Pharmaceuticals are drugs specifically designed to diagnose, treat, or prevent illnesses in pets, often requiring rigorous testing and regulatory approval to ensure safety and efficacy. Nutraceuticals, on the other hand, are products derived from food sources that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition, aiming to support overall wellness and prevent disease. Both pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals play crucial roles in pet health, with pharmaceuticals addressing acute or chronic conditions and nutraceuticals enhancing long-term vitality and immune function.
Table of Comparison
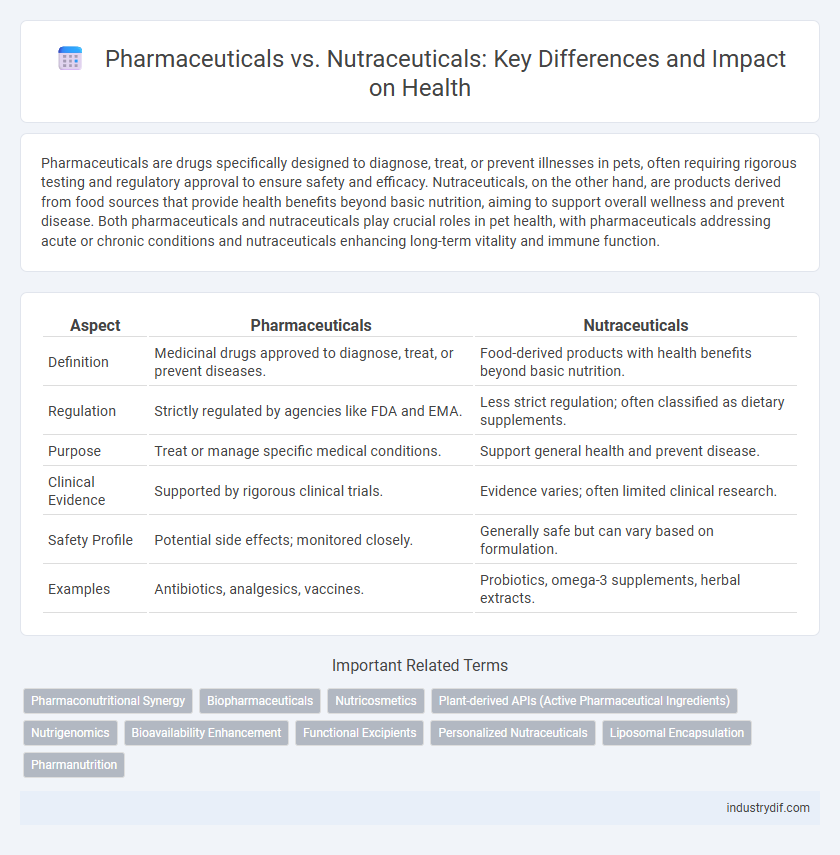
| Aspect | Pharmaceuticals | Nutraceuticals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Medicinal drugs approved to diagnose, treat, or prevent diseases. | Food-derived products with health benefits beyond basic nutrition. |
| Regulation | Strictly regulated by agencies like FDA and EMA. | Less strict regulation; often classified as dietary supplements. |
| Purpose | Treat or manage specific medical conditions. | Support general health and prevent disease. |
| Clinical Evidence | Supported by rigorous clinical trials. | Evidence varies; often limited clinical research. |
| Safety Profile | Potential side effects; monitored closely. | Generally safe but can vary based on formulation. |
| Examples | Antibiotics, analgesics, vaccines. | Probiotics, omega-3 supplements, herbal extracts. |
Defining Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals
Pharmaceuticals are chemically synthesized drugs designed to diagnose, treat, or prevent diseases, regulated by strict governmental standards to ensure safety and efficacy. Nutraceuticals, derived from natural food sources, provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition and are often used to improve health or reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Both play distinct roles in healthcare, with pharmaceuticals focusing on targeted medical interventions and nutraceuticals emphasizing preventive and supportive health functions.
Key Differences Between Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals
Pharmaceuticals are drugs developed through rigorous clinical trials and regulatory approval to treat or prevent specific medical conditions with standardized dosages and active ingredients. Nutraceuticals, derived from food sources, aim to provide health benefits or prevent chronic diseases but lack strict regulatory oversight and standardized dosing. The key difference lies in their regulatory status, intended use, and evidence-based efficacy, with pharmaceuticals targeting disease treatment and nutraceuticals focusing on health maintenance and wellness.
Regulatory Frameworks: Pharmaceuticals vs Nutraceuticals
Pharmaceuticals are regulated under stringent frameworks such as the FDA's drug approval process, requiring extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy before market access. Nutraceuticals fall under dietary supplement regulations, which mandate product safety and truthful labeling but do not require pre-market approval or rigorous clinical testing. This regulatory disparity affects consumer protection, product claims, and market entry timelines within the health industry.
Scientific Evidence and Efficacy
Pharmaceuticals undergo rigorous clinical trials and regulatory approval processes to establish safety, efficacy, and dosage, providing robust scientific evidence for their therapeutic claims. Nutraceuticals, often derived from natural sources like herbs and vitamins, have limited and less standardized research, with efficacy varying significantly due to differences in formulation and bioavailability. While pharmaceuticals target specific medical conditions with precise mechanisms, nutraceuticals mainly support general health and prevention, making their scientific validation less conclusive and more variable.
Common Applications in Healthcare
Pharmaceuticals are primarily used for diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases through chemically synthesized or biologically derived drugs with standardized dosages. Nutraceuticals, including vitamins, minerals, and herbal supplements, support overall health and wellness by providing nutritional benefits and potentially reducing disease risk. Both play critical roles in healthcare: pharmaceuticals address acute and chronic conditions, while nutraceuticals promote preventive care and enhance quality of life.
Safety, Side Effects, and Risk Profiles
Pharmaceuticals undergo rigorous clinical trials to ensure safety and have well-documented side effects and risk profiles, often requiring prescription and medical supervision due to potential adverse reactions. Nutraceuticals, derived from food sources, generally present lower risk and fewer side effects but lack standardized regulatory oversight, leading to variable safety and efficacy profiles. Consumers should evaluate both options carefully, considering pharmaceutical precision and nutraceutical natural benefits in relation to individual health conditions.
Market Trends and Growth Projections
Pharmaceuticals are witnessing steady growth driven by advancements in drug development and rising chronic disease prevalence, with the global market projected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2027. Nutraceuticals are experiencing rapid expansion due to increasing consumer demand for preventive health and wellness products, expected to surpass $350 billion by 2028. Market trends indicate a shift towards personalized medicine and natural ingredients, accelerating investment and innovation in both sectors.
Consumer Perceptions and Preferences
Consumers increasingly distinguish pharmaceuticals as medically necessary treatments regulated for safety and efficacy, while nutraceuticals are perceived as natural supplements promoting general wellness with fewer side effects. Market trends indicate a growing preference for nutraceuticals among health-conscious individuals seeking preventive care, driven by the demand for organic and plant-based ingredients. Despite this shift, pharmaceuticals remain the trusted choice for acute conditions due to rigorous clinical trials and regulatory approval.
Innovations and Future Directions
Pharmaceuticals leverage advanced biotechnological innovations such as gene editing and personalized medicine to enhance treatment efficacy and target specific diseases at the molecular level. Nutraceuticals are increasingly incorporating novel delivery systems like nanoencapsulation to improve bioavailability and therapeutic potential of natural compounds. Future directions emphasize the convergence of pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals through integrative approaches, utilizing AI-driven drug discovery and omics technologies to develop precision prevention and wellness strategies.
Choosing Between Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals
Choosing between pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals requires evaluating the specific health condition, desired outcomes, and evidence supporting efficacy and safety. Pharmaceuticals offer targeted treatment with rigorous clinical testing and standardized dosages, making them suitable for acute or severe medical issues. Nutraceuticals, derived from food sources and containing bioactive compounds, provide preventive health benefits and support overall wellness with fewer side effects but often less stringent regulation.
Related Important Terms
Pharmaconutritional Synergy
Pharmaconutritional synergy combines the targeted therapeutic effects of pharmaceuticals with the preventive and holistic benefits of nutraceuticals, optimizing patient outcomes through enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects. Integrating pharmaconutritional strategies supports improved metabolic pathways and immune modulation, fostering comprehensive health management and personalized treatment plans.
Biopharmaceuticals
Biopharmaceuticals are a subset of pharmaceuticals derived from biological sources using biotechnology, playing a crucial role in treating complex diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and genetic conditions. Unlike nutraceuticals, which are dietary supplements aimed at promoting general health, biopharmaceuticals undergo rigorous clinical trials and regulatory approval to ensure their safety and efficacy in targeted medical therapies.
Nutricosmetics
Nutricosmetics, a subset of nutraceuticals, combine the benefits of pharmaceuticals and nutrition by delivering bioactive compounds that enhance skin health from within, targeting aging, hydration, and elasticity. Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals focused on treating diseases, nutricosmetics emphasize preventive care and beauty enhancement through vitamins, antioxidants, and collagen peptides, leveraging scientific advancements in biochemistry and dermatology.
Plant-derived APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients)
Plant-derived APIs in pharmaceuticals offer highly specific therapeutic effects supported by rigorous clinical trials and standardized dosages, ensuring efficacy and safety in treating diseases. Nutraceuticals, while also sourced from plants, primarily provide health benefits through bioactive compounds aimed at prevention and wellness, often lacking the strict regulatory oversight characteristic of pharmaceuticals.
Nutrigenomics
Nutraceuticals, derived from food sources with extra health benefits, interact directly with an individual's genetic makeup to modulate gene expression, a field known as nutrigenomics. Unlike pharmaceuticals that target specific biochemical pathways to treat diseases, nutraceuticals aim to prevent or reduce disease risk by influencing genetic predispositions through diet-based interventions.
Bioavailability Enhancement
Pharmaceuticals utilize advanced drug delivery systems such as liposomes and nanoparticles to significantly enhance bioavailability, ensuring precise dosing and rapid therapeutic effects. Nutraceuticals primarily rely on natural absorption enhancers like piperine and formulation techniques such as emulsions to improve bioavailability, aiming to optimize nutrient uptake for preventive health benefits.
Functional Excipients
Pharmaceuticals use functional excipients to enhance drug stability, bioavailability, and targeted delivery through precise formulation techniques. Nutraceuticals rely on natural functional excipients like fibers and bio-polymers to improve nutrient absorption and support health benefits with minimal additives.
Personalized Nutraceuticals
Personalized nutraceuticals utilize genetic, metabolic, and lifestyle data to tailor supplements that optimize individual health outcomes, offering a targeted approach compared to the one-size-fits-all model of traditional pharmaceuticals. This customized strategy enhances efficacy in disease prevention and wellness by addressing specific nutrient needs and biological variations.
Liposomal Encapsulation
Liposomal encapsulation enhances the bioavailability of both pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals by protecting active ingredients from degradation and promoting targeted delivery to cells. This technology significantly improves the absorption of vitamins, minerals, and drugs, making treatments more effective and reducing required dosages.
Pharmanutrition
Pharmanutrition integrates pharmaceutical principles with nutraceuticals to develop targeted nutritional therapies that enhance drug efficacy and patient outcomes in chronic disease management. Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals that primarily treat symptoms, pharmanutrition leverages bioactive compounds in nutraceuticals to modulate metabolic pathways and support systemic health at the molecular level.
Pharmaceuticals vs Nutraceuticals Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com