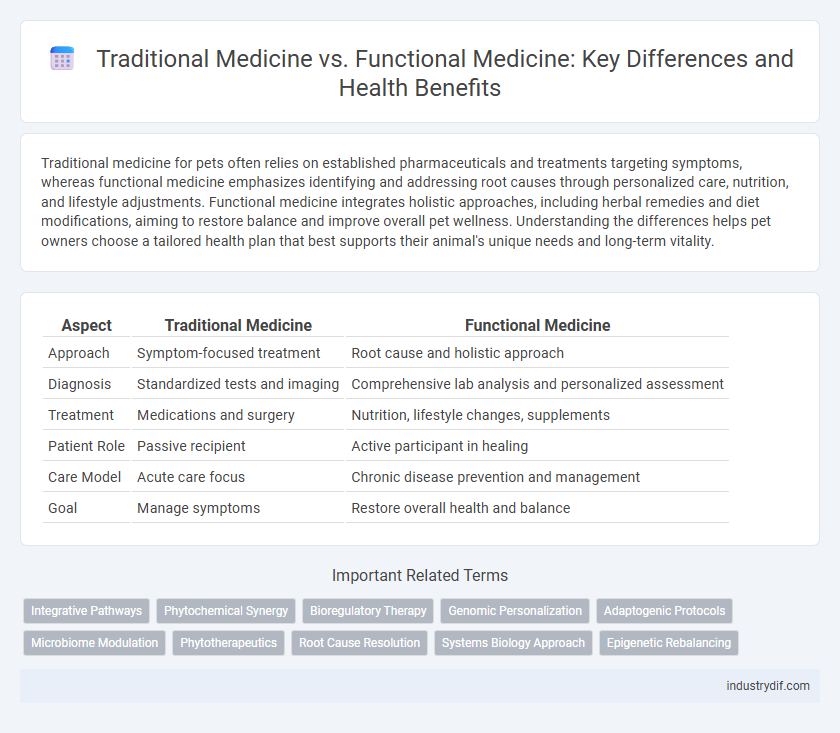
Traditional medicine for pets often relies on established pharmaceuticals and treatments targeting symptoms, whereas functional medicine emphasizes identifying and addressing root causes through personalized care, nutrition, and lifestyle adjustments. Functional medicine integrates holistic approaches, including herbal remedies and diet modifications, aiming to restore balance and improve overall pet wellness. Understanding the differences helps pet owners choose a tailored health plan that best supports their animal's unique needs and long-term vitality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Medicine | Functional Medicine |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Symptom-focused treatment | Root cause and holistic approach |
| Diagnosis | Standardized tests and imaging | Comprehensive lab analysis and personalized assessment |
| Treatment | Medications and surgery | Nutrition, lifestyle changes, supplements |
| Patient Role | Passive recipient | Active participant in healing |
| Care Model | Acute care focus | Chronic disease prevention and management |
| Goal | Manage symptoms | Restore overall health and balance |
Defining Traditional Medicine and Functional Medicine
Traditional medicine encompasses long-established healing practices rooted in cultural beliefs, often utilizing herbal remedies, acupuncture, and holistic approaches to diagnose and treat illness. Functional medicine focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of disease through personalized treatment plans, integrating advanced diagnostics, lifestyle modifications, and patient-centered care. Both approaches emphasize holistic health but differ significantly in methodology, evidence base, and individualization of treatment.
Historical Roots of Traditional Medicine
Traditional medicine, deeply rooted in ancient civilizations such as Ayurveda from India and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), relies on natural remedies and holistic approaches developed over thousands of years, emphasizing balance and harmony within the body. Functional medicine, by contrast, is a modern, science-based practice that emerged in the late 20th century, focusing on identifying and addressing the root causes of chronic diseases through personalized treatment plans. The historical roots of traditional medicine provide a rich foundation of empirical knowledge, integrating herbal medicine, acupuncture, and spiritual practices passed down through generations.
Principles and Approaches in Functional Medicine
Functional medicine emphasizes personalized care by addressing the root causes of disease through a systems biology approach, integrating genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This approach prioritizes patient-centered collaboration and utilizes advanced diagnostics to tailor interventions that restore balance and optimize health. Unlike traditional medicine which often targets symptoms, functional medicine seeks to enhance overall well-being by promoting long-term prevention and self-healing mechanisms.
Diagnostic Techniques: Traditional vs Functional
Traditional medicine relies heavily on symptom-based diagnosis and standardized laboratory tests, often focusing on identifying and treating specific diseases. Functional medicine employs a more comprehensive diagnostic approach, utilizing advanced biomarkers, genetic testing, and detailed patient histories to uncover underlying root causes and imbalances. This personalized diagnostic process aims to address systemic dysfunctions and promote long-term wellness rather than merely managing symptoms.
Treatment Modalities in Both Systems
Traditional medicine utilizes time-honored treatment modalities such as herbal remedies, acupuncture, and manual therapies that have been passed down through generations, emphasizing symptom relief and restoring balance. Functional medicine focuses on personalized treatment plans using advanced diagnostics, nutrition, lifestyle modifications, and targeted supplementation to address root causes and promote systemic health. Both approaches integrate patient history and holistic perspectives but differ in methodology, with traditional medicine relying on empirical knowledge and functional medicine on contemporary scientific research.
Patient-Centered Care: Contrasting Perspectives
Traditional medicine emphasizes standardized protocols and symptom suppression, often focusing on disease diagnosis and treatment. Functional medicine prioritizes individualized care by investigating root causes of illness and addressing complex interactions within the body. This patient-centered approach in functional medicine fosters personalized treatment plans tailored to unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Evidence Base: Research and Clinical Outcomes
Traditional medicine often relies on centuries-old practices and anecdotal evidence, with limited rigorous clinical trials to substantiate efficacy. Functional medicine emphasizes a systems biology approach supported by emerging research and personalized diagnostics, showing promise in chronic disease management through data-driven interventions. Clinical outcomes in functional medicine are increasingly documented in peer-reviewed studies, whereas traditional medicine's evidence base varies significantly depending on the specific modality and geographic region.
Integrating Traditional and Functional Medicine
Integrating traditional medicine with functional medicine offers a comprehensive approach that combines time-tested herbal remedies and holistic practices with personalized, science-based diagnostics and treatments. This synergy enhances patient outcomes by addressing root causes of illness while respecting cultural health practices and individual variability. Health practitioners employing this integrated model optimize wellness through tailored interventions that leverage both the natural pharmacology of traditional methods and the precision of functional medicine.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Traditional medicine benefits from well-established protocols and broad accessibility, supported by extensive clinical research and regulatory frameworks. Functional medicine emphasizes personalized care and root-cause diagnosis, integrating lifestyle, genetic, and environmental factors for a holistic approach. Limitations of traditional medicine include symptom-focused treatments and potential side effects, while functional medicine may face challenges in insurance coverage and requires longer patient commitment.
Future Trends in Health and Medicine
Future trends in health and medicine emphasize the integration of traditional medicine's holistic approaches with functional medicine's personalized, systems-based strategies. Advances in genomics, artificial intelligence, and biomarker analysis enable more precise treatments that combine herbal remedies and ancient practices with cutting-edge diagnostic tools. This convergence fosters a comprehensive, patient-centered care model that addresses root causes of disease and promotes long-term wellness.
Related Important Terms
Integrative Pathways
Traditional medicine relies on established practices like herbal treatments and acupuncture, emphasizing symptom management and cultural healing methods. Functional medicine integrates these approaches with modern diagnostics and personalized care, creating holistic and patient-centered therapeutic pathways that address root causes.
Phytochemical Synergy
Phytochemical synergy in traditional medicine leverages the combined effects of multiple plant compounds to enhance therapeutic outcomes, often involving whole herbs or complex mixtures that act on various biological pathways. Functional medicine applies this concept by integrating targeted phytochemicals into personalized treatment plans, optimizing bioavailability and interactions for improved patient-specific health benefits.
Bioregulatory Therapy
Bioregulatory therapy, a key component of functional medicine, emphasizes the body's innate ability to heal by restoring balance through targeted interventions like herbal medicine, homeopathy, and acupuncture. Unlike traditional medicine's symptomatic approach, this therapy integrates personalized diagnostics and holistic treatments to address root causes and promote long-term wellness.
Genomic Personalization
Genomic personalization in traditional medicine often relies on ancestral knowledge and broad genetic markers, while functional medicine integrates advanced genomic sequencing to tailor treatments to individual genetic variations for optimized health outcomes. This precision approach in functional medicine enhances disease prevention and management by targeting specific molecular pathways influenced by a person's unique genome.
Adaptogenic Protocols
Adaptogenic protocols in traditional medicine utilize herbs like Ashwagandha and Rhodiola to restore balance and support the body's natural stress response, emphasizing holistic and empirical applications. Functional medicine integrates these adaptogens with personalized diagnostics and lifestyle interventions to target root causes of dysfunction and optimize individual resilience.
Microbiome Modulation
Traditional medicine often relies on herbal remedies and established protocols to support microbiome balance, emphasizing symptom relief and broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects, while functional medicine prioritizes personalized microbiome modulation through targeted probiotics, diet adjustments, and lifestyle interventions to restore gut health and optimize immune function. Recent studies highlight functional medicine's focus on individualized gut microbiota profiling to develop tailored treatments that promote microbial diversity and enhance metabolic pathways critical for disease prevention and overall wellness.
Phytotherapeutics
Phytotherapeutics in traditional medicine utilize plant-based remedies rooted in centuries-old practices, emphasizing holistic treatment of symptoms and overall balance. Functional medicine integrates phytotherapeutic compounds with personalized diagnostics to target underlying causes of illness and optimize physiological function.
Root Cause Resolution
Traditional medicine primarily addresses symptoms through standardized treatments, while functional medicine emphasizes identifying and resolving the root causes of illness by examining genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Functional medicine offers personalized care plans that target underlying dysfunctions, promoting long-term health and disease prevention.
Systems Biology Approach
Traditional medicine often relies on symptom-based treatments and isolated interventions, whereas functional medicine employs a systems biology approach that considers complex interactions within the body's molecular, cellular, and organ systems to identify root causes of disease. This integrative model emphasizes personalized diagnostics and therapeutic strategies by analyzing genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors to restore systemic balance and optimize overall health.
Epigenetic Rebalancing
Traditional medicine typically targets symptom management through established protocols, whereas functional medicine emphasizes epigenetic rebalancing by addressing underlying genetic expressions and environmental factors to optimize health. Functional medicine utilizes personalized interventions such as nutrition, lifestyle changes, and supplements to modulate gene expression and promote long-term wellness.
Traditional Medicine vs Functional Medicine Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com