Information democratization empowers individuals to access, interpret, and utilize knowledge effectively, promoting informed decision-making across organizations. Data democratization involves making raw data widely available but often requires specialized skills to analyze and transform it into meaningful insights. Prioritizing information democratization ensures that users receive actionable knowledge, while data democratization focuses on broad data availability without guaranteed comprehension or utility.
Table of Comparison
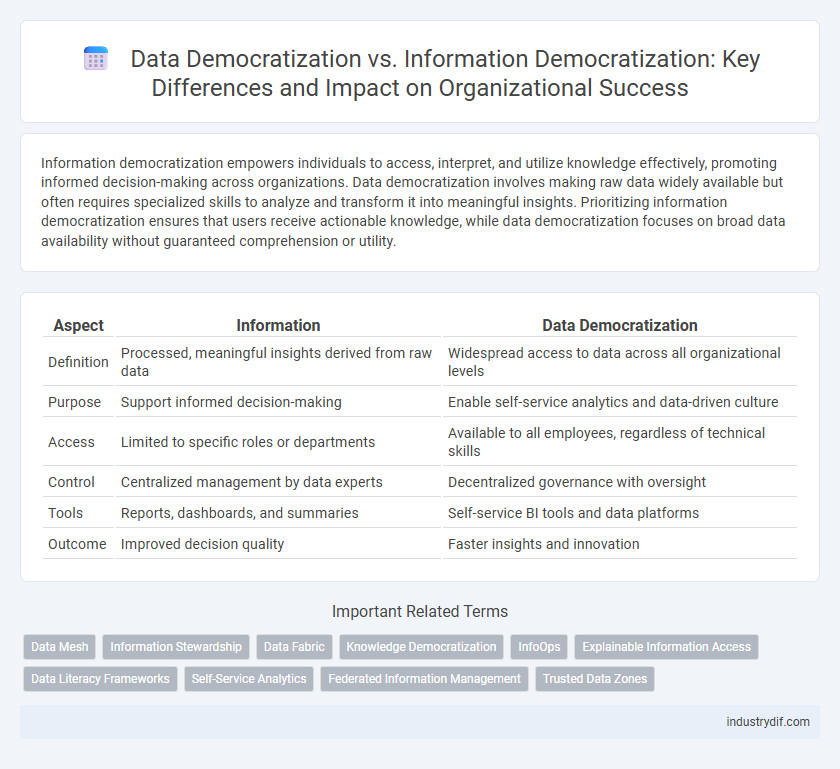
| Aspect | Information | Data Democratization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processed, meaningful insights derived from raw data | Widespread access to data across all organizational levels |
| Purpose | Support informed decision-making | Enable self-service analytics and data-driven culture |
| Access | Limited to specific roles or departments | Available to all employees, regardless of technical skills |
| Control | Centralized management by data experts | Decentralized governance with oversight |
| Tools | Reports, dashboards, and summaries | Self-service BI tools and data platforms |
| Outcome | Improved decision quality | Faster insights and innovation |
Understanding Information and Data: Key Definitions
Information refers to processed, organized data that provides meaning and context, enabling decision-making and insight generation. Data democratization involves making raw data accessible to a broader audience, promoting transparency and innovation through user empowerment. Understanding the distinction between data as raw facts and information as meaningful interpretation is essential for effective data management and organizational intelligence.
The Evolution from Data Democratization to Information Democratization
Data democratization enabled wider access to raw datasets across organizations, breaking down silos and encouraging data-driven decision-making. The evolution to information democratization emphasizes providing actionable insights and contextual understanding rather than just raw data, enhancing user comprehension and strategic application. This shift leverages advanced analytics, natural language processing, and visualization tools to transform data into meaningful information accessible to all business levels.
Core Principles of Data Democratization
Data democratization centers on granting all employees access to data without barriers, promoting transparency and fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making. Core principles include ensuring data accessibility, maintaining data quality, and providing user-friendly tools to enable non-technical users to analyze and interpret data effectively. Emphasizing data governance and security safeguards ensures that data democratization balances openness with compliance and protection.
Core Principles of Information Democratization
Information democratization emphasizes accessibility, ensuring that individuals across all organizational levels obtain meaningful insights without gatekeeping. It prioritizes data literacy, empowering users to interpret and apply information effectively for decision-making. Transparent governance and robust security protocols maintain data integrity while promoting an open information culture.
Comparing Data Access and Information Usability
Data democratization emphasizes broad access to raw data across an organization, enabling diverse users to extract insights independently. Information usability focuses on refining this data into meaningful, contextualized knowledge that is easily interpretable and actionable for decision-making. While data access drives inclusivity in data exploration, information usability ensures accuracy, relevance, and practical application of the derived insights.
Benefits and Challenges of Data Democratization
Data democratization enhances organizational agility by enabling broader access to data, leading to more informed decision-making and innovation across departments. However, challenges include ensuring data quality, maintaining security protocols, and providing adequate training to prevent misuse or misinterpretation. Overcoming these barriers results in empowered employees and a competitive advantage through faster insights and collaborative analytics.
Advantages and Pitfalls of Information Democratization
Information democratization enhances organizational agility by enabling employees at all levels to access and utilize critical insights, fostering innovation and informed decision-making. However, unrestricted access can lead to data misinterpretation, security vulnerabilities, and information overload, potentially compromising data integrity and operational efficiency. Implementing robust governance frameworks and role-based access controls mitigates these pitfalls while maximizing the benefits of widespread information availability.
Organizational Impact: Data vs Information Democratization
Data democratization empowers all organizational levels with raw datasets, increasing accessibility but often overwhelming users lacking context or analytical skills. Information democratization transforms data into actionable insights, enhancing decision-making and fostering a culture of informed collaboration across departments. Organizations embracing information democratization experience improved efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage by enabling employees to leverage meaningful knowledge rather than mere data access.
Best Practices for Implementing Democratization Strategies
Implementing data democratization strategies requires establishing clear governance policies to ensure data accuracy, security, and compliance across all organizational levels. Empowering employees with user-friendly analytics tools and comprehensive training promotes informed decision-making and drives business innovation. Continuous monitoring and feedback loops enhance data quality and accessibility, fostering a culture of transparency and collaborative problem-solving.
Future Trends in Information and Data Democratization
Future trends in information and data democratization emphasize the widespread adoption of AI-driven analytics platforms that enable non-technical users to extract actionable insights. Cloud-based data sharing ecosystems are evolving to enhance real-time collaboration and governance across global decentralized teams. Advances in data privacy technologies, such as differential privacy and federated learning, are shaping secure and compliant democratization practices in highly regulated industries.
Related Important Terms
Data Mesh
Data Mesh is a decentralized approach to data democratization that emphasizes domain-oriented ownership, self-serve data infrastructure, and federated governance to enable scalable data access across organizations. By treating data as a product and distributing responsibilities, Data Mesh contrasts traditional centralized data platforms, empowering teams to manage and utilize data more autonomously.
Information Stewardship
Information stewardship ensures responsible management and governance of data, emphasizing accuracy, privacy, and compliance across organizational processes. While data democratization promotes broad access to raw datasets, effective information stewardship transforms that data into reliable, actionable insights to drive informed decision-making.
Data Fabric
Data Fabric enables seamless integration and management of distributed data sources, enhancing data democratization by providing consistent, real-time access to reliable information across the organization. This approach transforms raw data into meaningful insights, fostering informed decision-making and operational agility.
Knowledge Democratization
Knowledge democratization empowers individuals and organizations by transforming raw data and fragmented information into accessible, actionable insights, fostering informed decision-making across all levels. Unlike data democratization, which emphasizes broad access to data sets, knowledge democratization prioritizes the contextual understanding and practical application of information to drive innovation and collaboration.
InfoOps
Information democratization empowers users with accessible, governed knowledge, while data democratization focuses on broad access to raw datasets; InfoOps integrates both by operationalizing information workflows, ensuring data quality, security, and usability across decentralized teams for strategic decision-making. This approach aligns data governance with user-centric insights, enabling organizations to leverage information as an actionable asset throughout the enterprise.
Explainable Information Access
Explainable Information Access enhances data democratization by providing transparent and interpretable insights, enabling users of varying expertise to make informed decisions confidently. This approach bridges the gap between raw data and actionable knowledge, ensuring that information is understandable, trustworthy, and accessible across organizational levels.
Data Literacy Frameworks
Data literacy frameworks are essential for effective data democratization, enabling individuals to interpret, analyze, and utilize data confidently across various organizational levels. These frameworks establish standardized skills, best practices, and educational resources that transform raw data into actionable information, fostering informed decision-making and a data-driven culture.
Self-Service Analytics
Self-service analytics empowers users across an organization to independently access and analyze data without relying on IT, driving faster decision-making and fostering a culture of data democratization. By providing intuitive tools and centralized data platforms, enterprises transform raw data into actionable information accessible to all stakeholders, enhancing transparency and business agility.
Federated Information Management
Federated Information Management enhances information democratization by enabling decentralized control and access to diverse data sources while maintaining data privacy and governance. This approach contrasts with traditional data democratization by prioritizing data ownership retention and metadata integration across distributed systems for seamless information retrieval.
Trusted Data Zones
Trusted Data Zones establish secure environments that ensure data democratization by providing controlled access to verified, high-quality information, enabling users to confidently leverage data for decision-making. This approach enhances information governance while balancing accessibility with compliance and data privacy requirements.
Information vs Data Democratization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com