Hierarchical structures centralize decision-making authority, creating clear lines of responsibility and control, which can enhance accountability and efficiency in larger organizations. Flat structures promote open communication and faster decision-making by reducing management layers, fostering innovation and employee empowerment. Choosing between hierarchical and flat structures depends on company size, culture, and the need for flexibility versus control.
Table of Comparison
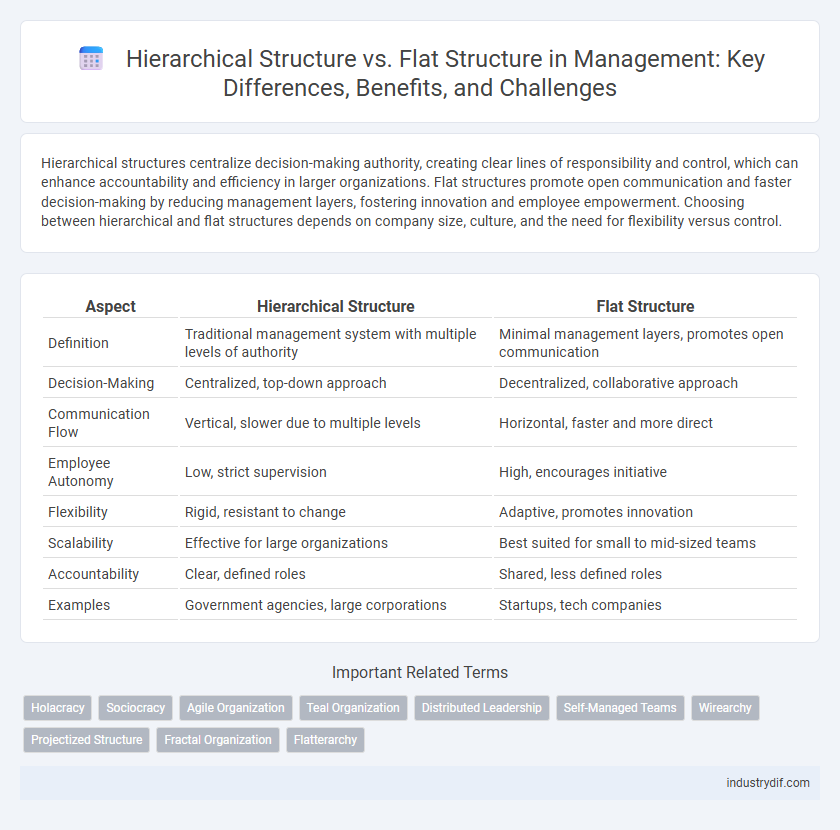
| Aspect | Hierarchical Structure | Flat Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional management system with multiple levels of authority | Minimal management layers, promotes open communication |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, top-down approach | Decentralized, collaborative approach |
| Communication Flow | Vertical, slower due to multiple levels | Horizontal, faster and more direct |
| Employee Autonomy | Low, strict supervision | High, encourages initiative |
| Flexibility | Rigid, resistant to change | Adaptive, promotes innovation |
| Scalability | Effective for large organizations | Best suited for small to mid-sized teams |
| Accountability | Clear, defined roles | Shared, less defined roles |
| Examples | Government agencies, large corporations | Startups, tech companies |
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Hierarchical structures feature multiple management levels, creating a clear chain of command and defined roles that enhance control and accountability within large organizations. Flat structures minimize management layers, promoting open communication, faster decision-making, and greater employee autonomy, often benefiting startups and small companies. Understanding these organizational structures assists managers in aligning company goals with efficient workflows and employee collaboration.
Defining Hierarchical Structure
Hierarchical structure organizes an organization into multiple levels of management, with clear lines of authority and responsibility from top executives to frontline employees. Each level controls the level below and is controlled by the level above, creating a pyramid-like chain of command that supports efficient decision-making and accountability. This structure is common in traditional corporations, government agencies, and large organizations requiring strict oversight and formal communication channels.
Understanding Flat Structure
Flat structures reduce management layers, promoting faster communication and increased employee autonomy. This design enhances flexibility and quicker decision-making by empowering teams to collaborate directly. Organizations adopting flat structures often report improved innovation and employee satisfaction due to minimized bureaucracy.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Flat Structures
Hierarchical structures feature multiple levels of management, clearly defining authority and responsibility, while flat structures have fewer layers, promoting open communication and faster decision-making. Hierarchical organizations emphasize formal roles and a chain of command, enabling specialized supervision, whereas flat organizations encourage employee autonomy and collaboration. The key difference lies in the balance between control and flexibility, with hierarchical models suited for large, complex organizations and flat models benefiting smaller, dynamic teams.
Decision-Making Processes
Hierarchical structures centralize decision-making, with clear authority levels enabling quick escalation and control, but potentially slowing responsiveness at lower levels. Flat structures promote decentralized decision-making, empowering employees to make faster, autonomous choices that foster innovation and agility. Organizations must balance control and flexibility to optimize operational efficiency and adaptability within their management approach.
Communication Flow in Both Structures
Hierarchical structures feature a top-down communication flow where messages pass through multiple managerial levels, often causing delays and information distortion. Flat structures promote direct, open communication among employees and management, enhancing speed and clarity but sometimes leading to information overload. Effective communication flow depends on the organization's size and complexity, with hierarchical models suiting large corporations and flat models benefiting startups and small teams.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Engagement
Hierarchical structures often result in clear roles and responsibilities but may limit employee autonomy, potentially reducing motivation and engagement due to rigid communication channels. Flat structures promote greater employee empowerment and faster decision-making, enhancing motivation by fostering a sense of ownership and direct involvement in company goals. Studies indicate that organizations with flat hierarchies report higher employee satisfaction and innovation rates compared to traditionally layered management systems.
Scalability and Adaptability
Hierarchical structures offer clear scalability through defined layers of authority, enabling consistent decision-making as organizations grow. Flat structures enhance adaptability by promoting faster communication and flexibility, allowing teams to respond swiftly to market changes. Balancing hierarchical scalability with flat adaptability supports sustained organizational growth and innovation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Structure
Hierarchical structures offer clear authority lines and defined roles, enhancing accountability and decision-making efficiency but often leading to slower communication and reduced flexibility. Flat structures promote faster decision-making and greater employee autonomy, fostering innovation and collaboration, yet can result in role ambiguity and challenges in managing larger teams. Organizations must balance control and agility when choosing between hierarchical and flat organizational designs.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Selecting the appropriate organizational structure depends on factors such as company size, decision-making speed, and communication flow. Hierarchical structures offer clear authority levels and specialized roles, ideal for large enterprises requiring controlled coordination. Flat structures promote agility and collaboration, suited for startups or smaller organizations prioritizing innovation and rapid response.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Holacracy emphasizes decentralized decision-making by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, contrasting with the hierarchical structure's clear chain of command. This flat organizational model enhances agility and employee empowerment, reducing managerial layers to promote responsiveness and innovation.
Sociocracy
Sociocracy integrates elements of both hierarchical and flat structures by promoting decentralized decision-making through interconnected circles, enhancing transparency and collaboration within organizations. Its circular governance model balances authority and autonomy, fostering adaptive management and efficient communication across all levels.
Agile Organization
Hierarchical structures centralize decision-making with multiple management layers, often slowing communication and innovation, while flat structures promote faster decision-making and greater employee autonomy, key factors for Agile organizations seeking flexibility and responsiveness. Agile organizations thrive in flat structures that empower cross-functional teams, enabling rapid adaptation to market changes and continuous improvement through collaborative workflows.
Teal Organization
Teal organizations emphasize self-management, decentralized decision-making, and evolutionary purpose, contrasting sharply with traditional hierarchical structures that rely on top-down control and rigid authority lines. By adopting a flat structure, Teal organizations foster greater employee autonomy, collaboration, and adaptability, which drives innovation and responsiveness in dynamic business environments.
Distributed Leadership
Hierarchical structure centralizes decision-making authority at the top levels, limiting distributed leadership, while flat structure promotes shared responsibility and empowers employees at all levels to lead initiatives. Distributed leadership thrives in flat structures by enabling collaborative problem-solving, faster decision-making, and increased organizational agility.
Self-Managed Teams
Self-managed teams thrive in flat organizational structures where decision-making authority is decentralized, promoting autonomy and faster problem-solving. In contrast, hierarchical structures often limit team empowerment due to rigid reporting lines and centralized control, reducing flexibility and innovation.
Wirearchy
Wirearchy fosters dynamic, decentralized communication by emphasizing knowledge flow and peer collaboration over rigid authority, contrasting with traditional hierarchical structures centered on top-down control. This network-based model enhances agility and innovation, enabling faster decision-making and adaptive management in complex environments.
Projectized Structure
Projectized structure centralizes authority within the project manager, enhancing agility and decision-making speed compared to hierarchical or flat structures. This structure optimizes resource allocation and accountability by dedicating teams exclusively to projects, driving focused execution and timely delivery.
Fractal Organization
Fractal organization integrates hierarchical and flat structures by replicating self-similar units that operate autonomously yet align with overall company strategy, enhancing adaptability and resilience. This approach decentralizes decision-making while maintaining clear accountability, enabling scalable and agile management across complex enterprises.
Flatterarchy
Flatterarchy combines the benefits of hierarchical and flat structures by promoting flexibility and faster decision-making while maintaining clear accountability. This hybrid model enhances innovation and employee empowerment by minimizing management layers and encouraging cross-functional collaboration.
Hierarchical Structure vs Flat Structure Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com