Population health analytics evaluates health outcomes across large groups, identifying trends and disparities to improve overall community well-being. SDoH (Social Determinants of Health) analytics delves deeper by examining factors like socioeconomic status, environment, and access to care that influence individual and population health. Integrating both approaches enhances targeted interventions and promotes more equitable pet health management.
Table of Comparison
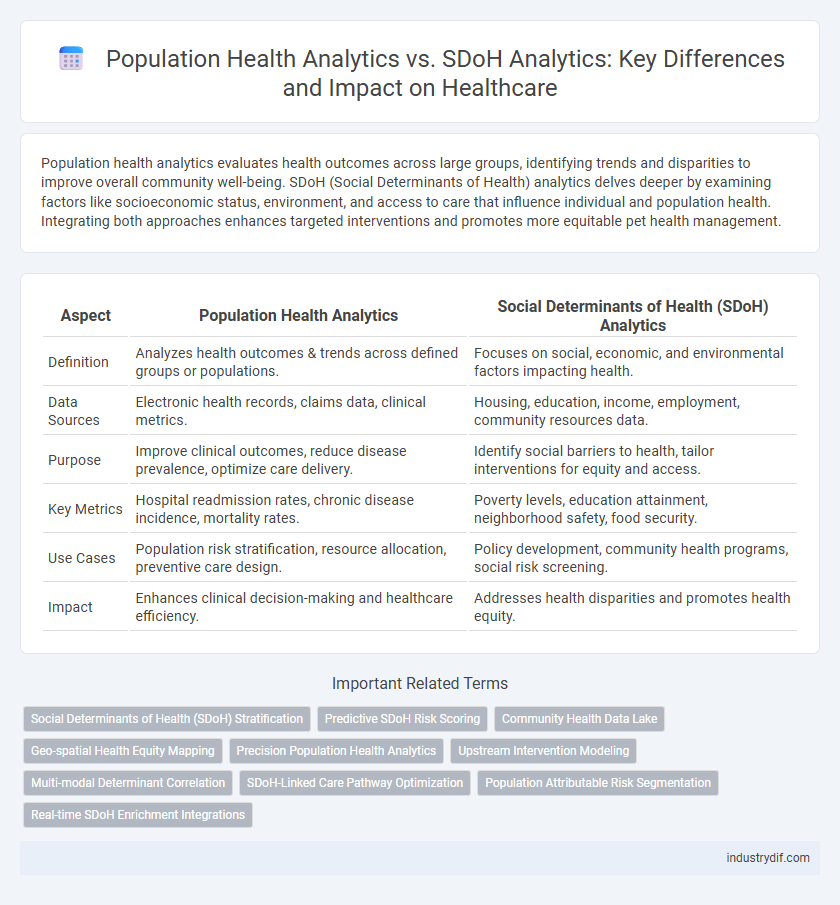
| Aspect | Population Health Analytics | Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes health outcomes & trends across defined groups or populations. | Focuses on social, economic, and environmental factors impacting health. |
| Data Sources | Electronic health records, claims data, clinical metrics. | Housing, education, income, employment, community resources data. |
| Purpose | Improve clinical outcomes, reduce disease prevalence, optimize care delivery. | Identify social barriers to health, tailor interventions for equity and access. |
| Key Metrics | Hospital readmission rates, chronic disease incidence, mortality rates. | Poverty levels, education attainment, neighborhood safety, food security. |
| Use Cases | Population risk stratification, resource allocation, preventive care design. | Policy development, community health programs, social risk screening. |
| Impact | Enhances clinical decision-making and healthcare efficiency. | Addresses health disparities and promotes health equity. |
Defining Population Health: Core Concepts
Population health centers on improving health outcomes and quality of life for entire groups by addressing broad factors such as genetics, behavior, and environment. Core concepts include measuring health indicators, tracking disparities across demographics, and integrating clinical data with social determinants of health (SDoH) analytics. This approach enables tailored interventions by understanding how social, economic, and environmental factors influence community health risks and resources.
Understanding Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) Analytics
Understanding Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) analytics involves analyzing factors such as socioeconomic status, education, neighborhood conditions, and access to healthcare that directly influence population health outcomes. Advanced SDoH analytics leverage data integration and machine learning to identify high-risk communities and target interventions more effectively. Insights from SDoH analytics enable healthcare providers and policymakers to address root causes of health disparities and improve overall community well-being.
Key Differences: Population Health vs SDoH Analytics
Population health analytics focuses on assessing health outcomes and disease patterns across defined groups, using clinical and demographic data to improve healthcare interventions. Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) analytics examines non-medical factors such as socioeconomic status, education, and environment that influence health outcomes and disparities. Key differences lie in the data sources and focus areas, with population health emphasizing clinical metrics and SDoH analytics prioritizing the social and economic contexts affecting health.
Data Sources in Population Health Management
Population Health Management relies heavily on diverse data sources such as electronic health records (EHRs), insurance claims, and patient-generated health data to provide comprehensive insights into patient populations. Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) analytics incorporate external data sets like census data, housing quality indices, education levels, and environmental factors to evaluate non-clinical influences on health outcomes. Integrating clinical and SDoH data sources enhances predictive modeling and targeted interventions, improving care coordination and reducing health disparities.
Collecting and Integrating SDoH Data
Collecting and integrating Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) data enhances population health analytics by providing a comprehensive understanding of factors such as socioeconomic status, education, and community environment. Advanced data integration techniques combine electronic health records, census data, and patient-reported outcomes to identify health disparities and target interventions more effectively. Leveraging machine learning models with diverse SDoH datasets improves predictive accuracy for population health management and personalized care strategies.
Measuring Outcomes: Metrics and KPIs
Measuring outcomes in Population Health and Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) analytics involves distinct yet complementary metrics and KPIs that assess overall health improvements and underlying social factors influencing health disparities. Population Health metrics often focus on clinical outcomes, hospitalization rates, and chronic disease prevalence, while SDoH analytics prioritize indicators such as housing stability, education levels, and access to nutritious food. Integrating these data points supports comprehensive evaluations of intervention effectiveness and guides targeted strategies to improve community health equity.
Role of Technology in Health Analytics
Technology in health analytics enables advanced data integration and real-time monitoring, improving population health management by identifying disease patterns and risk factors at a large scale. In SDoH analytics, technology facilitates the collection and analysis of social, economic, and environmental data, revealing critical determinants that influence health outcomes beyond clinical care. Machine learning algorithms and AI-driven platforms enhance predictive capabilities, supporting targeted interventions and resource allocation to address health disparities effectively.
Challenges in Implementing Population Health Initiatives
Implementing population health initiatives faces challenges such as integrating diverse data sources from electronic health records (EHR), social determinants of health (SDoH), and community resources to create a holistic view of patient populations. Addressing data privacy concerns, inconsistent data quality, and limited interoperability hampers effective analytics and decision-making processes. Furthermore, aligning multidisciplinary teams and securing sustainable funding present significant barriers to deploying scalable, technology-driven population health programs focused on improving health outcomes and reducing disparities.
Impact of SDoH Analytics on Health Equity
Social determinants of health (SDoH) analytics provide critical insights into factors such as socioeconomic status, education, and neighborhood conditions, directly influencing health outcomes and disparities. Leveraging SDoH data enables targeted interventions that address root causes of inequities, thereby advancing health equity across diverse populations. Integrating SDoH analytics into population health strategies improves resource allocation and policy development, enhancing overall community well-being.
Future Trends in Population Health and SDoH Analytics
Emerging trends in population health and social determinants of health (SDoH) analytics emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance predictive modeling and personalized care interventions. Advanced data linkage techniques facilitate real-time monitoring of community health patterns, enabling proactive resource allocation and policy development. Future innovations prioritize equity-driven analytics to address health disparities, harnessing diverse datasets to improve outcomes across socioeconomically varied populations.
Related Important Terms
Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) Stratification
Population health analytics integrates Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) stratification to identify and prioritize at-risk groups based on socioeconomic factors, enhancing targeted interventions and resource allocation. Advanced SDoH stratification models analyze data such as income, education, housing stability, and access to care to predict health outcomes and reduce disparities across communities.
Predictive SDoH Risk Scoring
Predictive SDoH risk scoring leverages social determinants of health data to identify individuals at higher risk for adverse health outcomes, enabling targeted interventions that improve population health management. Integrating SDoH analytics with clinical and demographic data enhances accuracy in risk stratification, reducing hospital readmissions and lowering healthcare costs.
Community Health Data Lake
Population Health analytics aggregates broad health metrics from diverse demographics, while SDoH Analytics specifically examines Social Determinants of Health to identify community factors affecting well-being. A Community Health Data Lake integrates these datasets, enabling comprehensive analysis that supports targeted interventions and policy development for improved population outcomes.
Geo-spatial Health Equity Mapping
Geo-spatial Health Equity Mapping leverages population health data and Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) analytics to identify health disparities and resource gaps across different regions, enabling targeted interventions. Integrating these analytics improves health outcomes by visualizing geographic patterns of disease prevalence, healthcare access, and social risk factors that influence community well-being.
Precision Population Health Analytics
Precision Population Health Analytics integrates granular social determinants of health (SDoH) data with clinical and behavioral metrics to tailor interventions for diverse populations, enhancing health outcomes and reducing disparities. This approach leverages advanced data modeling and machine learning to predict risks and optimize resource allocation, moving beyond traditional population health analytics that often overlook contextual socioeconomic factors.
Upstream Intervention Modeling
Population health analytics integrates large-scale data to identify health trends, while Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) analytics focus on upstream factors such as socioeconomic status, education, and environment that influence these trends. Upstream intervention modeling uses SDoH insights to simulate potential public health strategies, optimizing resource allocation and improving outcomes by addressing root causes rather than downstream symptoms.
Multi-modal Determinant Correlation
Population health analytics integrates clinical data, behavioral patterns, and environmental factors to assess health outcomes across diverse groups, while SDoH (Social Determinants of Health) analytics emphasizes socio-economic variables like income, education, and housing stability. Multi-modal determinant correlation enhances predictive accuracy by linking these heterogeneous data types, revealing complex interactions and enabling targeted interventions for improved community health management.
SDoH-Linked Care Pathway Optimization
SDoH-linked care pathway optimization leverages social determinants of health data to tailor interventions addressing socioeconomic factors impacting patient outcomes, improving healthcare equity and reducing readmission rates. Integrating SDoH analytics within population health management enables targeted resource allocation and personalized care plans, enhancing clinical effectiveness and patient engagement.
Population Attributable Risk Segmentation
Population Attributable Risk Segmentation in Population Health integrates Social Determinants of Health (SDoH) analytics to identify high-risk groups by quantifying the proportion of disease incidence attributable to specific social factors. This approach enhances targeted intervention strategies by linking population-level risk assessments with SDoH data, improving resource allocation and health outcome predictions.
Real-time SDoH Enrichment Integrations
Real-time SDoH enrichment integrations enhance population health analytics by incorporating dynamic social determinants of health data, enabling targeted interventions and improved patient outcomes. Leveraging APIs and machine learning models for continuous SDoH data updates allows healthcare systems to address social risks promptly and personalize care strategies effectively.
Population Health vs SDoH Analytics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com