Structured data is organized in defined formats such as tables and spreadsheets, enabling easy querying and analysis through databases. Unstructured data fabric integrates diverse, unmanaged data sources like text, images, and videos, providing a flexible architecture for comprehensive data management. Leveraging both approaches enhances data accessibility, scalability, and insight generation across complex information ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
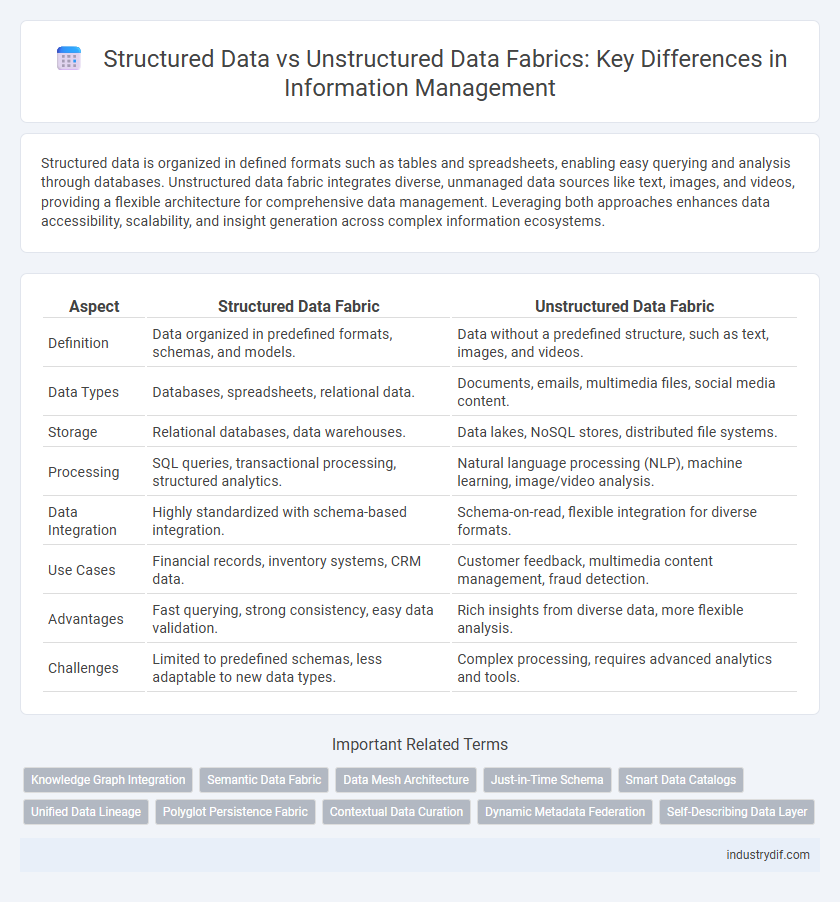
| Aspect | Structured Data Fabric | Unstructured Data Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data organized in predefined formats, schemas, and models. | Data without a predefined structure, such as text, images, and videos. |
| Data Types | Databases, spreadsheets, relational data. | Documents, emails, multimedia files, social media content. |
| Storage | Relational databases, data warehouses. | Data lakes, NoSQL stores, distributed file systems. |
| Processing | SQL queries, transactional processing, structured analytics. | Natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, image/video analysis. |
| Data Integration | Highly standardized with schema-based integration. | Schema-on-read, flexible integration for diverse formats. |
| Use Cases | Financial records, inventory systems, CRM data. | Customer feedback, multimedia content management, fraud detection. |
| Advantages | Fast querying, strong consistency, easy data validation. | Rich insights from diverse data, more flexible analysis. |
| Challenges | Limited to predefined schemas, less adaptable to new data types. | Complex processing, requires advanced analytics and tools. |
Overview of Structured Data and Unstructured Data
Structured data consists of highly organized information stored in fixed fields within databases, making it easily searchable and analyzable through SQL queries. Unstructured data lacks a predefined format, encompassing text, images, videos, and social media content, requiring advanced analytics and machine learning for processing. Data fabrics integrate these diverse data types into a unified architecture, enabling seamless access and management across complex data environments.
Key Definitions: Structured Data Fabric vs Unstructured Data Fabric
Structured Data Fabric integrates and manages data organized in predefined formats like relational databases, enabling efficient querying and analytics. Unstructured Data Fabric handles data lacking a fixed schema, such as text, images, and videos, by leveraging flexible storage and advanced indexing techniques. Both fabrics optimize data accessibility and governance across diverse data environments, supporting comprehensive enterprise data strategies.
Core Characteristics of Structured Data Fabric
Structured Data Fabric integrates data from multiple structured sources, enabling consistent data models and schema enforcement. It emphasizes data quality, governance, and real-time accessibility through predefined tables and relationships. This fabric supports efficient querying, high data integrity, and seamless interoperability across enterprise applications.
Essential Features of Unstructured Data Fabric
Unstructured Data Fabric excels in managing diverse data types such as text, images, and videos by providing seamless integration and advanced metadata tagging for enhanced searchability and retrieval. Its essential features include dynamic schema adaptability, real-time data processing, and support for complex analytics through machine learning algorithms. This framework ensures scalable, flexible data management, enabling organizations to unlock actionable insights from previously untapped or siloed unstructured data sources.
Data Storage Strategies in Modern Data Fabrics
Modern data fabrics integrate structured data storage, leveraging relational databases and data warehouses for organized, schema-based information management, alongside unstructured data storage solutions such as data lakes and object stores that handle diverse formats like text, images, and videos. Efficient data storage strategies in data fabrics employ metadata cataloging and indexing systems to unify access and improve searchability across disparate data types. This hybrid approach ensures scalability, flexibility, and optimized performance in managing the full spectrum of enterprise data assets.
Integration Challenges: Structured vs Unstructured Data
Integrating structured data, which follows a predefined schema, with unstructured data such as text, images, and videos presents significant challenges due to their inherent differences in format and storage. Data fabric solutions must employ advanced metadata management and machine learning techniques to harmonize these disparate data types for seamless access and analysis. Effective integration requires overcoming data silos and ensuring data quality, consistency, and real-time synchronization across diverse sources.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
Structured data fabric enables high scalability and performance through optimized indexing and schema enforcement, allowing efficient query processing and data integration at scale. Unstructured data fabric requires advanced metadata management and AI-driven analytics to handle diverse formats, which can impact latency and resource consumption but offers greater flexibility for dynamic datasets. Choosing the appropriate data fabric depends on the workload, with structured environments favoring predictable scalability and unstructured systems prioritizing adaptability and semantic richness.
Security and Compliance in Data Fabrics
Structured data fabric enforces robust security protocols through schema-based controls and automated compliance monitoring, ensuring regulated data handling. Unstructured data fabric integrates advanced encryption and dynamic access controls tailored for diverse data types, enhancing privacy and compliance across heterogeneous sources. Both fabrics leverage metadata to maintain traceability and auditing, critical for meeting industry regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Use Cases: Industry Applications of Both Data Types
Structured data fabric excels in industries like finance and healthcare, enabling efficient analysis of transactional data and patient records for regulatory compliance and real-time decision-making. Unstructured data fabric supports sectors such as media and telecommunications by managing vast volumes of text, audio, and video files, enhancing customer insights and content delivery. Hybrid approaches integrate both data types for comprehensive analytics in retail and manufacturing, optimizing supply chain management and personalized marketing strategies.
Future Trends in Data Fabric Technologies
Future trends in data fabric technologies emphasize the integration of structured and unstructured data to enhance real-time analytics and artificial intelligence capabilities. Advances in machine learning algorithms and automation are driving smarter data management solutions that optimize data discovery, governance, and security across diverse sources. The evolution of hybrid cloud environments further accelerates the adoption of adaptive data fabrics, enabling seamless data access and scalability for enterprise digital transformation.
Related Important Terms
Knowledge Graph Integration
Structured data in fabric systems is organized with standardized schemas, enabling efficient querying and integration using knowledge graphs that enhance semantic relationships between entities. Unstructured data fabric leverages knowledge graph integration to impose connections and contextual understanding on diverse, raw datasets, improving data discoverability and decision-making accuracy.
Semantic Data Fabric
Semantic Data Fabric enhances data integration by leveraging ontologies and metadata to create meaningful relationships between structured and unstructured data sources. This approach enables advanced analytics and real-time insights by providing a unified, context-rich view across diverse datasets within an enterprise.
Data Mesh Architecture
Data Mesh Architecture enhances data fabric by integrating both structured and unstructured data into a decentralized, domain-oriented framework that promotes data ownership and self-serve data infrastructure. This approach optimizes data accessibility and governance while enabling scalable analytics across diverse data types.
Just-in-Time Schema
Just-in-Time Schema in data fabrics enables dynamic structuring of unstructured data, enhancing flexibility and real-time data integration without predefined schemas. This approach streamlines data management by applying schemas only when data is accessed, optimizing storage and query performance in both structured and unstructured data environments.
Smart Data Catalogs
Smart data catalogs enhance data fabric by efficiently organizing and indexing both structured and unstructured data, enabling faster data discovery and improved metadata management. Their AI-driven capabilities automate data classification and lineage tracking, optimizing data governance across heterogeneous data sources in complex enterprise environments.
Unified Data Lineage
Unified data lineage in structured data fabric offers precise tracking and integration of data flows across predefined schemas, enhancing accuracy and governance. In contrast, unstructured data fabric leverages advanced metadata extraction and machine learning to map complex, dynamic data relationships, enabling comprehensive visibility across diverse data types.
Polyglot Persistence Fabric
Polyglot Persistence Fabric integrates diverse structured and unstructured data sources to enhance data management flexibility and scalability across enterprises. Leveraging this fabric enables seamless querying and analysis by unifying relational databases, NoSQL stores, and unstructured data repositories within a cohesive architecture.
Contextual Data Curation
Structured data fabric organizes information into defined schemas, enabling efficient contextual data curation by categorizing and linking data points for precise retrieval. Unstructured data fabric employs advanced algorithms and AI to interpret, tag, and integrate heterogeneous data sources, enhancing the depth and relevancy of contextual insights.
Dynamic Metadata Federation
Structured data integrates seamlessly within data fabrics through dynamic metadata federation, enabling real-time data harmonization and optimized schema alignment across diverse sources. Unstructured data fabric leverages dynamic metadata federation to classify, index, and contextualize heterogeneous content, enhancing data discoverability and accelerating intelligent processing pipelines.
Self-Describing Data Layer
Structured data fabric relies on a self-describing data layer that organizes information into defined schemas, enabling efficient querying and integration across systems. In contrast, unstructured data fabric manages heterogeneous data formats without predefined schemas, leveraging metadata and machine learning to interpret and link data dynamically.
Structured Data vs Unstructured Data Fabric Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com