Command-and-control management centralizes decision-making power, allowing leaders to issue directives that are expected to be followed precisely. Distributed authority, however, empowers teams by delegating decision-making to various levels, promoting autonomy and faster responsiveness. Organizations adopting distributed authority often experience increased innovation and employee engagement due to this flexible, collaborative approach.
Table of Comparison
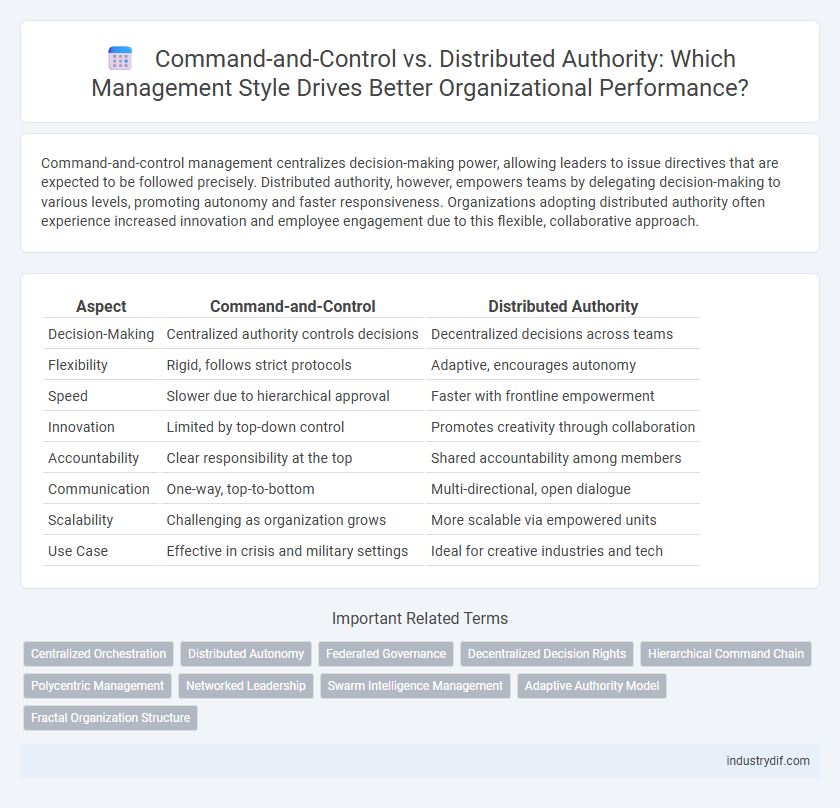
| Aspect | Command-and-Control | Distributed Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized authority controls decisions | Decentralized decisions across teams |
| Flexibility | Rigid, follows strict protocols | Adaptive, encourages autonomy |
| Speed | Slower due to hierarchical approval | Faster with frontline empowerment |
| Innovation | Limited by top-down control | Promotes creativity through collaboration |
| Accountability | Clear responsibility at the top | Shared accountability among members |
| Communication | One-way, top-to-bottom | Multi-directional, open dialogue |
| Scalability | Challenging as organization grows | More scalable via empowered units |
| Use Case | Effective in crisis and military settings | Ideal for creative industries and tech |
Understanding Command-and-Control Management
Command-and-Control management centralizes decision-making authority, with top executives issuing directives that flow downward through hierarchical layers to ensure compliance and consistency. This model emphasizes strict supervision, clear accountability, and standardized procedures, which can enhance efficiency in predictable environments. However, it may limit flexibility and responsiveness compared to more decentralized or distributed authority structures.
Defining Distributed Authority in Organizations
Distributed authority in organizations refers to a management structure where decision-making power is delegated across various levels and departments, rather than centralized at the top. This approach empowers employees to take initiative, fosters agility, and enhances responsiveness to dynamic market conditions. Studies indicate that organizations adopting distributed authority often experience increased innovation, faster problem-solving, and higher employee engagement compared to traditional command-and-control models.
Core Principles of Each Management Approach
Command-and-control management centers on hierarchical authority, clear directives, and strict oversight, ensuring consistency and accountability throughout the organization. Distributed authority emphasizes autonomy, decentralized decision-making, and collaborative networks, fostering agility, innovation, and responsiveness. Core principles for command-and-control include top-down communication and standardized processes, while distributed authority relies on empowerment, trust, and shared responsibility.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Command-and-control management centralizes decision-making authority, enabling quick, uniform decisions but often limiting adaptability across organizational levels. Distributed authority empowers teams with autonomy, fostering faster responses and innovation through localized decision-making tailored to specific contexts. This decentralized approach enhances flexibility and employee engagement but requires robust communication channels to maintain alignment with overall strategic goals.
Impact on Employee Empowerment and Motivation
Command-and-Control management structures centralize decision-making, often limiting employee autonomy and reducing motivation by restricting creativity and input. In contrast, distributed authority models delegate decision-making power across various organizational levels, enhancing employee empowerment and fostering a sense of ownership, which boosts engagement and innovation. Research by Harvard Business Review highlights that companies adopting distributed authority experience 20% higher employee satisfaction and 15% increased productivity.
Organizational Structure and Hierarchy Differences
Command-and-control organizational structures feature centralized authority where decision-making flows from top management down through distinct hierarchical layers, ensuring clear command chains and accountability. Distributed authority models empower multiple levels within the organization, fostering decentralized decision-making and enhancing flexibility, innovation, and responsiveness. This shift from a rigid hierarchy to a more networked structure often results in increased autonomy for teams and faster adaptation to dynamic market conditions.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies in management reveal that command-and-control structures often succeed in environments requiring clear, rapid decision-making, exemplified by military operations and crisis management scenarios. In contrast, distributed authority models thrive in innovative tech companies like Google, enabling agility and employee empowerment but sometimes causing coordination challenges. Failure in command-and-control cases frequently stems from rigidity and slow adaptation, while distributed authority can falter due to lack of clear accountability and inconsistent communication.
Adapting Management Styles for Modern Workforces
Command-and-control management relies on centralized decision-making and strict supervision, which can limit flexibility and employee autonomy in modern workforces. Distributed authority empowers teams by delegating decision-making to multiple levels, enhancing responsiveness and innovation in dynamic environments. Adapting management styles to incorporate distributed authority supports improved collaboration, faster problem-solving, and increased employee engagement in today's agile workplaces.
Balancing Centralization and Decentralization
Balancing centralization and decentralization in management involves integrating command-and-control structures with distributed authority to optimize decision-making efficiency and organizational agility. Centralized command-and-control ensures uniformity and accountability, while distributed authority empowers teams with autonomy, fostering innovation and responsiveness. Effective management requires a hybrid approach that aligns the level of central oversight with the degree of delegated autonomy based on strategic priorities and operational complexity.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Choosing the right management approach depends on organizational size, culture, and industry dynamics, with command-and-control fitting highly structured environments requiring clear directives and fast decision-making. Distributed authority empowers teams through decentralized decision rights, fostering innovation and responsiveness in dynamic, collaborative settings. Evaluating operational complexity and strategic goals ensures alignment between leadership style and organizational effectiveness for optimal performance.
Related Important Terms
Centralized Orchestration
Centralized orchestration in management prioritizes a Command-and-Control structure where decision-making authority is concentrated at the top levels, ensuring consistent strategic alignment and streamlined execution. This model enhances accountability and clarity but may reduce agility and innovation compared to Distributed Authority systems.
Distributed Autonomy
Distributed autonomy enhances organizational agility by empowering decentralized teams with decision-making authority, fostering innovation and rapid response to market changes. This approach leverages collaborative leadership and cross-functional expertise, resulting in increased employee engagement and improved operational efficiency.
Federated Governance
Federated governance integrates distributed authority by allocating decision-making powers across autonomous units while maintaining centralized oversight for strategic alignment, enhancing organizational agility and accountability. This hybrid approach balances the rigid hierarchy of command-and-control systems with the flexibility of decentralized management, optimizing resource allocation and innovation.
Decentralized Decision Rights
Decentralized decision rights empower employees at various organizational levels to make timely and context-specific decisions, enhancing responsiveness and innovation. This contrasts with command-and-control structures, where authority is centralized, often leading to slower decision-making and reduced adaptability in dynamic environments.
Hierarchical Command Chain
Hierarchical command chain centralizes decision-making authority in upper management, ensuring clear lines of accountability and streamlined communication. This structure contrasts with distributed authority by limiting autonomy at lower levels, which can affect responsiveness and innovation in complex environments.
Polycentric Management
Polycentric management enhances organizational agility by distributing authority across multiple centers, allowing localized decision-making that aligns with specific operational contexts. This contrasts with traditional command-and-control models by promoting flexibility, innovation, and responsiveness through decentralized governance structures.
Networked Leadership
Networked leadership enhances organizational agility by decentralizing decision-making authority across interconnected teams, contrasting with traditional command-and-control models that concentrate power at the top. This distributed authority fosters collaboration, accelerates innovation, and improves responsiveness to complex market dynamics through empowered, cross-functional networks.
Swarm Intelligence Management
Swarm intelligence management leverages decentralized decision-making processes inspired by natural systems, enhancing adaptability and resilience compared to traditional command-and-control hierarchies. This model improves organizational responsiveness by empowering distributed authority, facilitating real-time collaboration and innovation across autonomous teams.
Adaptive Authority Model
The Adaptive Authority Model integrates the hierarchical clarity of Command-and-Control with the flexibility of Distributed Authority, enabling rapid decision-making and innovation in dynamic environments. This model leverages real-time data and empowers frontline employees to respond autonomously while maintaining strategic alignment through centralized oversight.
Fractal Organization Structure
Fractal organization structures enhance agility by embedding decentralized decision-making within self-similar, autonomous units that mimic the whole system's complexity. This contrasts with traditional command-and-control models by distributing authority across interconnected teams, enabling faster responses and increased innovation in dynamic environments.
Command-and-Control vs Distributed Authority Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com