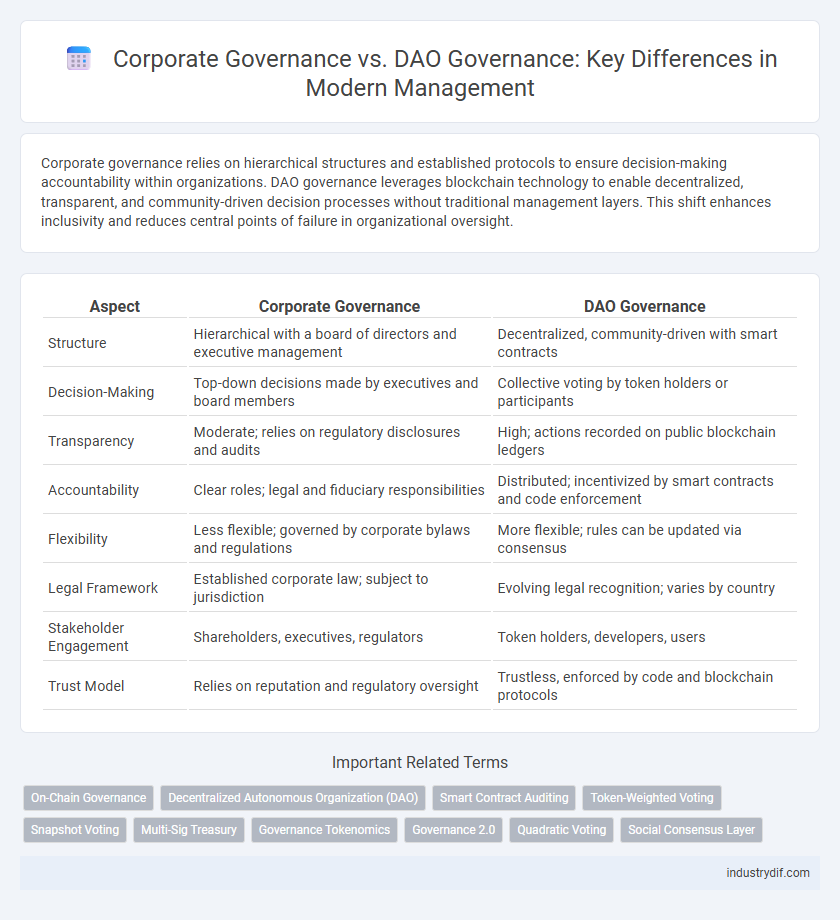
Corporate governance relies on hierarchical structures and established protocols to ensure decision-making accountability within organizations. DAO governance leverages blockchain technology to enable decentralized, transparent, and community-driven decision processes without traditional management layers. This shift enhances inclusivity and reduces central points of failure in organizational oversight.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Corporate Governance | DAO Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical with a board of directors and executive management | Decentralized, community-driven with smart contracts |
| Decision-Making | Top-down decisions made by executives and board members | Collective voting by token holders or participants |
| Transparency | Moderate; relies on regulatory disclosures and audits | High; actions recorded on public blockchain ledgers |
| Accountability | Clear roles; legal and fiduciary responsibilities | Distributed; incentivized by smart contracts and code enforcement |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; governed by corporate bylaws and regulations | More flexible; rules can be updated via consensus |
| Legal Framework | Established corporate law; subject to jurisdiction | Evolving legal recognition; varies by country |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Shareholders, executives, regulators | Token holders, developers, users |
| Trust Model | Relies on reputation and regulatory oversight | Trustless, enforced by code and blockchain protocols |
Overview of Corporate Governance
Corporate governance encompasses the systems, principles, and processes by which companies are directed and controlled, emphasizing accountability, transparency, and stakeholder engagement within traditional hierarchical structures. It involves the roles of boards of directors, executive management, and shareholders in ensuring compliance, risk management, and strategic decision-making. The framework supports sustainable business practices, regulatory adherence, and alignment with shareholder interests to enhance long-term value creation.
Introduction to DAO Governance
DAO governance introduces a decentralized framework where stakeholders participate directly in decision-making through blockchain-based voting mechanisms, enhancing transparency and accountability. Unlike traditional corporate governance, which relies on hierarchical structures and centralized control, DAOs operate via smart contracts that enforce rules autonomously without intermediaries. This paradigm shift reduces agency costs and fosters stakeholder empowerment by aligning governance with collective consensus.
Key Principles: Corporate vs DAO Governance
Corporate governance emphasizes hierarchical structures, accountability through a board of directors, and established regulatory compliance to ensure shareholder interests are protected. DAO governance operates on decentralized decision-making, leveraging blockchain technology to enable transparent, automated consensus mechanisms among token holders. The key principles contrast centralized control and legal frameworks with distributed authority and algorithmic enforcement in managing organizational objectives.
Structure and Decision-Making Processes
Corporate governance relies on hierarchical structures with boards of directors making strategic decisions, ensuring accountability through formal roles and established procedures. DAO governance employs decentralized, blockchain-based mechanisms where token holders participate directly in decision-making via proposals and voting, enhancing transparency and inclusivity. While corporate governance emphasizes control and compliance, DAO governance prioritizes distributed authority and real-time stakeholder engagement.
Transparency and Accountability in Governance Models
Corporate governance emphasizes established hierarchies and regulatory compliance to ensure transparency and accountability through structured reporting and board oversight. DAO governance leverages blockchain technology to provide decentralized, transparent decision-making processes with accountability enforced via smart contracts and token-holder voting. Both models aim to foster trust and responsibility, but DAOs offer a novel approach by enabling real-time, immutable tracking of governance activities.
Stakeholder Participation and Voting Mechanisms
Corporate governance typically centralizes decision-making authority within a board of directors, limiting direct stakeholder participation to shareholder voting rights on major issues. DAO governance leverages blockchain technology to enable decentralized stakeholder participation, where token holders can propose and vote on initiatives continuously through smart contracts. This transparent and automated voting mechanism enhances inclusivity and aligns decision-making power more equitably among all stakeholders.
Regulatory Compliance: Traditional vs Decentralized Systems
Corporate governance frameworks emphasize regulatory compliance through established legal standards and centralized oversight, ensuring accountability and risk management within corporations. DAO governance operates on decentralized protocols, leveraging smart contracts to enforce transparent rules, yet faces challenges with regulatory ambiguity and jurisdictional enforcement. These contrasting approaches highlight the balance between structured compliance and innovative, autonomous decision-making in organizational management.
Risk Management and Security Approaches
Corporate governance relies on hierarchical risk management frameworks combining internal controls, audits, and compliance protocols to mitigate organizational risks and ensure security. DAO governance employs decentralized consensus mechanisms and smart contract automation to enhance transparency, reduce single points of failure, and distribute security responsibilities among stakeholders. Both approaches address risk management through distinct structures, where corporate governance emphasizes regulatory adherence and DAO governance leverages blockchain technology for immutable security and real-time monitoring.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Governance Model
Corporate governance faces challenges in stakeholder alignment and bureaucratic inefficiencies, often struggling with transparency and slow decision-making processes. DAO governance, while promoting decentralization and enhanced stakeholder participation through blockchain technology, encounters limitations such as regulatory uncertainty, scalability issues, and potential vulnerabilities in smart contract execution. Both models require balancing control and flexibility to effectively address accountability, risk management, and organizational adaptability.
Future Trends in Corporate and DAO Governance
Corporate governance is evolving with increased adoption of blockchain technology to enhance transparency, while DAO governance leverages decentralized decision-making to promote inclusivity and agility in organizational control. Future trends indicate a convergence where hybrid models integrate traditional oversight mechanisms with smart contracts and token-based voting to balance accountability and stakeholder engagement. Emphasis on regulatory clarity, cybersecurity, and ethical frameworks will shape the sustainable development of both corporate and DAO governance structures.
Related Important Terms
On-Chain Governance
On-chain governance in DAO governance leverages blockchain technology to enable transparent, automated decision-making processes, enhancing accountability and stakeholder participation compared to traditional corporate governance structures. This method reduces reliance on centralized authorities by recording votes and proposals on an immutable ledger, ensuring real-time tracking and auditability of governance actions.
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO)
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) governance leverages blockchain technology to enable transparent, democratic decision-making processes without centralized leadership, contrasting traditional corporate governance that relies on hierarchical structures and board oversight. DAOs facilitate real-time stakeholder voting power encoded in smart contracts, enhancing accountability and reducing the risks of managerial misconduct prevalent in conventional corporate frameworks.
Smart Contract Auditing
Corporate governance ensures accountability through structured oversight by boards and regulatory compliance, while DAO governance relies on decentralized decision-making enabled by blockchain technology. Smart contract auditing plays a critical role in DAO governance by identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring the integrity of automated protocols that enforce rules and transactions without centralized control.
Token-Weighted Voting
Token-weighted voting in corporate governance traditionally centralizes decision-making power among major shareholders, aligning influence with equity stakes. In DAO governance, token-weighted voting enables decentralized control by distributing voting power proportionally to token holdings, fostering transparency and community-driven decisions.
Snapshot Voting
Corporate Governance typically relies on centralized decision-making frameworks with hierarchical voting processes, whereas DAO Governance utilizes decentralized methods such as Snapshot Voting, enabling token holders to participate in proposals without on-chain gas fees. Snapshot Voting leverages off-chain votes recorded through cryptographic signatures, promoting transparent, efficient consensus in decentralized autonomous organizations.
Multi-Sig Treasury
Corporate Governance relies on traditional hierarchical decision-making processes with centralized control over treasury management, while DAO Governance utilizes decentralized multi-signature (Multi-Sig) wallets to enhance transparency and security by requiring multiple approvals for treasury transactions. Multi-Sig Treasury in DAO Governance reduces risks of single-point failures and fosters collective accountability among stakeholders, contrasting with the typically bureaucratic nature of corporate treasury oversight.
Governance Tokenomics
Corporate governance relies on hierarchical decision-making structures with defined roles and responsibilities, while DAO governance operates on decentralized protocols where token holders influence decisions through voting power linked to governance tokenomics. Governance tokenomics in DAOs incentivize participation, align stakeholder interests, and ensure transparent, tamper-resistant decision processes through blockchain-based token distribution and utility models.
Governance 2.0
Governance 2.0 represents an evolution from traditional Corporate Governance by integrating decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), enabling transparent, blockchain-based decision-making processes that enhance stakeholder participation and reduce hierarchical control. This shift leverages smart contracts and token-based voting mechanisms to foster accountability, agility, and inclusivity in organizational management.
Quadratic Voting
Corporate governance relies on hierarchical decision-making frameworks, whereas DAO governance leverages decentralized mechanisms like quadratic voting to enhance stakeholder influence by weighting votes according to the square root of token holdings, reducing the dominance of large shareholders. Quadratic voting in DAO governance promotes more equitable and transparent decision-making by balancing individual preferences and collective interests within blockchain-based organizations.
Social Consensus Layer
Corporate Governance relies on hierarchical decision-making structures and formal regulations to establish a social consensus layer, ensuring accountability through centralized oversight and clear stakeholder responsibilities. DAO Governance utilizes blockchain technology and decentralized protocols to create a transparent, algorithm-driven social consensus layer, enabling trustless collaboration and collective decision-making without centralized authority.
Corporate Governance vs DAO Governance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com