The Chain of Command emphasizes a hierarchical structure where decisions flow from top management to lower levels, ensuring clear authority and responsibility. In contrast, a Teal Organization operates with self-management principles, promoting autonomy, decentralized decision-making, and collaborative teamwork. This shift from rigid control to fluid roles enhances innovation and employee engagement in modern management practices.
Table of Comparison
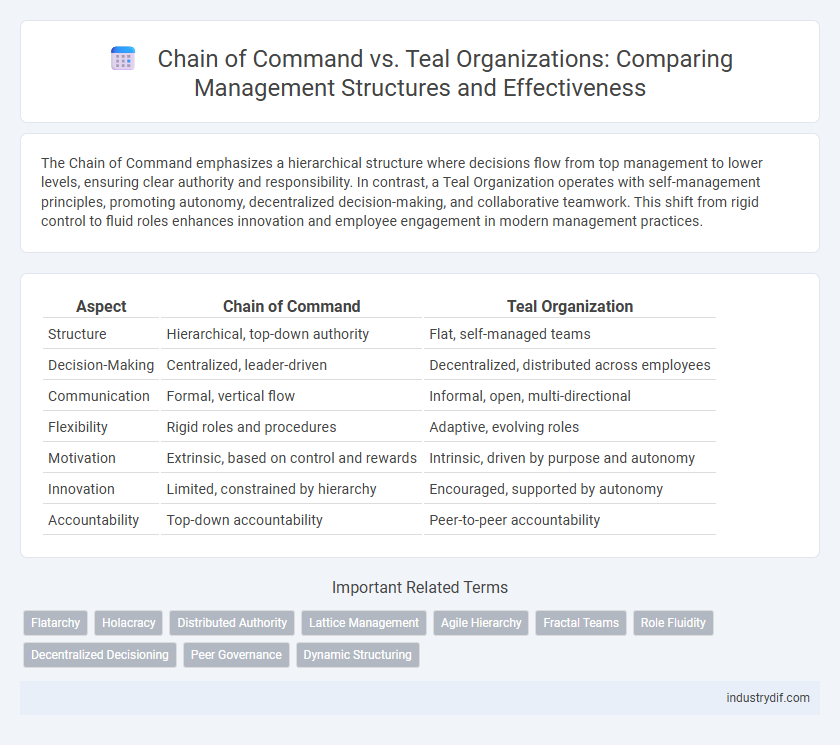
| Aspect | Chain of Command | Teal Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical, top-down authority | Flat, self-managed teams |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, leader-driven | Decentralized, distributed across employees |
| Communication | Formal, vertical flow | Informal, open, multi-directional |
| Flexibility | Rigid roles and procedures | Adaptive, evolving roles |
| Motivation | Extrinsic, based on control and rewards | Intrinsic, driven by purpose and autonomy |
| Innovation | Limited, constrained by hierarchy | Encouraged, supported by autonomy |
| Accountability | Top-down accountability | Peer-to-peer accountability |
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Chain of Command represents a traditional hierarchical organizational structure where authority flows vertically from top management to lower levels, ensuring clear reporting lines and centralized decision-making. Teal Organizations emphasize decentralized authority and self-management, promoting autonomous teams that operate with shared purpose and trust rather than rigid hierarchy. Understanding these contrasting structures helps organizations balance control and adaptability in dynamic business environments.
Defining the Chain of Command
The chain of command in traditional management establishes a clear hierarchical structure where authority and decision-making flow from top executives to lower-level employees, ensuring accountability and streamlined communication. This linear framework delineates specific roles and responsibilities, enabling efficient supervision and control within the organization. In contrast, the teal organization challenges this model by promoting decentralized authority and self-management, but a well-defined chain of command remains essential for clarity in complex operational environments.
What is a Teal Organization?
A Teal Organization operates with decentralized decision-making, emphasizing self-management, wholeness, and evolutionary purpose, contrasting sharply with traditional hierarchical chain of command structures. In Teal Organizations, employees are empowered to take initiative and collaboratively solve problems without relying on rigid authority lines. This approach fosters innovation, agility, and adaptive learning, crucial for modern complex business environments.
Key Features of Traditional Hierarchies
Traditional hierarchies in management feature a clear chain of command with defined levels of authority and central decision-making, ensuring structured communication and accountability. Roles and responsibilities are explicitly assigned, promoting efficiency through routine and compliance with established procedures. This framework supports control and predictability but may limit flexibility and employee autonomy compared to emergent models like Teal organizations.
Core Principles of Teal Organizations
Teal organizations prioritize self-management, wholeness, and evolutionary purpose, contrasting with the rigid hierarchy of traditional chain of command structures. Decision-making in Teal organizations is decentralized, empowering employees at all levels to take initiative and contribute meaningfully. This approach fosters innovation, adaptability, and a deeper sense of responsibility across the organization, breaking down silos and hierarchical barriers.
Decision-Making: Top-Down vs Self-Management
In traditional chain of command structures, decision-making follows a top-down approach where authority flows from senior management to lower levels, ensuring clear accountability and control. Teal organizations embrace self-management, empowering teams and individuals to make decisions autonomously based on purpose and context, fostering agility and innovation. This shift from hierarchical directives to decentralized decision-making enhances responsiveness and employee engagement in dynamic business environments.
Communication Flow: Centralized vs Decentralized
In traditional Chain of Command structures, communication flow is centralized, with information passing through defined hierarchical levels, ensuring clear authority and control but potentially slowing decision-making. Teal Organizations embrace decentralized communication, promoting autonomous, self-managing teams that share information openly and make decisions collaboratively, enhancing agility and responsiveness. This shift from a top-down to a networked communication model fosters transparency, innovation, and faster problem-solving within modern management practices.
Adaptability and Organizational Agility
Traditional chain of command structures offer clear hierarchical authority that can slow decision-making, limiting adaptability in dynamic markets. Teal organizations empower decentralized teams with autonomy, fostering rapid responses and enhanced organizational agility. Emphasizing self-management and distributed decision rights enables Teal models to navigate complexity and change more effectively than rigid hierarchical systems.
Employee Engagement and Empowerment
Traditional Chain of Command structures centralize decision-making authority, often limiting employee engagement and empowerment by creating rigid hierarchies. In contrast, Teal Organizations promote decentralized authority and self-management, fostering higher levels of employee autonomy, intrinsic motivation, and proactive involvement in organizational goals. Research in organizational behavior highlights that companies implementing Teal principles typically experience increased job satisfaction, innovation, and collaborative problem-solving among employees.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Business
Selecting the ideal organizational structure hinges on your business's size, culture, and strategic goals. Traditional chain of command provides clear authority lines and streamlined decision-making ideal for hierarchical environments, while teal organizations promote decentralized autonomy and self-management, fostering innovation and employee engagement. Evaluating operational complexity and the desired level of flexibility helps determine whether a rigid hierarchy or a fluid teal framework better supports sustainable growth and adaptability.
Related Important Terms
Flatarchy
Flatarchy combines the hierarchical clarity of a chain of command with the flexibility of teal organizations, promoting decentralized decision-making while maintaining clear lines of responsibility. This hybrid model enhances innovation and responsiveness by empowering teams and reducing bureaucratic delays inherent in traditional management structures.
Holacracy
Holacracy decentralizes power by distributing decision-making authority through self-organizing teams, contrasting sharply with the traditional chain of command's hierarchical control. This approach enhances agility and accountability by enabling roles to evolve dynamically, fostering transparency and collaborative governance within organizations.
Distributed Authority
Distributed authority in a Chain of Command centralizes decision-making within hierarchical levels, enabling clear accountability but often slowing responsiveness. In contrast, Teal Organizations embrace distributed authority by empowering teams and individuals to make autonomous decisions, fostering agility and innovation.
Lattice Management
Lattice management in teal organizations replaces traditional chain of command by fostering decentralized decision-making and dynamic role fluidity, enhancing employee autonomy and collaboration. This structure supports self-management and transparent communication, driving innovation and adaptability in complex, evolving business environments.
Agile Hierarchy
Chain of command relies on a traditional, hierarchical structure with clear, top-down authority and decision-making, ensuring clarity but often reducing flexibility. Teal organizations adopt an agile hierarchy that promotes self-management, distributed authority, and adaptive teamwork, enhancing responsiveness and innovation.
Fractal Teams
Fractal teams in teal organizations promote decentralized decision-making and self-management, contrasting with the rigid hierarchy of traditional chain of command structures, which centralize authority and control. This approach fosters agility, innovation, and employee empowerment by aligning roles dynamically with organizational purpose rather than fixed supervisory layers.
Role Fluidity
Chain of Command emphasizes rigid role definitions and clear hierarchical authority, often limiting flexibility and rapid decision-making. In contrast, Teal Organizations promote role fluidity by allowing individuals to adapt responsibilities based on situational needs, fostering adaptability and employee empowerment.
Decentralized Decisioning
Decentralized decision-making in teal organizations empowers employees at all levels to take initiative, contrasting with the rigid hierarchy of traditional chain of command structures where authority flows top-down. This shift enhances agility and innovation by distributing accountability and encouraging autonomous problem-solving across teams.
Peer Governance
Peer governance in teal organizations replaces the traditional chain of command by empowering self-managed teams to make decisions collaboratively, enhancing agility and employee engagement. Unlike hierarchical structures, teal organizations prioritize distributed authority and transparent communication, fostering trust and continuous innovation.
Dynamic Structuring
Chain of command emphasizes a fixed hierarchy with clear lines of authority, facilitating controlled decision-making and accountability. In contrast, teal organizations adopt dynamic structuring, enabling self-management and fluid roles that enhance adaptability and innovation in complex environments.
Chain of Command vs Teal Organization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com