Outpatient clinics offer convenient, cost-effective care for routine pet health issues, providing quick access to vaccinations, check-ups, and minor treatments. Microhospitals deliver comprehensive services including emergency care, advanced diagnostics, and overnight monitoring, ideal for serious or complex conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the severity of the pet's health needs and the level of care required.
Table of Comparison
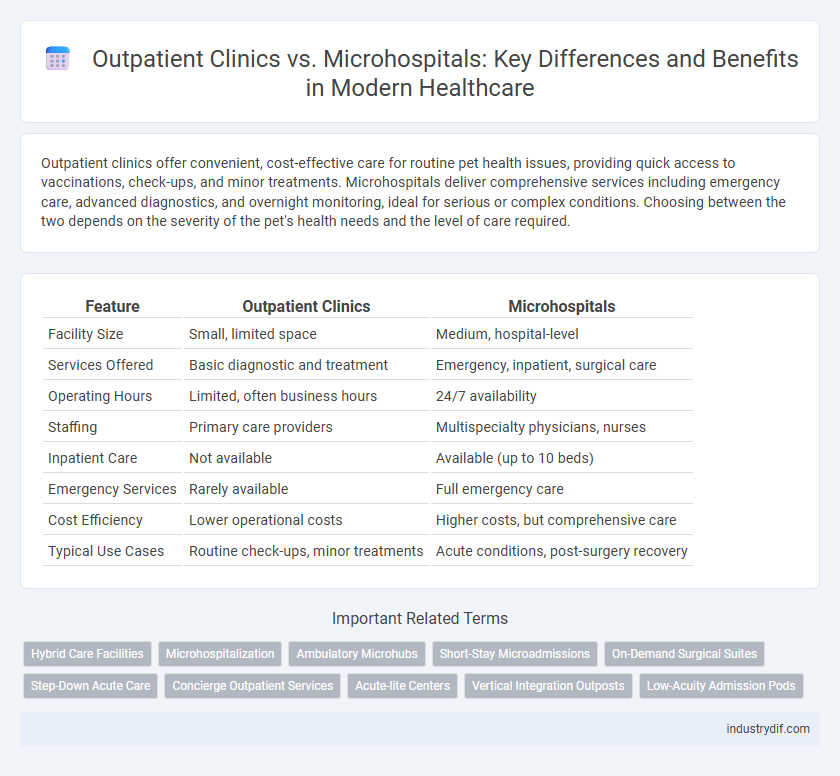
| Feature | Outpatient Clinics | Microhospitals |
|---|---|---|
| Facility Size | Small, limited space | Medium, hospital-level |
| Services Offered | Basic diagnostic and treatment | Emergency, inpatient, surgical care |
| Operating Hours | Limited, often business hours | 24/7 availability |
| Staffing | Primary care providers | Multispecialty physicians, nurses |
| Inpatient Care | Not available | Available (up to 10 beds) |
| Emergency Services | Rarely available | Full emergency care |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs | Higher costs, but comprehensive care |
| Typical Use Cases | Routine check-ups, minor treatments | Acute conditions, post-surgery recovery |
Definition and Scope: Outpatient Clinics vs Microhospitals
Outpatient clinics provide non-emergency medical services such as consultations, diagnostic tests, and minor procedures without overnight stays, serving primarily routine or preventive care needs. Microhospitals are small-scale inpatient facilities equipped to handle emergency care, minor surgeries, and inpatient admissions, typically ranging from 8 to 50 beds, bridging the gap between outpatient clinics and full-scale hospitals. The scope of outpatient clinics centers on convenience and accessibility for low-acuity cases, whereas microhospitals offer a broader spectrum of acute and short-term care within localized communities.
Core Services Offered: Comparing Clinical Capabilities
Outpatient clinics primarily offer basic diagnostic services, minor surgical procedures, preventive care, and routine medical consultations designed for quick access and lower costs. Microhospitals provide a broader range of clinical capabilities including emergency services, advanced diagnostics, inpatient care, and surgical interventions within a smaller, community-focused facility. The distinction lies in microhospitals supporting more complex treatments and continuous monitoring, while outpatient clinics focus on non-invasive and short-duration care.
Patient Volume and Throughput Differences
Outpatient clinics typically manage higher patient volumes with shorter visit durations, emphasizing rapid throughput for routine care and diagnostic services. Microhospitals accommodate moderate patient volumes but offer extended services, including overnight stays and minor surgeries, resulting in longer throughput times compared to outpatient clinics. The structural and operational differences between these facilities directly influence patient flow efficiency and capacity management.
Staffing Models: Key Roles in Each Setting
Outpatient clinics typically rely on a lean staffing model with key roles including nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and registered nurses to provide efficient ambulatory care. Microhospitals, by contrast, incorporate a more robust multidisciplinary team encompassing hospitalists, emergency medicine physicians, registered nurses, and specialized technicians to support 24/7 acute care services. Staffing optimization in each setting directly influences patient throughput, care quality, and operational costs.
Facility Size and Infrastructure Requirements
Outpatient clinics typically require smaller facility sizes with limited infrastructure, focusing on basic medical services and quick patient turnover. Microhospitals, spanning 10,000 to 40,000 square feet, demand more advanced infrastructure including emergency rooms, inpatient beds, and diagnostic equipment to provide comprehensive acute care. The larger scale and complex facilities of microhospitals support extended services beyond primary care, distinguishing them from outpatient clinics.
Patient Experience: Accessibility and Wait Times
Outpatient clinics offer enhanced accessibility with numerous locations and flexible hours, reducing travel time and easing appointment scheduling, which significantly improves patient experience. Microhospitals provide a more comprehensive range of services than outpatient clinics, often enabling faster diagnosis and treatment during a single visit, minimizing wait times. Patients benefit from outpatient clinics' convenience for routine care while microhospitals deliver quicker access to advanced diagnostic and emergency services.
Cost Structures and Reimbursement Strategies
Outpatient clinics typically maintain lower cost structures due to minimal facility overhead and streamlined staffing, enabling more affordable patient care compared to microhospitals. Microhospitals, with their expanded services and inpatient capabilities, incur higher operational costs but benefit from diverse reimbursement strategies, including facility fees and higher payer rates. Effective reimbursement optimization in both models hinges on accurate coding, resource utilization, and alignment with value-based payment programs.
Emergency and Specialty Care Availability
Outpatient clinics primarily offer basic emergency services with limited specialty care options, focusing on quick assessments and minor treatments. Microhospitals provide a broader scope of emergency care capabilities, including advanced diagnostics and specialty services like cardiology, orthopedics, and acute care. The expanded availability of specialty care in microhospitals enhances patient outcomes by ensuring timely and comprehensive treatment in critical cases.
Integration with Health Systems and Continuity of Care
Outpatient clinics offer targeted, same-day services that enhance health system integration by facilitating swift referrals and follow-ups, promoting seamless continuity of care. Microhospitals bridge the gap between inpatient care and outpatient services, providing 24/7 acute care with advanced diagnostics and treatment capabilities while maintaining strong ties to larger health networks. Both settings improve patient outcomes through coordinated care pathways, data sharing, and real-time communication with primary care providers and specialists.
Trends, Challenges, and Future Developments
Outpatient clinics are expanding rapidly due to increased demand for cost-effective, accessible care, while microhospitals gain traction by offering 24/7 services and inpatient capabilities in smaller communities. Challenges include regulatory hurdles, reimbursement variations, and staffing shortages impacting both models. Future developments will likely involve telemedicine integration, advanced diagnostic technologies, and personalized patient management to enhance healthcare delivery efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Care Facilities
Hybrid care facilities combine the accessibility of outpatient clinics with the advanced medical capabilities of microhospitals, offering a versatile healthcare environment that supports both routine and urgent treatments. These integrated centers optimize patient outcomes by providing comprehensive services such as diagnostic imaging, minor surgical procedures, and short-term inpatient care under one roof, reducing the need for hospital transfers.
Microhospitalization
Microhospitals provide a middle ground between outpatient clinics and full-scale hospitals by offering 24/7 care with advanced diagnostic and treatment services in a compact setting. This model enhances patient outcomes through timely interventions and reduces healthcare costs by avoiding unnecessary hospital admissions.
Ambulatory Microhubs
Ambulatory microhubs combine the convenience of outpatient clinics with the advanced diagnostic and treatment capabilities of microhospitals, offering efficient, cost-effective care for non-emergency medical needs. These facilities optimize patient flow and reduce hospital admissions by providing specialized services such as imaging, minor surgeries, and lab testing in accessible neighborhood locations.
Short-Stay Microadmissions
Short-stay microadmissions in microhospitals bridge the gap between outpatient clinics and full hospital stays by providing enhanced monitoring and treatment for acute conditions within 24 to 48 hours. These facilities optimize resource utilization and patient outcomes by offering around-the-clock care, advanced diagnostics, and immediate interventions without the extended commitment required in traditional hospitals.
On-Demand Surgical Suites
Outpatient clinics offer limited surgical capabilities suitable for minor procedures, whereas microhospitals provide on-demand surgical suites equipped for a broader range of surgeries with faster patient turnover. On-demand surgical suites in microhospitals enhance efficiency by enabling same-day surgeries and reducing hospitalization time, improving patient outcomes and resource utilization.
Step-Down Acute Care
Outpatient clinics offer limited post-acute care services, often requiring patients to transfer to other facilities for step-down acute care; microhospitals provide a more integrated approach with 24/7 acute care capabilities and step-down units, facilitating smoother patient transitions and better management of complex conditions. Research indicates microhospitals reduce hospital readmissions by up to 30% due to their capacity for continuous monitoring and targeted rehabilitation during the step-down phase.
Concierge Outpatient Services
Concierge outpatient services within microhospitals provide personalized, rapid-access healthcare that combines the convenience of outpatient clinics with the comprehensive medical capabilities of inpatient facilities. These services enhance patient experience by offering tailored care plans, reduced wait times, and seamless coordination between specialty consultations and advanced diagnostic resources.
Acute-lite Centers
Outpatient clinics provide ambulatory care for non-emergency conditions, offering convenience and cost-efficiency, while microhospitals, particularly acute-lite centers, deliver short-term inpatient services with advanced diagnostics and urgent care capabilities. Acute-lite centers bridge the gap between outpatient clinics and full-scale hospitals by treating moderately severe illnesses with 24/7 monitoring, reducing hospital admissions and enhancing patient outcomes.
Vertical Integration Outposts
Outpatient clinics and microhospitals serve distinct roles within vertically integrated healthcare systems by offering complementary care levels close to patient communities, enhancing access and continuity of care. Vertical integration outposts strategically deploy these facilities to streamline patient transitions, reduce hospital admissions, and optimize resource utilization across the care continuum.
Low-Acuity Admission Pods
Low-acuity admission pods in outpatient clinics provide streamlined, cost-effective care for patients with minor illnesses or injuries, reducing the burden on emergency departments. Microhospitals offer similar low-acuity services but include enhanced diagnostic and treatment capabilities, bridging the gap between outpatient clinics and full-scale hospitals.
Outpatient Clinics vs Microhospitals Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com