Hierarchy management establishes clear authority levels and defined roles, enhancing accountability and decision-making efficiency. Flat management fosters open communication and collaboration by minimizing layers of supervision, encouraging employee empowerment and innovation. Choosing between these structures depends on organizational size, culture, and goals, balancing control with flexibility to optimize performance.
Table of Comparison
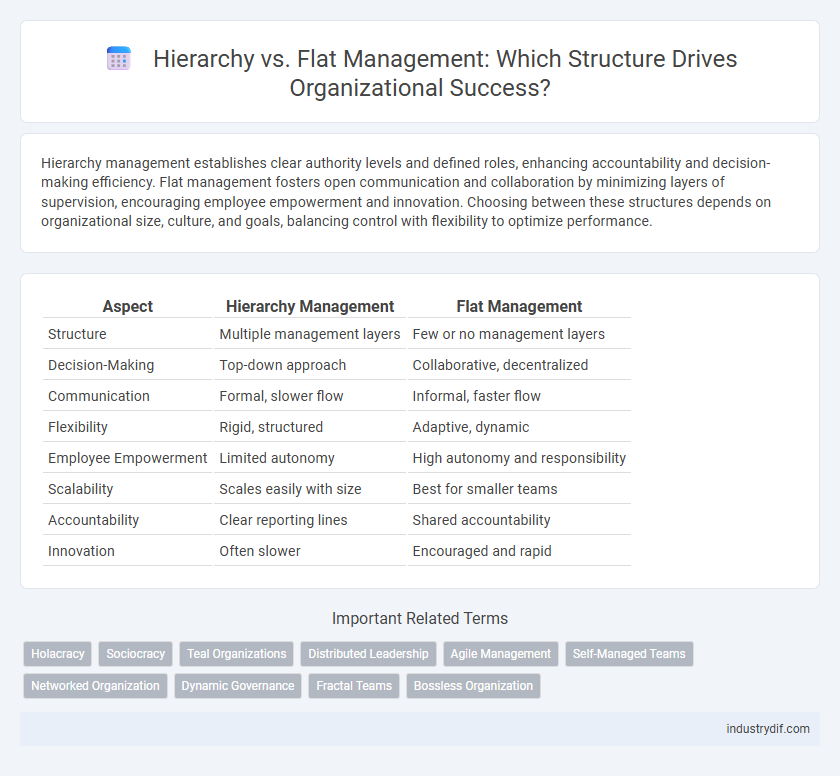
| Aspect | Hierarchy Management | Flat Management |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple management layers | Few or no management layers |
| Decision-Making | Top-down approach | Collaborative, decentralized |
| Communication | Formal, slower flow | Informal, faster flow |
| Flexibility | Rigid, structured | Adaptive, dynamic |
| Employee Empowerment | Limited autonomy | High autonomy and responsibility |
| Scalability | Scales easily with size | Best for smaller teams |
| Accountability | Clear reporting lines | Shared accountability |
| Innovation | Often slower | Encouraged and rapid |
Understanding Hierarchical Management Structures
Hierarchical management structures organize employees into clear, ranked levels of authority, facilitating defined roles and streamlined decision-making processes. This system promotes accountability through a top-down approach, where communication flows from senior executives to frontline workers, enabling efficient oversight and control. Understanding this structure helps organizations implement clear reporting lines and maintain operational order, enhancing productivity and strategic alignment.
What Is Flat Management?
Flat management is an organizational structure with few or no middle managers, promoting a more collaborative and transparent work environment. Employees have increased autonomy and direct communication with leadership, fostering faster decision-making and innovation. This approach contrasts with traditional hierarchical models by reducing layers of management and encouraging empowerment at all levels.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Flat Organizations
Hierarchical organizations feature multiple management levels, creating a clear chain of command that facilitates defined roles and responsibilities. Flat management structures reduce layers, promoting open communication and faster decision-making among employees at various levels. The key differences between these models lie in their approach to authority distribution, communication flow, and organizational agility.
Advantages of Hierarchical Management
Hierarchical management provides clear lines of authority and responsibility, which enhances decision-making efficiency and accountability within organizations. This structure facilitates effective communication through well-defined roles, reducing ambiguity and streamlining workflow. The clarity in supervision fosters employee development by offering distinct career progression paths and specialized leadership guidance.
Benefits of Flat Management Structures
Flat management structures enhance communication flow by reducing layers of approval, resulting in faster decision-making and increased agility. Employees experience greater autonomy and empowerment, which fosters innovation and accountability across teams. The streamlined hierarchy also lowers operational costs and improves collaboration, contributing to higher overall organizational efficiency.
Challenges of Hierarchical Organizations
Hierarchical organizations often face challenges such as slower decision-making processes due to multiple layers of approval, which can hinder responsiveness and innovation. Communication barriers frequently arise as information must pass through various management levels, increasing the risk of distortion or delay. Employee autonomy may be limited, reducing motivation and engagement, as rigid structures constrain creativity and flexibility.
Common Pitfalls in Flat Management Models
Flat management models often face challenges such as blurred authority lines leading to decision-making delays and role ambiguity affecting accountability. Lack of clear supervision can result in inconsistent performance evaluations and reduced employee motivation. Communication overload may occur as employees have to coordinate widely without a defined chain of command, impacting productivity and operational efficiency.
When to Use Hierarchical vs. Flat Structures
Hierarchical management suits large organizations requiring clear authority lines and specialized roles, enhancing accountability and decision-making efficiency. Flat management benefits small to medium-sized teams emphasizing collaboration, quick communication, and innovation through reduced managerial layers. Companies undergoing rapid change or innovation-focused projects often adopt flat structures, while stable, process-driven industries typically rely on hierarchical systems.
Case Studies: Companies Adopting Flat Management
Zappos, a leading online retailer, successfully implemented a flat management structure through Holacracy, fostering employee autonomy and faster decision-making. Morning Star, a tomato processing company, empowered employees with self-management principles, resulting in enhanced accountability and operational efficiency. Valve Corporation, renowned for its gaming software, thrives with a flat hierarchy that encourages innovation and collaborative project management.
Future Trends in Organizational Management Structures
Future trends in organizational management emphasize hybrid structures blending hierarchical clarity with flat flexibility to enhance agility and innovation. Increasingly, companies adopt decentralized decision-making supported by digital collaboration tools that empower frontline employees. AI-driven analytics facilitate dynamic role allocation, optimizing workforce efficiency and responsiveness in evolving market conditions.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchical management with a decentralized structure, distributing decision-making authority across self-organizing teams called circles. This system enhances agility and employee empowerment by assigning roles based on expertise rather than rank, fostering transparency and continuous adaptation.
Sociocracy
Sociocracy fosters a flat management structure by distributing decision-making authority through interconnected circles, enhancing transparency and collective responsibility. This method contrasts with traditional hierarchical systems by promoting equivalence and rapid feedback, driving increased organizational agility and employee empowerment.
Teal Organizations
Teal organizations embrace a flat management structure that empowers employees with autonomy and self-management, eliminating traditional hierarchical layers to foster transparency and adaptability. This evolution in organizational design promotes increased innovation, rapid decision-making, and a culture of trust by distributing authority across all levels.
Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership in flat management structures empowers team members by decentralizing decision-making and fostering collaboration, enhancing responsiveness and innovation. Hierarchical models often centralize authority, which can slow communication and reduce individual autonomy compared to the dynamic nature of distributed leadership in flatter organizations.
Agile Management
Agile management favors flat management structures that promote flexibility, faster decision-making, and enhanced team collaboration over traditional hierarchical models with rigid layers of authority. By reducing bureaucratic barriers, flat management supports iterative development, continuous feedback, and empowered cross-functional teams essential for Agile methodologies.
Self-Managed Teams
Self-managed teams enhance organizational agility by distributing decision-making authority among team members, reducing dependence on hierarchical oversight and fostering innovation. This management style improves employee engagement and accountability, leading to increased productivity and faster problem-solving in dynamic business environments.
Networked Organization
Networked organizations eliminate rigid hierarchical structures by fostering interconnected teams that enhance communication, collaboration, and agility; this decentralization enables faster decision-making and innovation by leveraging diverse expertise across the network. Emphasizing flexible roles and decentralized authority, networked management structures improve organizational responsiveness and empower employees to contribute proactively without traditional chain-of-command constraints.
Dynamic Governance
Dynamic Governance integrates elements of hierarchy and flat management by enabling adaptable decision-making structures that balance clear roles with collaborative autonomy. This approach fosters responsiveness and innovation within organizations, optimizing efficiency while empowering teams through real-time feedback and distributed authority.
Fractal Teams
Fractal teams integrate the benefits of both hierarchy and flat management by structuring small, autonomous units that replicate organizational goals at every level, enhancing agility and decision-making efficiency. This model leverages decentralized authority and clear accountability, promoting innovation while maintaining coherence across complex projects.
Bossless Organization
Bossless organizations eliminate traditional hierarchy to foster autonomy, enhance collaboration, and accelerate decision-making by empowering all team members equally. This flat management approach drives innovation and adaptability by minimizing managerial layers and promoting direct communication across the organization.
Hierarchy vs Flat Management Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com