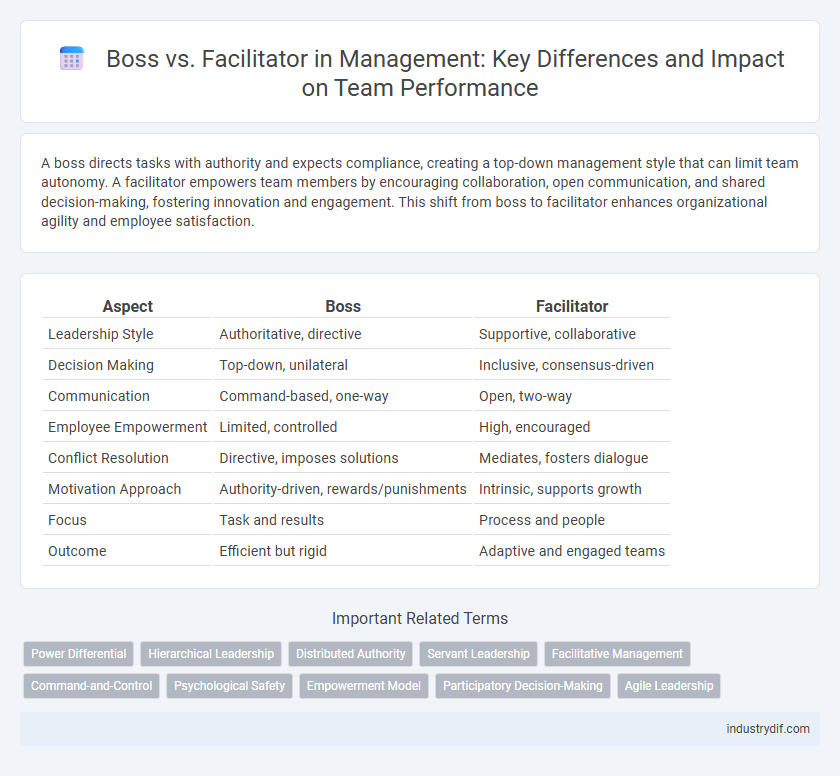
A boss directs tasks with authority and expects compliance, creating a top-down management style that can limit team autonomy. A facilitator empowers team members by encouraging collaboration, open communication, and shared decision-making, fostering innovation and engagement. This shift from boss to facilitator enhances organizational agility and employee satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Boss | Facilitator |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Authoritative, directive | Supportive, collaborative |
| Decision Making | Top-down, unilateral | Inclusive, consensus-driven |
| Communication | Command-based, one-way | Open, two-way |
| Employee Empowerment | Limited, controlled | High, encouraged |
| Conflict Resolution | Directive, imposes solutions | Mediates, fosters dialogue |
| Motivation Approach | Authority-driven, rewards/punishments | Intrinsic, supports growth |
| Focus | Task and results | Process and people |
| Outcome | Efficient but rigid | Adaptive and engaged teams |
Definition: Boss vs Facilitator
A boss exercises authority by directing and controlling tasks, emphasizing hierarchical decision-making and compliance. A facilitator promotes collaboration by guiding teams through problem-solving and supporting open communication to achieve collective goals. The distinction lies in leadership style: command-driven management versus empowerment and facilitation of group dynamics.
Core Leadership Styles Compared
Core leadership styles contrast a boss's directive approach with a facilitator's collaborative method, emphasizing control versus empowerment. Bosses often use authoritative tactics to enforce rules and drive results, while facilitators prioritize team input and foster open communication to enhance innovation. Understanding these differences improves organizational dynamics and aligns management strategies with employee engagement and productivity goals.
Decision-Making Approaches
Bosses typically adopt a directive decision-making approach, asserting authority to make unilateral choices that streamline processes and enforce accountability. Facilitators emphasize collaborative decision-making, encouraging input from team members to foster inclusive solutions and enhance engagement. This shift from top-down control to participative involvement leads to diverse perspectives being integrated, improving overall decision quality and team cohesion.
Communication Methods
Bosses typically rely on top-down communication methods such as directives and formal meetings to convey instructions and expectations. Facilitators prioritize open dialogue, active listening, and collaborative platforms to encourage team input and foster mutual understanding. Effective communication in management balances clarity of authority with inclusiveness to enhance productivity and employee engagement.
Power Dynamics in Teams
Power dynamics in teams shift significantly when comparing a boss-centric model to a facilitator approach. A boss typically exercises top-down authority, centralizing decision-making and control, which can suppress team autonomy and limit collaborative innovation. In contrast, a facilitator empowers team members by distributing influence, fostering open communication, and promoting shared leadership to enhance engagement and collective problem-solving.
Employee Empowerment and Engagement
Bosses typically exert control through authoritative decisions, which can limit employee empowerment and hinder engagement. Facilitators prioritize collaboration and open communication, fostering a work environment where employees feel valued and motivated to contribute ideas. This approach enhances empowerment by encouraging autonomy and strengthens engagement by promoting a sense of ownership and trust within the team.
Conflict Resolution Strategies
Bosses typically rely on authoritative conflict resolution strategies, emphasizing control and decision-making to quickly resolve disputes. Facilitators use collaborative techniques, encouraging open communication and mutual understanding to address underlying issues and foster long-term cooperation. This approach enhances team cohesion and promotes a positive organizational culture.
Impact on Workplace Culture
Bosses often enforce strict hierarchies that may breed compliance but can stifle creativity and employee engagement. Facilitators promote collaboration and open communication, fostering a positive workplace culture where innovation and trust thrive. This shift from authoritative to supportive leadership directly impacts employee satisfaction and overall organizational performance.
Performance Outcomes
Bosses often rely on authority and directive control, which can lead to compliance but may stifle creativity and intrinsic motivation, negatively affecting long-term performance outcomes. Facilitators prioritize collaboration, empowerment, and removing obstacles, fostering a culture of trust that enhances employee engagement and drives sustainable productivity. Performance outcomes improve significantly under facilitative leadership as teams become more agile, innovative, and self-directed.
Choosing the Right Approach for Management
Selecting the right management approach depends on organizational culture and team dynamics; a boss-style leader emphasizes authority and control, driving task completion through clear directives. In contrast, a facilitator encourages collaboration and autonomy, fostering innovation and employee engagement by removing obstacles and supporting problem-solving. Effective management balances directive leadership with facilitation to optimize performance and motivate diverse teams.
Related Important Terms
Power Differential
The power differential between a boss and a facilitator significantly influences organizational dynamics, with bosses typically exerting authoritative control that can limit employee autonomy. Facilitators, by contrast, reduce power distance by encouraging collaboration and empowering team members, which fosters innovation and engagement.
Hierarchical Leadership
Hierarchical leadership emphasizes top-down decision-making where the boss holds authority and controls workflow, ensuring directive management and clear task delegation within the organizational structure. In contrast, a facilitator in hierarchical settings encourages collaboration and open communication, prompting teams to contribute ideas while maintaining chain-of-command discipline.
Distributed Authority
In management, a facilitator promotes distributed authority by empowering team members to make decisions and take ownership, which enhances collaboration and innovation. Unlike a traditional boss who centralizes control, a facilitator fosters an environment where responsibility is shared, leading to increased autonomy and accountability across the organization.
Servant Leadership
Servant leadership emphasizes a facilitator's role in empowering and supporting teams to achieve collective goals, contrasting with a traditional boss who directs and controls. This leadership style fosters trust, collaboration, and employee development by prioritizing the needs of the team over authority.
Facilitative Management
Facilitative management enhances team collaboration by empowering employees to take initiative, fostering a culture of open communication and collective problem-solving. Unlike traditional bosses who command and control, facilitators guide processes, remove obstacles, and support skill development to maximize team potential and innovation.
Command-and-Control
Command-and-control leadership in management emphasizes hierarchical authority and top-down decision-making, where the boss issues directives and expects compliance. Facilitators instead promote collaboration and empower team members, minimizing rigid control to enhance communication and innovation.
Psychological Safety
Psychological safety in management significantly improves when leaders transition from a boss-centric approach, focused on authority and control, to a facilitator role that encourages open communication, trust, and collaboration. Facilitators promote a safe environment where employees feel valued and secure in expressing ideas without fear of judgment or retribution, boosting innovation and team performance.
Empowerment Model
The empowerment model in management shifts the dynamic from a traditional boss who directs tasks to a facilitator who enables team members to take ownership and make decisions, fostering autonomy and innovation. This approach enhances employee engagement and productivity by providing resources, support, and trust rather than command and control.
Participatory Decision-Making
A facilitator promotes participatory decision-making by encouraging team input, fostering collaboration, and ensuring all voices are heard, leading to more innovative and inclusive solutions. In contrast, a boss typically centralizes authority and makes decisions unilaterally, which can limit employee engagement and reduce the diversity of ideas.
Agile Leadership
Agile leadership thrives when leaders act as facilitators, empowering teams to self-organize and adapt swiftly to change, in contrast to traditional bosses who exert top-down control and limit creativity. This shift enhances collaboration, accelerates decision-making, and drives continuous improvement within dynamic work environments.
Boss vs Facilitator Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com