IT Governance structures policies and frameworks to ensure effective management and control of IT resources, aligning technology with business objectives. Data Fabric integrates and orchestrates data across various platforms, providing seamless access and real-time insights through a unified architecture. Understanding the distinction between IT Governance and Data Fabric is essential for organizations aiming to optimize data management and enforce compliance simultaneously.
Table of Comparison
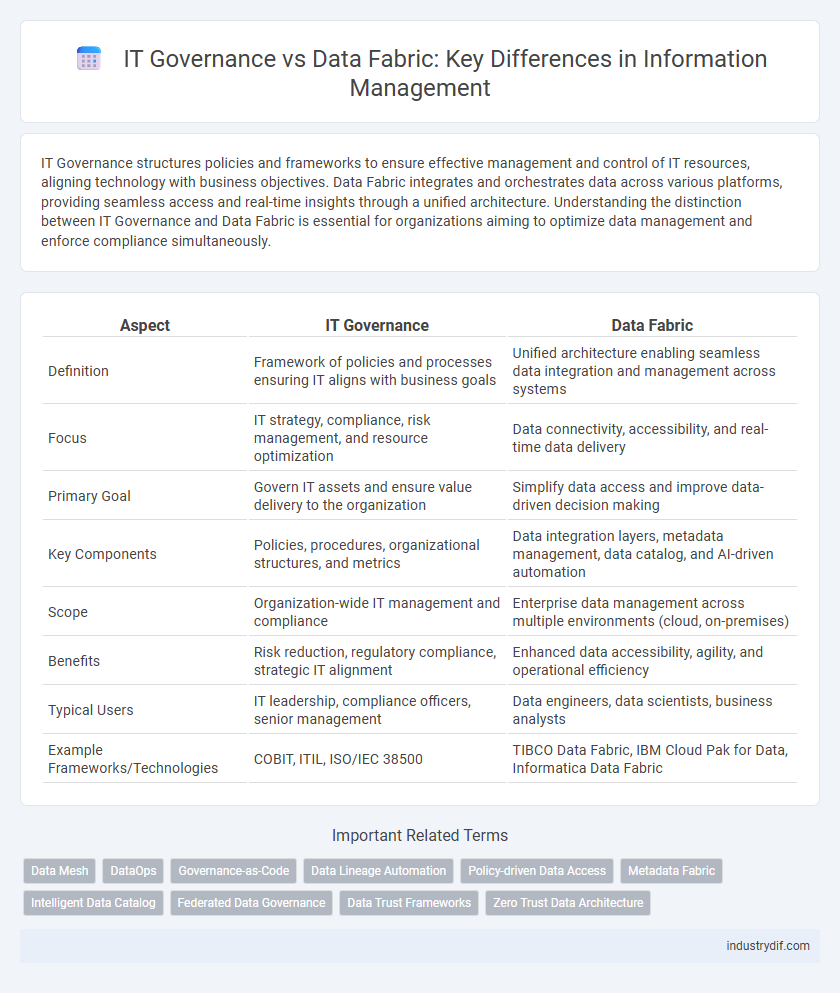
| Aspect | IT Governance | Data Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework of policies and processes ensuring IT aligns with business goals | Unified architecture enabling seamless data integration and management across systems |
| Focus | IT strategy, compliance, risk management, and resource optimization | Data connectivity, accessibility, and real-time data delivery |
| Primary Goal | Govern IT assets and ensure value delivery to the organization | Simplify data access and improve data-driven decision making |
| Key Components | Policies, procedures, organizational structures, and metrics | Data integration layers, metadata management, data catalog, and AI-driven automation |
| Scope | Organization-wide IT management and compliance | Enterprise data management across multiple environments (cloud, on-premises) |
| Benefits | Risk reduction, regulatory compliance, strategic IT alignment | Enhanced data accessibility, agility, and operational efficiency |
| Typical Users | IT leadership, compliance officers, senior management | Data engineers, data scientists, business analysts |
| Example Frameworks/Technologies | COBIT, ITIL, ISO/IEC 38500 | TIBCO Data Fabric, IBM Cloud Pak for Data, Informatica Data Fabric |
Defining IT Governance and Data Fabric
IT Governance refers to the framework and processes that ensure effective and efficient use of IT in enabling an organization to achieve its goals, emphasizing accountability, risk management, and strategic alignment. Data Fabric is an integrated data management architecture that enables seamless access, processing, and sharing of data across diverse platforms and environments. While IT Governance focuses on policies and control over IT resources, Data Fabric centers on unifying data infrastructure to enhance accessibility and usability.
Core Principles of IT Governance
IT Governance centers on aligning IT strategy with business goals through accountability, transparency, and risk management to ensure effective decision-making and resource utilization. Core principles include establishing clear roles and responsibilities, enforcing compliance with regulatory requirements, and fostering stakeholder engagement to optimize IT investments. Unlike Data Fabric, which focuses on seamless data integration across platforms, IT Governance provides the framework for managing IT assets and policies to support organizational objectives.
Key Components of Data Fabric Architecture
Data Fabric architecture integrates core components such as data cataloging, metadata management, and unified data access to streamline data governance and analytics. It leverages AI-driven data integration, real-time data processing, and automated data lineage tracking to enhance data quality and compliance. This architecture supports scalable data virtualization and distributed data management, enabling seamless data orchestration across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Strategic Objectives: IT Governance vs. Data Fabric
IT Governance prioritizes aligning IT strategy with business goals, ensuring compliance, risk management, and resource optimization across the organization. Data Fabric focuses on creating a unified data architecture to enable seamless data integration, accessibility, and real-time analytics, driving agile decision-making. While IT Governance emphasizes control and accountability, Data Fabric enhances data-driven innovation and strategic insights.
Data Management in IT Governance Frameworks
Data management in IT governance frameworks ensures the accuracy, security, and accessibility of information across the organization. IT governance establishes policies and procedures that align data management practices with business goals, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation. Data fabric technology enhances these frameworks by providing a unified architecture for seamless data integration, real-time access, and consistent data quality across diverse IT environments.
How Data Fabric Enhances Data Integration
Data fabric enhances data integration by creating a unified architecture that seamlessly connects diverse data sources across cloud environments, on-premises systems, and edge devices. It uses intelligent automation and metadata-driven processes to ensure consistent data access, quality, and governance, reducing silos and improving real-time data availability. This approach surpasses traditional IT governance frameworks by enabling dynamic, scalable, and flexible data integration essential for modern analytics and decision-making.
Compliance and Security: A Comparative Perspective
IT Governance establishes structured policies and controls to ensure organizational compliance with regulatory standards, prioritizing risk management and secure IT operations. Data Fabric integrates diverse data sources, enhancing real-time visibility and data lineage, which supports continuous compliance monitoring and strengthens data security frameworks. Together, IT Governance provides the strategic backbone while Data Fabric delivers operational agility for robust compliance and security management.
Roles and Responsibilities in IT Governance and Data Fabric
IT Governance assigns roles and responsibilities to ensure alignment between IT strategy and business objectives, focusing on risk management, compliance, and resource allocation. Data Fabric emphasizes roles related to data integration, management, and accessibility, enabling seamless data flow across hybrid environments. Effective collaboration between governance committees and data fabric teams is crucial for maintaining data integrity and supporting informed decision-making.
Impact on Business Agility and Innovation
IT governance establishes structured policies and control mechanisms crucial for aligning IT strategy with business objectives, ensuring risk management, and maintaining compliance, which stabilizes business operations but may slow agility. Data fabric integrates diverse data sources through intelligent automation and real-time analytics, enabling rapid access to critical insights that accelerate decision-making and foster innovation. Combining robust IT governance frameworks with adaptive data fabric technologies creates an optimized environment where enhanced data accessibility drives agile responses and cultivates continuous innovation.
Best Practices for Aligning IT Governance with Data Fabric
Aligning IT governance with data fabric involves establishing clear policies that ensure data quality, security, and compliance across distributed data environments. Best practices include integrating governance frameworks like COBIT or ITIL with data fabric architectures to oversee data lineage, access control, and metadata management effectively. Implementing automated monitoring tools and fostering collaboration between IT and data teams enhances transparency and accountability in managing data assets.
Related Important Terms
Data Mesh
Data Mesh decentralizes data ownership by assigning domain-specific teams responsibility for their data products, promoting scalability and agility compared to centralized IT governance models. Unlike Data Fabric, which emphasizes integration through a unified architecture, Data Mesh prioritizes organizational change and federated governance to enable data democratization and self-service analytics.
DataOps
DataOps integrates seamlessly within IT governance frameworks by automating data pipeline management and enhancing data quality controls to ensure compliance and agility in data-driven decision-making. Data Fabric architectures leverage DataOps methodologies to provide unified access and real-time data orchestration across distributed environments, optimizing data governance and operational efficiency.
Governance-as-Code
Governance-as-Code integrates IT governance policies directly into automated workflows, ensuring consistent, real-time compliance within agile data fabric environments. This approach streamlines regulatory adherence and risk management by embedding governance controls into infrastructure as code, enabling dynamic enforcement across distributed data assets.
Data Lineage Automation
Data lineage automation enhances IT governance by providing real-time visibility into data flow, ensuring compliance and accuracy across complex data fabrics. It enables automated tracking, auditing, and impact analysis, reducing risks and improving data quality within enterprise architectures.
Policy-driven Data Access
Policy-driven data access in IT governance enforces strict compliance, ensuring that data usage aligns with organizational policies and regulatory requirements, thereby reducing risks associated with unauthorized access. Data fabric enhances this by integrating data management across distributed environments, enabling seamless, real-time policy enforcement and fine-grained access controls across heterogeneous data sources.
Metadata Fabric
Metadata Fabric enhances IT Governance by providing a unified layer that integrates, manages, and governs metadata across diverse data environments, ensuring consistent data lineage, quality, and compliance. Unlike traditional IT Governance frameworks, Metadata Fabric enables dynamic data discovery and real-time metadata synchronization, improving agility and decision-making in complex data ecosystems.
Intelligent Data Catalog
Intelligent Data Catalog enhances IT governance by automating metadata management, data lineage tracking, and compliance monitoring, ensuring accurate data classification and secure access controls. Integrating a Data Fabric architecture with an Intelligent Data Catalog creates a unified data ecosystem that simplifies data discovery, accelerates decision-making, and enforces governance policies across distributed environments.
Federated Data Governance
Federated Data Governance integrates decentralized data management with centralized control, enhancing compliance and security across distributed IT environments. IT governance frameworks set policies and accountability, while Data Fabric architectures enable seamless data access and integration, driving efficient decision-making in complex organizational ecosystems.
Data Trust Frameworks
Data Trust Frameworks play a crucial role in bridging IT Governance and Data Fabric by establishing standardized policies, security protocols, and compliance measures that ensure data integrity, privacy, and accessibility across distributed environments. These frameworks enable organizations to maintain governance control while leveraging the dynamic, scalable architecture of Data Fabric to optimize data management and trustworthiness.
Zero Trust Data Architecture
Zero Trust Data Architecture within IT Governance enforces strict access controls and continuous verification to secure data across distributed environments, minimizing risks associated with data breaches. Data Fabric complements this approach by providing an integrated, real-time data management layer that ensures consistent policy enforcement and seamless data access across hybrid cloud infrastructures.
IT Governance vs Data Fabric Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com