Information refers to raw data that is collected, processed, and disseminated to support decision-making and communication. Infonomics explores the economic value of information as a tangible asset, emphasizing its role in driving business strategy, innovation, and competitive advantage. Understanding the distinction between mere information and its monetization through infonomics is crucial for organizations aiming to leverage data as a strategic resource.
Table of Comparison
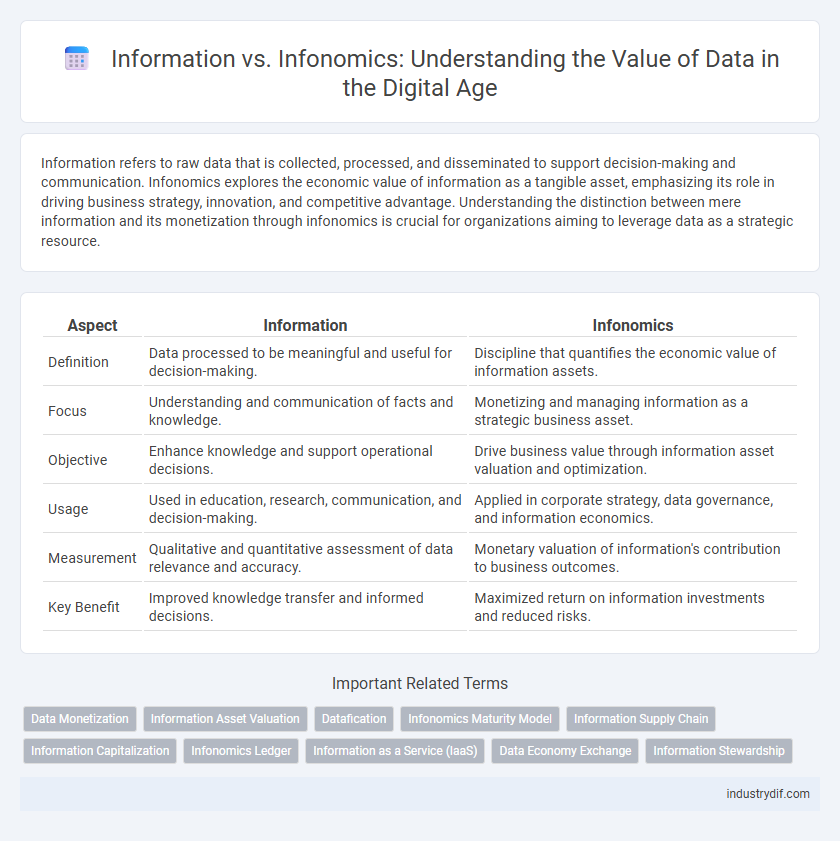
| Aspect | Information | Infonomics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data processed to be meaningful and useful for decision-making. | Discipline that quantifies the economic value of information assets. |
| Focus | Understanding and communication of facts and knowledge. | Monetizing and managing information as a strategic business asset. |
| Objective | Enhance knowledge and support operational decisions. | Drive business value through information asset valuation and optimization. |
| Usage | Used in education, research, communication, and decision-making. | Applied in corporate strategy, data governance, and information economics. |
| Measurement | Qualitative and quantitative assessment of data relevance and accuracy. | Monetary valuation of information's contribution to business outcomes. |
| Key Benefit | Improved knowledge transfer and informed decisions. | Maximized return on information investments and reduced risks. |
Defining Information: Concepts and Characteristics
Information represents organized data that conveys meaning and reduces uncertainty through context, structure, and relevance. Core characteristics of information include accuracy, timeliness, completeness, and accessibility, which determine its value and usability. Infonomics extends this by treating information as a quantifiable business asset, emphasizing its economic impact and strategic management within organizations.
Infonomics Explained: The Economics of Information
Infonomics explains how information is treated as a valuable economic asset, quantifying its impact on business performance and decision-making. It emphasizes measuring information's value, cost, and risk to optimize data management and drive competitive advantage. Organizations adopting infonomics integrate data valuation methods to maximize returns from their information resources.
Key Differences Between Information and Infonomics
Information refers to raw data processed to provide meaning, serving as the foundation for decision-making and knowledge creation. Infonomics treats information as a strategic asset, emphasizing its economic value, governance, and measurement within organizational contexts. Key differences include Information's role as data-based insight versus Infonomics' focus on monetizing and managing information to drive business value.
The Value Proposition: Information vs Infonomics
The value proposition of Information centers on its role as raw data that supports decision-making and operational efficiency within organizations. Infonomics, however, advances this by treating information as a strategic asset, emphasizing its monetization, governance, and valuation to drive competitive advantage and business growth. This approach quantifies information's economic impact, transforming it from a mere resource into a measurable source of enterprise value.
Measuring Information: Metrics and Methodologies
Measuring information requires robust metrics such as data quality, accuracy, completeness, and timeliness to evaluate its value and effectiveness within organizations. Infonomics emphasizes quantitative methodologies like information valuation models, data ROI analysis, and information lifecycle assessments to optimize data as a strategic asset. These approaches enable businesses to drive informed decisions and enhance competitive advantage through precise information measurement.
Infonomics: Impact on Business Decision-Making
Infonomics transforms data into a strategic asset by quantifying the economic value of information, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions that enhance competitive advantage. Its impact on business decision-making lies in optimizing information management, improving risk assessment, and driving innovation through actionable insights. By treating information as a quantifiable asset, companies can better allocate resources, measure ROI on data initiatives, and foster data governance aligned with organizational goals.
Information Ownership and Governance
Information ownership establishes legal and ethical rights over data, defining who controls, accesses, and utilizes it within organizations. Infonomics integrates economic principles into information governance, treating data as a tangible asset with measurable value and accountability. Effective governance frameworks align ownership with strategic data management to maximize business value and mitigate risks.
Information as an Asset: Infonomics Perspective
Information as an asset represents a critical organizational resource that drives strategic decision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage. From an Infonomics perspective, the value of data and information must be quantified, managed, and optimized similarly to physical or financial assets. This approach emphasizes measuring information's economic impact, ensuring data quality, and leveraging information capital to enhance business performance and agility.
Real-World Applications of Infonomics in Industry
Infonomics transforms traditional information management by treating data as a strategic asset with measurable economic value, driving innovation and efficiency across industries. In healthcare, it enables personalized treatment plans through data monetization and analytics, improving patient outcomes while optimizing costs. Manufacturing leverages infonomics to enhance supply chain transparency and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and maximizing profitability through data-driven decision-making.
Future Trends in Information Management and Infonomics
Future trends in information management emphasize AI-driven analytics, real-time data processing, and enhanced data governance frameworks to optimize decision-making and operational efficiency. Infonomics integrates information as a strategic asset, focusing on monetization, valuation, and risk management to drive competitive advantage in digital economies. Emerging technologies like blockchain and machine learning enable organizations to transform raw data into valuable information products, shaping the future landscape of both fields.
Related Important Terms
Data Monetization
Information represents raw data collected from various sources, while Infonomics emphasizes the strategic management and monetization of that data as a critical business asset. Data monetization involves transforming information into measurable financial value through analytics, licensing, or targeted marketing, driving competitive advantage and revenue growth.
Information Asset Valuation
Information asset valuation quantifies the economic value of data as a strategic business resource, integrating methods from Infonomics to assess data's impact on organizational performance and decision-making. Accurate valuation drives informed investment in data governance, security, and monetization, enhancing competitive advantage through optimized information management.
Datafication
Datafication transforms raw information into structured, quantifiable data that drives business intelligence and decision-making. Infonomics examines the economic value of this data as a strategic asset, emphasizing its role beyond traditional information management.
Infonomics Maturity Model
The Infonomics Maturity Model assesses an organization's ability to leverage data as a strategic asset, emphasizing stages from basic data awareness to advanced data monetization and governance. This model guides enterprises in optimizing information value by integrating data management, analytics, and economic principles to drive informed business decisions.
Information Supply Chain
The Information Supply Chain manages the flow, transformation, and distribution of data to ensure accuracy and accessibility throughout an organization, differing from Infonomics by emphasizing operational processes rather than data valuation and monetization. Optimizing the Information Supply Chain enhances data quality, reduces redundancy, and supports informed decision-making by aligning information management with business goals.
Information Capitalization
Information capitalization transforms raw data into valuable assets by systematically managing and leveraging information to drive business growth and innovation. Infonomics quantifies information as a strategic economic resource, emphasizing measurement, governance, and exploitation to maximize its value within organizational ecosystems.
Infonomics Ledger
Infonomics Ledger optimizes the monetization and management of information assets by applying data-driven accounting principles to track data value, usage, and compliance systematically. This approach surpasses traditional information handling by transforming data into a measurable economic resource, enhancing strategic decision-making and operational efficiency.
Information as a Service (IaaS)
Information as a Service (IaaS) delivers scalable, on-demand access to data resources via cloud-based platforms, enabling organizations to efficiently manage, analyze, and leverage information for strategic decision-making. Unlike Infonomics, which emphasizes the economic value of information as an asset, IaaS focuses on the operational delivery and integration of information services to optimize business processes.
Data Economy Exchange
Information represents raw, unprocessed facts critical for decision-making, while Infonomics treats information as a quantifiable economic asset driving value creation and competitive advantage. The Data Economy Exchange facilitates the trading and monetization of data assets, enabling organizations to optimize information use and capitalize on data-driven opportunities within dynamic digital markets.
Information Stewardship
Information stewardship emphasizes the ethical management, governance, and utilization of data to optimize organizational value, aligning closely with Infonomics principles that treat information as a strategic asset. Effective stewardship integrates data quality, privacy, and security measures, fostering trust and enabling data-driven decision-making within the framework of Infonomics.
Information vs Infonomics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com