Leadership emphasizes clear authority and decision-making roles to drive organizational success, fostering accountability and vision through centralized control. Holacracy distributes authority across self-managing teams, promoting agility and employee empowerment by eliminating traditional hierarchies. Both approaches aim to optimize management effectiveness but differ fundamentally in structure and control dynamics.
Table of Comparison
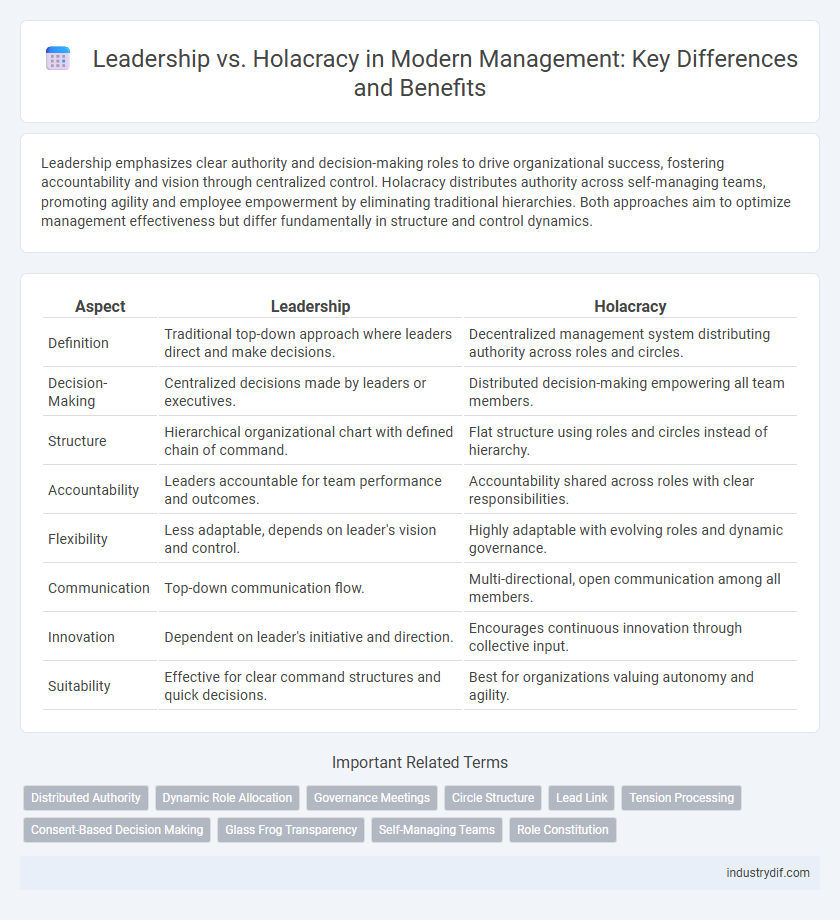
| Aspect | Leadership | Holacracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional top-down approach where leaders direct and make decisions. | Decentralized management system distributing authority across roles and circles. |
| Decision-Making | Centralized decisions made by leaders or executives. | Distributed decision-making empowering all team members. |
| Structure | Hierarchical organizational chart with defined chain of command. | Flat structure using roles and circles instead of hierarchy. |
| Accountability | Leaders accountable for team performance and outcomes. | Accountability shared across roles with clear responsibilities. |
| Flexibility | Less adaptable, depends on leader's vision and control. | Highly adaptable with evolving roles and dynamic governance. |
| Communication | Top-down communication flow. | Multi-directional, open communication among all members. |
| Innovation | Dependent on leader's initiative and direction. | Encourages continuous innovation through collective input. |
| Suitability | Effective for clear command structures and quick decisions. | Best for organizations valuing autonomy and agility. |
Defining Leadership and Holacracy
Leadership traditionally involves a hierarchical structure where leaders set vision, make decisions, and guide teams toward organizational goals. Holacracy replaces conventional leadership with a decentralized governance system, distributing authority across roles and circles to foster autonomy and agility. This management approach emphasizes dynamic role assignment and transparency, contrasting with the fixed power dynamics found in typical leadership models.
Historical Evolution of Management Structures
Leadership as a traditional management approach emerged from hierarchical and centralized systems, emphasizing top-down decision-making and individual authority. Holacracy, introduced in the early 21st century, represents a shift towards decentralized, self-managed teams with distributed authority and dynamic roles. This evolution reflects broader organizational trends favoring agility, transparency, and employee empowerment over rigid command-and-control structures.
Core Principles of Leadership Models
Leadership models emphasize vision, direction, and decision-making authority centralized in individuals or teams to guide organizational goals. Holacracy distributes authority through self-organizing teams and defined roles, fostering transparency and adaptability within a flat hierarchy. Core principles in leadership models prioritize accountability, empowerment, and alignment with company values to drive performance and innovation.
Fundamentals of Holacratic Governance
Holacratic governance replaces traditional leadership hierarchies with distributed authority through clearly defined roles and circles, enabling agile decision-making and enhanced organizational transparency. Each circle operates autonomously with its own governance process, ensuring continuous evolution of policies aligned with the organization's purpose. This structure cultivates accountability and empowerment by linking individual roles directly to organizational objectives without reliance on top-down command.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Leadership in traditional management centralizes decision-making authority, enabling swift, top-down directives that ensure clear accountability and alignment with organizational goals. Holacracy distributes decision-making through self-organizing teams, promoting autonomy and evolving roles that adapt dynamically to operational needs. This decentralized approach fosters agility and innovation but requires robust communication frameworks to maintain coherence across the organization.
Power Dynamics in Traditional vs. Holacratic Systems
Traditional leadership models concentrate power within a hierarchical structure where decision-making authority is centralized, often leading to clear but rigid power dynamics. In contrast, holacracy distributes authority across self-organizing teams, decentralizing power to foster adaptability and collective accountability. This shift in power dynamics can enhance organizational agility but requires a cultural commitment to transparency and trust.
Adaptability and Innovation in Both Approaches
Leadership fosters adaptability by enabling decisive guidance and clear vision, encouraging innovation through strategic direction and empowered teams. Holacracy enhances adaptability by distributing authority across self-organizing teams, promoting rapid response to change and continuous process evolution. Both approaches drive innovation by supporting flexible structures that can adjust to dynamic business environments.
Case Studies: Successes and Challenges
Case studies reveal that traditional leadership models excel in clear decision-making and accountability but often struggle with employee autonomy and innovation. Holacracy's decentralized approach fosters agility and participative governance, as seen in organizations like Zappos and Medium, yet challenges arise in role clarity and scalability during rapid growth. Balancing structured leadership with Holacratic principles can optimize organizational performance by integrating accountability with adaptability.
Impacts on Organizational Culture and Employee Engagement
Leadership structures based on hierarchical models often cultivate a clear chain of command, fostering stability but potentially limiting employee autonomy and innovation within organizational culture. Holacracy emphasizes decentralized decision-making and self-management, significantly enhancing employee engagement by empowering individuals to take ownership of their roles while promoting transparency and adaptability. Organizations implementing holacracy report increased collaboration and a dynamic culture that supports continuous learning and responsiveness to change.
Choosing the Right Management Framework for Your Business
Choosing the right management framework involves evaluating traditional leadership models against holacracy's decentralized approach to decision-making and team accountability. Leadership frameworks emphasize hierarchical roles and clear authority lines, fostering swift decision processes and unified strategic direction. Holacracy promotes agility and employee empowerment through self-organizing teams, suitable for innovative environments where adaptability and distributed governance drive business success.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Authority
Leadership models with centralized authority often rely on top-down decision-making, whereas holacracy emphasizes distributed authority by empowering self-organizing teams to make decisions within defined roles and circles. This approach increases organizational agility and accountability by decentralizing power structures and fostering collaborative governance.
Dynamic Role Allocation
Dynamic role allocation in leadership models contrasts traditional hierarchical authority with holacracy's fluid, self-managed roles, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing demands. This approach emphasizes distributed decision-making and continuous role reassessment, fostering agility and enhanced collaboration across teams.
Governance Meetings
Leadership governance meetings typically emphasize hierarchical decision-making, with a clear chain of command directing strategic goals and accountability. Holacracy governance meetings distribute authority through structured roles and circles, enabling dynamic, collaborative decision-making that adapts to evolving organizational needs.
Circle Structure
Circle structure in holacracy replaces traditional hierarchical leadership with distributed authority among self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and transparency. Unlike conventional leadership models centered on individual decision-making, circles emphasize clear roles and accountabilities within decentralized governance frameworks.
Lead Link
Lead Link in Holacracy serves as a defined role coordinating circle activities and aligning team efforts, contrasting traditional leadership's broader authoritative scope. This role enhances clarity in decision-making and distributes accountability, fostering adaptive management within self-organizing teams.
Tension Processing
Leadership in traditional management models often relies on hierarchical decision-making structures that can slow tension processing due to centralized authority, while holacracy distributes decision-making roles across teams to accelerate tension identification and resolution. By embedding tension processing into regular governance meetings, holacracy enables continuous adaptation and fosters a dynamic environment where challenges are addressed collaboratively and transparently.
Consent-Based Decision Making
Consent-based decision making in leadership emphasizes inclusive input while retaining ultimate authority, fostering alignment through dialogue and mutual agreement. Holacracy distributes decision-making power across self-organizing teams, enabling faster, decentralized consent that adapts dynamically to evolving organizational needs.
Glass Frog Transparency
GlassFrog enhances transparency in holacracy by providing a centralized platform that visualizes roles, responsibilities, and governance records, enabling real-time access to organizational processes. Unlike traditional leadership models where decisions are top-down, GlassFrog supports distributed authority and accountability through clear, accessible data on circle meetings and tensions management.
Self-Managing Teams
Self-managing teams in holacracy operate without traditional hierarchical leadership, distributing authority across roles to enhance agility and ownership. Leadership in conventional management centers on directive decision-making and accountability, contrasting with holacracy's emphasis on distributed governance and dynamic role allocation.
Role Constitution
Leadership in traditional management centers on hierarchical authority where roles are clearly defined and decisions flow top-down, ensuring accountability through designated leaders. Holacracy distributes authority across self-organizing teams, with roles dynamically assigned based on evolving project needs, promoting agility and decentralized decision-making.
Leadership vs Holacracy Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com