, reduce human error, and minimize tissue damage through advanced 3D visualization and articulated instruments. These benefits contribute to shorter recovery times, less postoperative pain, and decreased risk of infection compared to traditional surgery. Patients undergoing robotic-assisted procedures often experience improved surgical outcomes and faster returns to daily activities.
Patient Outcomes: Traditional vs Robotic-assisted Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery often results in reduced blood loss, smaller incisions, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional surgery, enhancing patient outcomes significantly. Studies indicate lower complication rates and decreased postoperative pain with robotic techniques due to precision and minimally invasive approaches. However, traditional surgery remains critical in complex cases where tactile feedback and surgeon experience directly impact success rates.
Recovery Time and Postoperative Complications
Robotic-assisted surgery generally offers shorter recovery times compared to traditional surgery due to smaller incisions and enhanced precision, which reduce tissue damage and pain. Studies show that patients undergoing robotic procedures experience fewer postoperative complications, such as infections and bleeding, contributing to faster overall healing. Hospital stays are often shorter after robotic-assisted surgery, enabling quicker return to daily activities and improved patient outcomes.
Cost Considerations in Surgery Options
Robotic-assisted surgery often involves higher upfront costs due to expensive equipment and maintenance compared to traditional surgery. However, potential benefits include shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times, which can reduce overall healthcare expenses. Patients and providers must weigh initial investment against long-term savings and clinical outcomes when considering surgical options.
Surgeon Training and Skill Requirements
Surgeon training for traditional surgery emphasizes manual dexterity, hands-on experience, and mastery of tactile feedback during procedures. Robotic-assisted surgery requires specialized training in operating advanced robotic systems, enhanced hand-eye coordination, and proficiency in manipulating remote surgical instruments with precision. Continuous skill development and certification are critical in both methods to ensure patient safety and optimal surgical outcomes.
Future Trends in Surgical Innovation
Robotic-assisted surgery is rapidly advancing with enhanced precision, reduced recovery times, and integration of artificial intelligence for real-time decision support, positioning it as the forefront of future surgical innovation. Traditional surgery remains essential but faces increasing augmentation by minimally invasive robotic systems that lower complication rates and improve patient outcomes. Emerging trends include the use of machine learning algorithms to customize surgical procedures and telesurgery capabilities, expanding access to expert care globally.
Related Important Terms
Telesurgery
Telesurgery enables surgeons to perform robotic-assisted procedures remotely, enhancing access to specialized care and reducing patient recovery time compared to traditional surgery. This advanced technology leverages high-speed internet and precise robotic instruments to improve surgical accuracy and minimize invasiveness.
Haptic Feedback Integration
Robotic-assisted surgery enhances precision through advanced haptic feedback integration, allowing surgeons to feel tactile sensations that mimic real tissue interaction, which traditional surgery relies on direct manual touch. This sensory technology improves surgical accuracy and reduces the risk of tissue damage during minimally invasive procedures.
Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery (MIRS)
Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery (MIRS) enhances precision and reduces recovery time compared to traditional surgery by utilizing advanced robotic systems that allow for smaller incisions and greater dexterity. This technology minimizes tissue damage, lowers the risk of infection, and typically results in less postoperative pain and shorter hospital stays.
Single-Port Robotic Surgery
Single-port robotic surgery enhances traditional surgery by using a single incision to perform complex procedures with precision, reducing patient recovery time and minimizing postoperative pain. This minimally invasive technique leverages advanced robotic technology to improve surgical accuracy, decrease complications, and promote faster healing compared to conventional multi-port or open surgeries.
Open vs. Laparoscopic Approach
Traditional open surgery involves large incisions to access the surgical site, resulting in longer recovery times and increased risk of infection, whereas laparoscopic surgery uses small incisions and a camera for minimally invasive procedures, promoting faster healing and reduced postoperative pain. Robotic-assisted surgery enhances the laparoscopic approach by providing surgeons with improved precision, dexterity, and 3D visualization, leading to greater accuracy and potentially better clinical outcomes.
Surgical Console Ergonomics
Robotic-assisted surgery offers superior surgical console ergonomics by enabling surgeons to operate in a seated, comfortable position with enhanced wrist and finger dexterity, reducing physical strain during lengthy procedures. Traditional surgery often requires awkward postures and repetitive movements, increasing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders among surgeons.
Robotic Arm Articulation
Robotic-assisted surgery offers enhanced precision through advanced robotic arm articulation, allowing for greater dexterity and range of motion than traditional surgery methods. This increased articulation enables surgeons to perform complex procedures with minimal invasiveness, reducing recovery time and improving patient outcomes.
Augmented Reality-Guided Surgery
Augmented Reality-Guided Surgery enhances traditional and robotic-assisted procedures by overlaying digital imaging onto the surgical field, improving precision and visualization of critical anatomy. This technology reduces intraoperative risks and shortens recovery times by allowing surgeons to navigate complex structures with real-time, three-dimensional guidance.
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Protocols
Robotic-assisted surgery integrates precision technology with Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols to minimize tissue trauma and accelerate postoperative recovery times compared to traditional surgery. Studies demonstrate that patients undergoing robotic-assisted procedures experience reduced opioid use, shorter hospital stays, and earlier return to normal activities within ERAS frameworks.
Precision Tissue Dissection
Robotic-assisted surgery offers enhanced precision in tissue dissection through advanced 3D visualization and articulating instruments, reducing damage to surrounding tissues compared to traditional surgery. This improved accuracy promotes faster recovery, less postoperative pain, and lower complication rates for patients undergoing complex procedures.
Traditional Surgery vs Robotic-assisted Surgery Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com