Information security focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and threats by implementing robust technical controls and protocols. Data privacy by design integrates privacy measures into the development process, ensuring that personal information is handled with confidentiality and compliance from the outset. Both concepts work synergistically to safeguard sensitive information throughout its lifecycle while maintaining user trust.
Table of Comparison
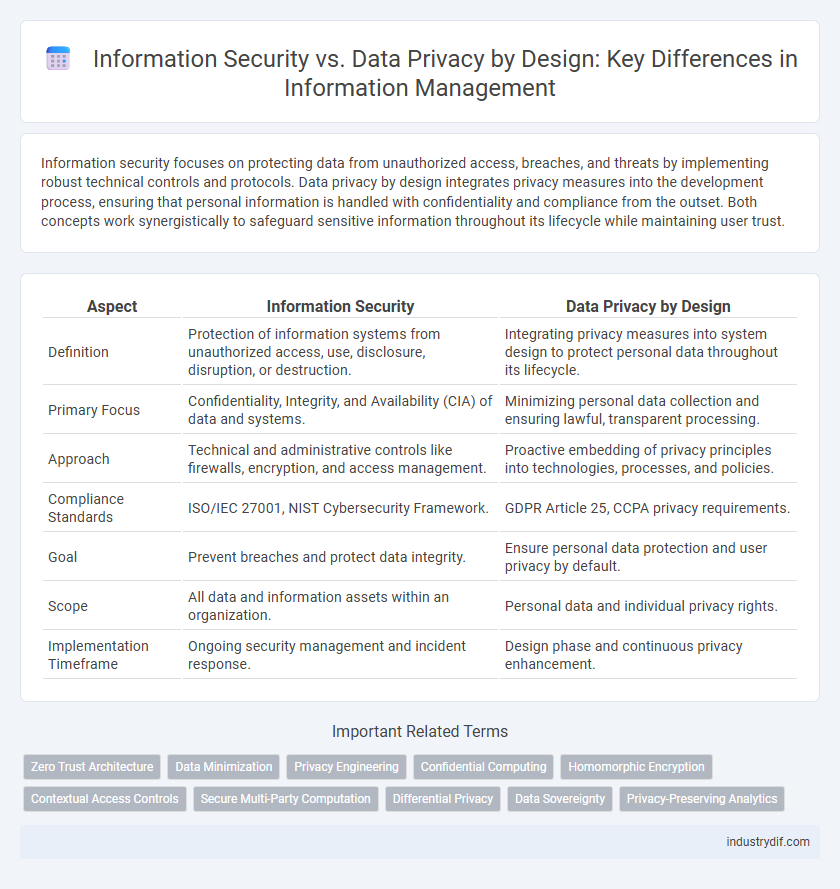
| Aspect | Information Security | Data Privacy by Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protection of information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, or destruction. | Integrating privacy measures into system design to protect personal data throughout its lifecycle. |
| Primary Focus | Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) of data and systems. | Minimizing personal data collection and ensuring lawful, transparent processing. |
| Approach | Technical and administrative controls like firewalls, encryption, and access management. | Proactive embedding of privacy principles into technologies, processes, and policies. |
| Compliance Standards | ISO/IEC 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework. | GDPR Article 25, CCPA privacy requirements. |
| Goal | Prevent breaches and protect data integrity. | Ensure personal data protection and user privacy by default. |
| Scope | All data and information assets within an organization. | Personal data and individual privacy rights. |
| Implementation Timeframe | Ongoing security management and incident response. | Design phase and continuous privacy enhancement. |
Understanding Information Security and Data Privacy by Design
Information Security ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data through protective technologies and protocols, safeguarding against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Data Privacy by Design integrates privacy measures directly into the development lifecycle of systems and processes, promoting proactive data protection aligned with regulatory requirements such as GDPR and CCPA. Combining both approaches helps organizations build secure, compliant environments that protect sensitive information while respecting user privacy.
Key Principles of Information Security
Information security revolves around the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad) of data, ensuring protection against unauthorized access, alteration, and disruptions. Key principles include risk management, access control, encryption, authentication, and regular security audits to mitigate vulnerabilities effectively. Data privacy by design complements these principles by embedding privacy considerations and compliance with regulations like GDPR directly into system architectures from inception.
Core Concepts of Data Privacy by Design
Data Privacy by Design integrates privacy measures into the development of products and systems from the outset, ensuring personal data is protected through techniques like data minimization, access controls, and encryption. It emphasizes proactive risk management by embedding privacy-enhancing technologies and compliance with regulations such as GDPR. Core concepts include user-centric data control, transparency in data processing, and accountability mechanisms to safeguard confidentiality and integrity throughout the data lifecycle.
Differences Between Information Security and Data Privacy
Information security focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats through technical measures such as encryption, firewalls, and access controls. Data privacy by design centers on embedding privacy principles into processes and systems to ensure the proper handling, consent, and minimization of personal data. The main difference lies in information security safeguarding the data's integrity and availability, while data privacy ensures the ethical use and compliance with data protection regulations.
Regulatory Frameworks Impacting Security and Privacy
Regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA mandate stringent requirements for both information security and data privacy by design, ensuring organizations implement robust technical and organizational measures to protect personal data. These regulations emphasize encryption, access controls, and data minimization as core components to mitigate risks and prevent unauthorized access. Compliance with evolving legal standards drives continuous improvement in security architectures and privacy policies, aligning technological safeguards with individual rights and regulatory obligations.
Integrating Privacy by Design Into Security Strategies
Integrating Privacy by Design into security strategies ensures that data protection is embedded from the initial stages of system development, minimizing risks of breaches and unauthorized access. This approach aligns with frameworks such as ISO/IEC 27001 and GDPR, promoting proactive measures like encryption, anonymization, and access controls. Embedding privacy principles directly within information security policies enhances overall compliance and strengthens organizational trust.
Best Practices for Safeguarding Information
Implementing Information Security vs Data Privacy by Design requires a focus on encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Best practices include integrating privacy impact assessments early in the system development lifecycle, ensuring data minimization, and applying role-based access permissions. Regular training on security protocols and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA enhances organizational resilience against cyber threats.
Challenges in Balancing Security and Privacy
Balancing security and privacy presents significant challenges, as information security aims to protect data from unauthorized access while data privacy by design ensures personal information is handled with minimal exposure. Implementing robust encryption and access controls often conflicts with privacy principles that limit data collection and usage, creating tension between safeguarding information and respecting user confidentiality. Organizations must navigate regulatory requirements such as GDPR and CCPA, which impose strict privacy standards that can constrain traditional security measures, complicating the alignment of both objectives in system design.
The Role of Technology in Data Protection
Technology plays a critical role in data protection by integrating security measures directly into the design of information systems, ensuring robust defenses against cyber threats and unauthorized access. Encryption, access controls, and automated monitoring technologies help maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data throughout its lifecycle. By embedding privacy-enhancing technologies and secure coding practices, organizations can enforce data privacy by design while strengthening overall information security frameworks.
Future Trends in Information Security and Privacy by Design
Emerging future trends in information security emphasize integrating privacy by design principles directly into system architectures to proactively safeguard sensitive data. Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain are being leveraged to enhance real-time threat detection and ensure data integrity while maintaining user privacy. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to mandate stronger data protection measures, driving organizations to adopt privacy-focused security models that balance compliance and operational efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict identity verification and micro-segmentation to minimize attack surfaces, crucial for both Information Security and Data Privacy by Design. Integrating Zero Trust principles ensures sensitive data remains protected through continuous monitoring, access controls, and least privilege policies, thereby supporting regulatory compliance and mitigating insider threats.
Data Minimization
Data minimization is a core principle in both Information Security and Data Privacy by Design that involves collecting, processing, and retaining only the essential personal data necessary to fulfill specific purposes. Implementing strict data minimization techniques reduces exposure to data breaches and enhances compliance with regulations like GDPR by limiting unnecessary data collection and storage.
Privacy Engineering
Privacy engineering integrates data privacy principles directly into the design and development of information systems, ensuring proactive protection of personal data throughout its lifecycle. Information security focuses on safeguarding data from unauthorized access and breaches using technical controls, while privacy engineering emphasizes embedding compliance, user consent, and data minimization to uphold privacy by design standards.
Confidential Computing
Confidential computing enhances information security by encrypting data in use, ensuring sensitive information remains protected even during processing, which aligns with data privacy by design principles to minimize exposure risks. This approach integrates hardware-based trusted execution environments (TEEs) that securely isolate workloads, enabling organizations to comply with stringent data protection regulations while maintaining data confidentiality and integrity.
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption enables secure information processing by allowing computations on encrypted data without decryption, enhancing data privacy by design in information security frameworks. This cryptographic technique ensures sensitive data remains protected throughout processing, supporting compliance with privacy regulations and minimizing risks of data breaches.
Contextual Access Controls
Contextual Access Controls enhance Information Security by dynamically adjusting permissions based on user behavior, location, and device, ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible under predefined, secure conditions. This approach integrates Data Privacy by Design principles by minimizing unauthorized data exposure and enforcing strict access policies tailored to specific contextual factors, reducing risks of data breaches and compliance violations.
Secure Multi-Party Computation
Secure Multi-Party Computation (SMPC) enhances information security by enabling multiple parties to jointly compute functions over their inputs while keeping those inputs private, embodying data privacy by design principles. SMPC mitigates data exposure risks in collaborative environments, ensuring confidentiality and integrity without compromising data utility.
Differential Privacy
Differential Privacy enhances data privacy by introducing controlled noise to datasets, ensuring individual information remains confidential while enabling accurate aggregate analysis. Implementing Differential Privacy within Information Security frameworks supports Data Privacy by Design by minimizing re-identification risks and protecting sensitive user data from unauthorized access.
Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty emphasizes the legal and regulatory control over data based on its geographic location, impacting how information security frameworks and data privacy by design principles are implemented to ensure compliance with jurisdiction-specific laws. Incorporating data sovereignty into data privacy by design enhances protection measures by embedding regulatory requirements directly into the system architecture, minimizing risks related to unauthorized access and cross-border data transfers.
Privacy-Preserving Analytics
Privacy-preserving analytics integrates data privacy by design principles to protect personal information while enabling insightful analysis, employing techniques such as differential privacy and secure multiparty computation. This approach ensures compliance with information security standards by minimizing data exposure and maintaining confidentiality throughout the data processing lifecycle.
Information Security vs Data Privacy by Design Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com