Top-down management relies on hierarchical decision-making where leaders set clear goals and directives, streamlining execution but potentially limiting employee creativity. Bottom-up innovation encourages input from all organizational levels, fostering diverse ideas and adaptability that can lead to breakthrough solutions. Balancing both approaches can enhance strategic alignment while promoting a culture of innovation and engagement.
Table of Comparison
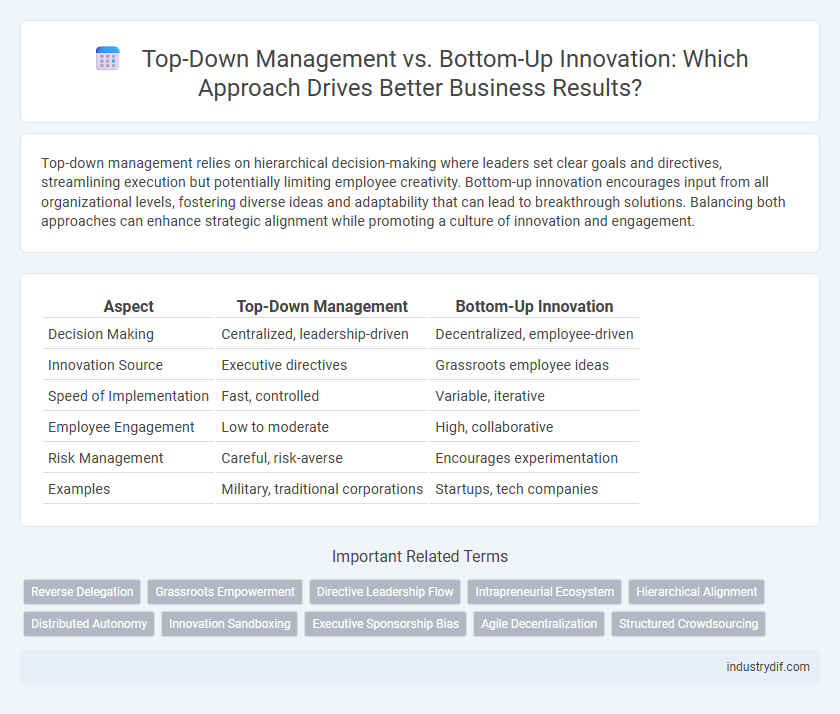
| Aspect | Top-Down Management | Bottom-Up Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Centralized, leadership-driven | Decentralized, employee-driven |
| Innovation Source | Executive directives | Grassroots employee ideas |
| Speed of Implementation | Fast, controlled | Variable, iterative |
| Employee Engagement | Low to moderate | High, collaborative |
| Risk Management | Careful, risk-averse | Encourages experimentation |
| Examples | Military, traditional corporations | Startups, tech companies |
Understanding Top-Down Management
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority at the executive level, enabling swift implementation of strategic objectives and consistent alignment with organizational goals. This hierarchical approach streamlines communication by setting clear directives from leadership to subordinates, ensuring accountability and efficient resource allocation. However, it may limit employee creativity and responsiveness to frontline challenges, requiring leaders to balance control with adaptive feedback mechanisms.
Defining Bottom-Up Innovation
Bottom-up innovation emphasizes employee-driven ideas and solutions, empowering teams at all organizational levels to contribute to problem-solving and creative processes. This approach leverages grassroots insights and fosters a culture of collaboration, leading to more adaptive and diverse innovations. By prioritizing local knowledge and frontline feedback, bottom-up innovation enhances responsiveness and drives continuous improvement.
Core Differences Between Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches
Top-down management enforces decisions through hierarchical authority, streamlining execution and ensuring alignment with organizational goals. Bottom-up innovation leverages employee insights and collaborative problem-solving, fostering creativity and responsive adaptability to market changes. Core differences lie in decision-making control, flexibility, and the source of innovative ideas driving organizational growth.
Benefits of Top-Down Management in Organizations
Top-down management streamlines decision-making by centralizing authority, allowing organizations to implement strategies swiftly and maintain consistent direction across all departments. This approach ensures clear accountability, making it easier to monitor progress and enforce policies effectively. Furthermore, top-down management fosters alignment with corporate goals, reducing ambiguity and enhancing overall organizational efficiency.
Advantages of Bottom-Up Innovation for Business Growth
Bottom-up innovation fosters employee engagement by empowering teams to contribute ideas, leading to increased creativity and practical solutions tailored to operational challenges. This approach enhances adaptability and responsiveness to market changes, as frontline employees possess firsthand customer insights. Organizations embracing bottom-up innovation often experience accelerated business growth through continuous improvement and collaborative problem-solving.
Common Challenges in Top-Down Management
Top-down management often faces challenges such as limited employee engagement, restricted creativity, and slower adaptability to change due to centralized decision-making. This hierarchical approach may suppress innovative ideas from lower-level employees, leading to reduced motivation and missed opportunities for improvement. Overcoming communication barriers and fostering a culture of openness are crucial to mitigating these common obstacles in top-down management systems.
Obstacles Faced in Implementing Bottom-Up Innovation
Implementing bottom-up innovation often encounters obstacles such as resistance from middle management, limited employee empowerment, and inadequate communication channels. Organizational culture that favors hierarchical decision-making can stifle creativity and slow the adoption of employee-generated ideas. Additionally, lack of resources and insufficient training hinder employees' ability to contribute effectively to innovation processes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Company
Selecting the appropriate management approach hinges on company size, culture, and innovation goals, with top-down management offering clear direction and quick decision-making in hierarchical organizations. Bottom-up innovation fosters employee engagement and diverse idea generation, ideal for companies aiming to leverage grassroots creativity and agility. Balancing centralized strategies with decentralized input ensures optimal alignment between leadership vision and workforce innovation.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Both Models
Case studies highlight that top-down management in corporations like Apple drives innovation through centralized decision-making and clear strategic vision, enabling rapid execution of product development. Conversely, bottom-up innovation thriving at companies like Google encourages employee-driven creativity and iterative improvements, leading to breakthrough ideas and a culture of continuous innovation. Examining these models reveals that integrating structured leadership with grassroots innovation fosters sustainable competitive advantage.
Integrating Top-Down and Bottom-Up for Optimal Results
Integrating top-down management directives with bottom-up innovation fosters a dynamic organizational environment where strategic goals align with employee-driven creativity. Leveraging top-down frameworks ensures clear objectives and resource allocation, while empowering bottom-up contributions enhances adaptability and intrapreneurship. This synergy optimizes decision-making processes, accelerates innovation cycles, and drives sustainable competitive advantage.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Delegation
Reverse delegation occurs when lower-level employees bypass middle management to seek decisions or approvals directly from top executives, often undermining authority and slowing workflow. This dynamic highlights the tension between top-down management structures and bottom-up innovation processes, where empowering frontline employees can clash with traditional hierarchical controls.
Grassroots Empowerment
Grassroots empowerment in management enhances bottom-up innovation by enabling employees at all levels to contribute ideas and drive change, fostering a culture of engagement and creativity. Unlike top-down management, which centralizes decisions, this approach leverages diverse insights from frontline teams, resulting in more adaptive and responsive organizational strategies.
Directive Leadership Flow
Directive leadership flow in top-down management enforces clear, centralized decision-making that accelerates execution but may stifle employee creativity and responsiveness. In contrast, bottom-up innovation thrives on decentralized input, fostering diverse ideas and adaptability while requiring strong facilitation to align initiatives with strategic goals.
Intrapreneurial Ecosystem
Top-down management establishes clear strategic direction and resource allocation essential for a structured intrapreneurial ecosystem, while bottom-up innovation leverages employee creativity and frontline insights to drive agile problem-solving and organic growth. Balancing hierarchical oversight with grassroots ideation cultivates a dynamic environment that maximizes intrapreneurial potential and accelerates sustainable innovation within organizations.
Hierarchical Alignment
Hierarchical alignment in top-down management streamlines decision-making by enforcing clear authority, ensuring organizational goals are consistently executed across all levels. In contrast, bottom-up innovation fosters alignment through collective input, promoting adaptability and leveraging frontline insights to drive strategic initiatives.
Distributed Autonomy
Distributed autonomy enhances innovation by empowering teams with decision-making authority within a top-down management framework, balancing centralized strategic goals with decentralized creativity. This hybrid approach accelerates adaptability and leverages collective expertise to drive sustainable organizational growth.
Innovation Sandboxing
Innovation sandboxing enables organizations to test bottom-up ideas within controlled environments, minimizing risks while fostering creativity. Top-down management can leverage sandboxing to align experimental projects with strategic goals, balancing hierarchical oversight with grassroots innovation.
Executive Sponsorship Bias
Executive sponsorship bias in top-down management often limits innovation by privileging leader-driven decisions over grassroots ideas, reducing the diversity of potential solutions. Bottom-up innovation mitigates this bias by empowering employees at all levels to contribute insights, fostering a more inclusive and dynamic innovation process.
Agile Decentralization
Agile decentralization enhances organizational responsiveness by empowering teams with decision-making authority, contrasting traditional top-down management that centralizes control and limits innovation flow. Bottom-up innovation thrives in decentralized Agile environments, enabling continuous improvement through collaborative feedback and adaptive strategies aligned with market dynamics.
Structured Crowdsourcing
Structured crowdsourcing in top-down management leverages clearly defined goals and hierarchical directives to channel employee input efficiently, enhancing strategic alignment and decision-making speed. Conversely, bottom-up innovation thrives on decentralized idea generation and collective problem-solving, fostering creativity and grassroots engagement through open participation frameworks.
Top-Down Management vs Bottom-Up Innovation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com